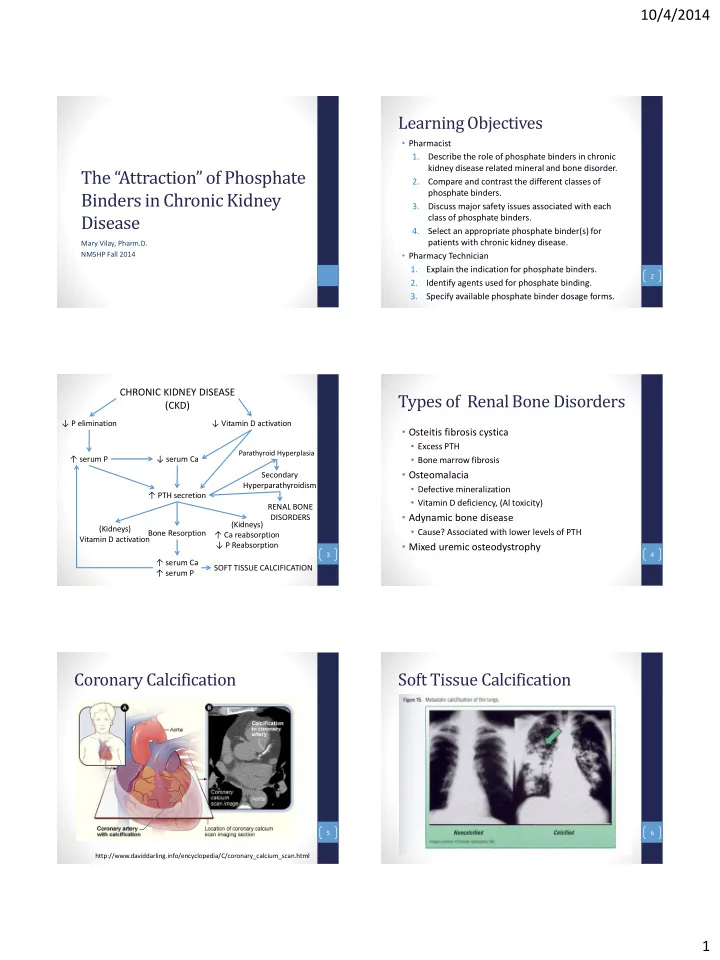

10/4/2014 Learning Objectives • Pharmacist 1. Describe the role of phosphate binders in chronic kidney disease related mineral and bone disorder. The “Attraction” of Phosphate 2. Compare and contrast the different classes of Binders in Chronic Kidney phosphate binders. 3. Discuss major safety issues associated with each Disease class of phosphate binders. 4. Select an appropriate phosphate binder(s) for patients with chronic kidney disease. Mary Vilay, Pharm.D. • Pharmacy Technician NMSHP Fall 2014 1. Explain the indication for phosphate binders. 2 2. Identify agents used for phosphate binding. 3. Specify available phosphate binder dosage forms. CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Types of Renal Bone Disorders (CKD) ↓ P elimination ↓ Vitamin D activation • Osteitis fibrosis cystica • Excess PTH Parathyroid Hyperplasia • Bone marrow fibrosis ↑ serum P ↓ serum Ca • Osteomalacia Secondary Hyperparathyroidism • Defective mineralization ↑ PTH secretion • Vitamin D deficiency, (Al toxicity) RENAL BONE • Adynamic bone disease DISORDERS (Kidneys) (Kidneys) • Cause? Associated with lower levels of PTH Bone Resorption ↑ Ca reabsorption Vitamin D activation • Mixed uremic osteodystrophy ↓ P Reabsorption 3 4 ↑ serum Ca SOFT TISSUE CALCIFICATION ↑ serum P Coronary Calcification Soft Tissue Calcification 5 6 http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/C/coronary_calcium_scan.html 1
10/4/2014 Soft Tissue Calcification Soft Tissue Calcification 7 8 Calciphylaxis Case 1 – T. S. 61 y.o. female • PMH • Labs • DM Type 2 • SCr 1.5 mg/dL • HTN • eGFR 33 mL/min/1.73m 2 • CKD • Ca 9.2 mg/dL (8.4- • Meds 10.4) • Ramipril 5 mg PO daily • P 6.7 mg/dL (2.3-5.6) • Ferrous fumarate 300 • iPTH 314 pg/mL (11- mg PO TID 80) • Lantus 24 U SC daily • Humalog TIDcc • PE 9 10 • 1+ bilateral edema http://www.primehealthchannel.com/calciphylaxis.html CKD Mineral and Bone CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Disorder Guidelines (CKD) Vitamin D Analogs ↓ P elimination ↓ Vitamin D activation • KDIGO (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes) Phosphate Binders • http://kdigo.org/home/mineral-bone-disorder/ Parathyroid Hyperplasia • Kidney International 2009; 76 (Suppl 113): S1- ↑ serum P ↓ serum Ca S130. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism ↑ PTH secretion Calcimimetic • KDOQI (Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative) RENAL BONE • http://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/guid DISORDERS (Kidneys) elines_bone/index.htm (Kidneys) Bone Resorption ↑ Ca reabsorption • American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2003; 42(4) Vitamin D activation ↓ P Reabsorption Suppl 3: S1-S201. 11 12 ↑ serum Ca SOFT TISSUE CALCIFICATION ↑ serum P 2
10/4/2014 Guideline Recommendations Guideline Recommendations Phosphorus KDIGO KDOQI Calcium KDIGO KDOQI Stage 3 Normal serum P 2.7-4.6 mg/dL Stage 3 Normal serum Ca Normal serum Ca (GFR 30-59) (GFR 30-59) Stage 4 Normal serum P 2.7-4.6 mg/dL Stage 4 Normal serum Ca Normal serum Ca (GFR 15-29) (GFR 15-29) Stage 5ND Normal serum P 3.5-5.5 mg/dL Stage 5ND Normal serum Ca Normal serum Ca (GFR <15) (GFR <15) range, preferably lower end Stage 5D Lower towards 3.5-5.5 mg/dL (8.4-9.5 mg/dL) (PD/HD) normal serum P range Stage 5D Normal serum Ca Normal serum Ca (PD/HD) range, preferably 13 14 lower end (8.4-9.5 mg/dL) Dietary Phosphorus Phosphate Binders Restriction Rx Formulations Place in • Beverages: • Protein: Therapy • Ale • Carp Aluminum hydroxide No Liquid, tablet, Alternate capsule • Beer • Fish roe Calcium-based Preferred • Cocoa • Organ meets Ca acetate Yes/no Capsule, tablet • Dark colas • Oysters • Dairy products: • Sardines Ca carbonate No Liquid, tablet, chewable, capsule • Dried beans & peas • Cheese Lanthanum carbonate Yes Chewable tablet Alternate • Ice cream • Others: Sevelamer Preferred • Milk • Bran cereals Sevelamer HCl Yes Tablet • Cream soups • Whole grain products (Renagel) • Yogurt 15 16 • Nuts Sevelamer Yes Tablet, powder carbonate (Renvela) www.kidney.org Biochemical Endpoints Bone Histology Summary Treat to Goal RIND • No major difference between calcium (Prevalent HD) (Incident HD) carbonate with lanthanum carbonate or SVR Ca P-value SVR Ca P-value (n=99) (n=101) (n=54) (n=55) sevelamer P 5.1±1.2 5.1±1.4 NS P 5.2±0.9 5.1±0.8 NS • Changes in bone turnover were Ca 9.5±0.6 9.7±0.7 <0.05 Ca 9.1±0.5 9.6±0.5 <0.05 ↑ Ca 5% 16% <0.05 heterogenous iPTH 224 138 NS iPTH 298±152 243±16 <0.05 • Some patients improved while others ↓ iPTH 30% 57% <0.05 TC 141±28 182±49 <0.05 TC 134±52 160±32 <0.05 worsened LDL 65±21 103±43 <0.05 LDL 60±34 81±26 <0.05 • Results influenced by baseline turnover HDL 43±10 45±12 NS 17 18 rates Trig 137 150 NS Trig 171±108 191±106 NS Chertow. Kidney Int 2002;62:245. Block. Kidney Int 2005;68:1815. KDIGO. Kidney International 2009; 76 (Suppl 113): S1-S130. 3
10/4/2014 * P<0.05 Ca vs Sevelamer Treat to Goal Treat to Goal * P<0.05 Ca vs Baseline Sevelamer vs Calcium Sevelamer vs Calcium Coronary Artery Calcification Aortic Calcification Coronary Artery Aorta 30 30 800 1400 * 700 * 1200 * 25 25 Median Change 600 Median Change 1000 Median % Change Median % Change 500 20 20 800 400 300 600 * 15 15 200 400 100 10 10 200 0 0 5 5 0 0 19 20 Wk 26 Wk 52 Wk 26 Wk 52 Chertow. Kidney Int 2002;62:245-252. Chertow. Kidney Int 2002;62:245-252. RIND RIND • CAC = 0 at baseline, none progressed to CAC >30 by study end • CAC >30 at baseline, progressive CAC increase (in sevelamer and Ca arm) • Ca arm: more rapid and severe increase in CAC Baseline CAC = Baseline CAC 0 >0 (n=37) (n=72) Mean 45 ± 12 y 64 ± 11 y P<0.0001 21 22 age Block. Kidney Int 2005;68:1815-1824. Block. Kidney Int 2005;68:1815-1824. RIND RIND Follow up • During parent study, subjects remained on their assigned phosphate binder P=0.002 (sevelamer vs calcium) • After final scan, subjects given phosphate binders at discretion of primary nephrologist • Median follow up = 44 months 23 24 Adjusted (age, race, gender, diabetes) Block. Kidney Int 2005;68:1815-1824. Block. Kidney Int 2007;71:438-441. Block. Kidney Int 2007;71:438-441. 4
10/4/2014 RIND Follow up DCOR P=0.016 • Prospective, multi-center, randomized, open-labeled, parallel design • Adult HD (>3 mo) • Required phosphate binder • Medicare = primary insurance • Powered to detect all-cause mortality Adjusted (age, race, gender, DM, history artherosclerotic 25 26 cardiovascular disease, CRP, albumin, Kt/V, baseline CAC) Suki. Kidney Int 2007;72:1130-7. Block. Kidney Int 2007;71:438-441. DCOR DCOR Sevelamer Calcium P-value All-cause Mortality Cardiovascular Mortality (n=99) (n=101) P=0.40 P=0.53 P 5.8±1.3 5.7±1.3 <0.01 Ca 9.2±0.7 9.5±0.7 <0.0001 iPTH, median 278 (200,476) 226 (142,387) <0.0001 TC 146±34 161±35 <0.0001 LDL 69±26 85±31 <0.0001 HDL 45±15 44±16 NS 27 28 Calcium = black line Sevelamer = green line Suki. Kidney Int 2007;72:1130-7. Suki. Kidney Int 2007;72:1130-7. DCOR Suki. Kidney Int 2007;72:1130-7. DCOR Patient disposition All-cause Mortality Cardiovascular Mortality ≥65 y ≥65 y Randomized P=0.02 (N=2103) P=0.10 Sevelamer Calcium (N=1053) (N=1050) D/C (N=502) D/C (N=533) <65 y <65 y A/E (N=81 ) A/E (N=50 ) P=0.21 P=0.37 Completed Completed 29 30 (N=551) (N=517) Suki. Kidney Int 2007;72:1130-7. 5
Recommend
More recommend