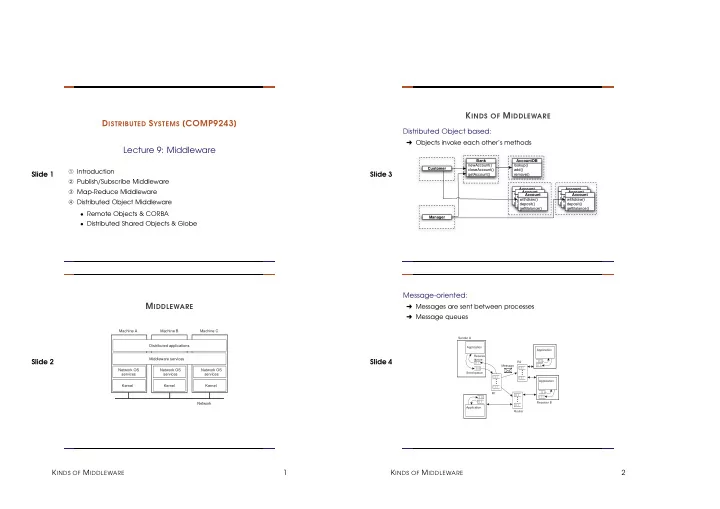

K INDS OF M IDDLEWARE D ISTRIBUTED S YSTEMS [COMP9243] Distributed Object based: ➜ Objects invoke each other’s methods Lecture 9: Middleware Bank AccountDB newAccount() lookup() Customer closeAccount() add() ➀ Introduction Slide 1 Slide 3 getAccount() remove() ➁ Publish/Subscribe Middleware Account Account ➂ Map-Reduce Middleware Account Account withdraw() withdraw() Account Account withdraw() withdraw() deposit() deposit() withdraw() withdraw() ➃ Distributed Object Middleware deposit() deposit() getBalance() getBalance() deposit() deposit() getBalance() getBalance() getBalance() getBalance() • Remote Objects & CORBA Manager • Distributed Shared Objects & Globe Message-oriented: M IDDLEWARE ➜ Messages are sent between processes ➜ Message queues Machine A Machine B Machine C Sender A Distributed applications Application Application Receive Middleware services queue Slide 2 Slide 4 R2 Message Network OS Network OS Network OS Send queue services services services Application Kernel Kernel Kernel R1 Network Receiver B Application Router K INDS OF M IDDLEWARE 1 K INDS OF M IDDLEWARE 2
Coordination-based: Transaction Processing Monitors: ➜ Tuple space A Write A B Write B T Read T Server Reply C Transaction Request Requests Slide 5 Look for Slide 7 Request Insert a Insert a tuple that Client� Server copy of B TP monitor copy of A matches T application Reply B Return C Reply A A (and optionally Request remove it) B B Reply Tuple instance C Server A JavaSpace Web Services: ➜ Publish/Subscribe Stock Service query_stock buy sell Subscriber Subscriber Publisher XML−RPC Bank Service Client balance tansfer HTTP HTTP Slide 6 Slide 8 ��� ��� ��� ��� XML−RPC ��� ��� Subscription ��� ��� Data Item SOAP �� �� HTTP ���� ���� �� �� Auction Service search ���� ���� ������ ������ �� �� get_auction ������ ������ ���� ���� manage_auction Match ������ ������ bid Photo Service search add_photo Match delete_photo update_photo Publish/Subscribe Middleware K INDS OF M IDDLEWARE 3 P UBLISH /S UBSCRIBE (E VENT -B ASED ) M IDDLEWARE 4
E XAMPLES Real-time Control Systems: P UBLISH /S UBSCRIBE (E VENT -B ASED ) M IDDLEWARE ➜ External events (e.g. sensors) ➜ Event monitors Subscriber Subscriber Publisher Stock Market Monitoring: ➜ Stock updates ➜ Traders subscribed to updates ��� ��� Slide 9 Slide 11 ��� ��� Network Monitoring: ��� ��� Subscription ��� ��� Data Item ➜ Status logged by routers, servers ➜ Monitors screen for failures, intrusion attempts �� �� ������ ������ ���� ���� ���� ���� ������ ������ �� �� ���� ���� ������ ������ Enterprise Application Integration: Match ������ ������ ➜ Independent applications Match ➜ Produce output as events Publish/Subscribe Middleware ➜ Consume events as input ➜ Decoupled C HALLENGES M ESSAGE F ILTERING Transparency: ➜ loose coupling → good transparency Subscriber Publisher Scalability: Topic-based ��� ��� ➜ Potentially good due to loose coupling ��� ��� ��� ��� Subscription: Data item: comp.os.* comp.os.distributed � In practice hard to achieve �� �� ����� ����� ����� ����� ➜ Number of subscriptions �� �� ����� ����� Match ����� ����� comp.os.unix Slide 10 Slide 12 ➜ Number of messages Publish/Subscribe Middleware Flexibility: Content-based Publisher Subscriber ➜ Loose coupling gives good flexibility ➜ Language & platform independence ➜ Policy separate from mechanism ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� Subscription: Data item: name=john name=john Programmability: age=30 ��� ��� ������ ������ ��� ��� ➜ Inherent distributed design ������ ������ Match ������ ������ name=john gender = male ➜ Doesn’t use non-distributed concepts Publish/Subscribe Middleware E XAMPLES 5 A RCHITECTURE 6
A RCHITECTURE R EPLICATION Centralised: Peer-to-Peer: Replicated Brokers: Broker Send Subscriber Publisher Publisher ➜ Copy subscription info on all nodes Subscribe Subscriber Publisher Subscriber Send ➜ Keep nodes consistent Event ��� ��� ��� ��� Send Send ���� ���� ��� ��� Event ���� ���� Send Event ���� ���� Event ���� ���� ➜ What level of consistency is needed? Publisher Subscriber Slide 13 Slide 15 ➜ Avoid sending redundant subscription update messages Publisher Subscriber Multicast-based: Partitioned Brokers: ➜ Different subscription info on different nodes Subscriber Subscriber Publisher Publisher ➜ Events have to travel through all nodes No Match Match No Match ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ➜ Route events to nodes that contain their subscriptions ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� Send Event F AULT T OLERANCE C OMMUNICATION Reliable Communication: ➜ Point-to-point ➜ Reliable multicast ➜ Multicast Process Resilience (Broker): • hard part is building appropriate multicast tree Slide 14 Slide 16 ➜ Process groups ➜ Content-based routing ➜ Active replication by subscribing to group messages • point-to-point based router network Routing: • make forwarding decisions based on message content • store subscription info at router nodes ➜ Stabilise routing if a broker crashes ➜ Lease entries in routing tables R EPLICATION 7 E XAMPLE S YSTEMS 8
E XAMPLE S YSTEMS TIB/Rendezvous: C ONTEXT ➜ Topic-based ➜ Multicast-based Computations conceptually straightforward, but: Java Message Service (JMS): ➜ Input data is usually large ➜ Need to finish in reasonable time ➜ API for MOM ➜ Computations widely distributed (thousands of machines) ➜ Topic-based Slide 17 Slide 19 ➜ centralised or peer-to-peer implementations possible How to: Scribe: ➜ Parallelize the computation? ➜ Topic-based ➜ Distribute the data? ➜ Handle failures? ➜ Peer-to-peer architecture, based on Pastry (DHT) ➜ Balance the load? ➜ Topics have unique IDs and map onto nodes ➜ Multicast for sending events • Tree is built up as nodes subscribe S OLUTION M AP -R EDUCE Map-Reduce: ➜ New abstraction for simple computations. ➜ Hide dirty details. ➜ Based on map and reduce primitives from Lisp (functional language). Slide 18 Slide 20 Basic computation: ➜ Takes set of input <key, value> pairs ➜ Produces set of output <key, value> pairs Implementation: ➜ Google’s version: MapReduce ➜ Open source version: Hadoop C ONTEXT 9 S OLUTION 10
E XAMPLE : W ORD C OUNT Count word occurances in in collection of documents: map(String key, String value): User supplied functions: // key: document name ➜ Map Accepts: one input pair <key, value> // value: document contents Produces: a set of intermediate <key, value> pairs for each word w in value: ➜ System groups intermediate values with same key together. EmitIntermediate(w, "1"); ➜ Reduce Accepts: intermediate key, set of values for that key Slide 21 Slide 23 Produces: output list (typically small) reduce(String key, Iterator values): More formally: // key: a word ➜ map ( k 1 , v 1 ) → list ( k 2 , v 2 ) // values: a list of counts ➜ reduce ( k 2 , list ( v 2 )) → list ( v 2) int result = 0; for each v in values: result += ParseInt(v); Emit(AsString(result)); E XAMPLE : W ORD C OUNT E XECUTION O VERVIEW Slide 22 Slide 24 E XAMPLE : W ORD C OUNT 11 M ASTER 12
Recommend
More recommend