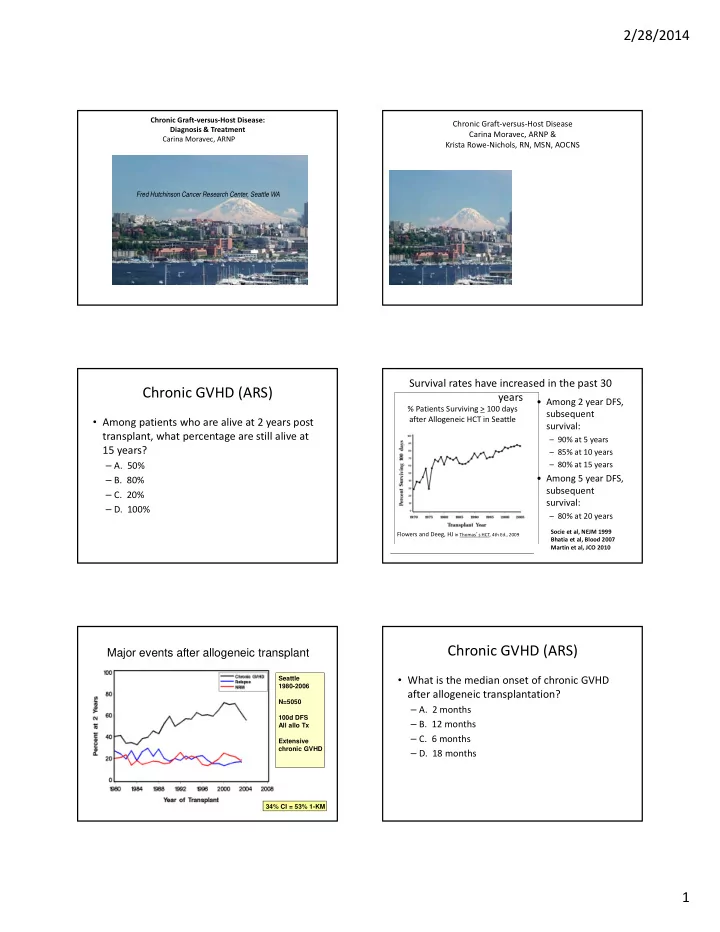

2/28/2014 Chronic Graft ‐ versus ‐ Host Disease: Chronic Graft ‐ versus ‐ Host Disease Diagnosis & Treatment Carina Moravec, ARNP & Carina Moravec, ARNPARNP Krista Rowe ‐ Nichols, RN, MSN, AOCNS Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle WA Survival rates have increased in the past 30 Chronic GVHD (ARS) years • Among 2 year DFS, % Patients Surviving > 100 days subsequent after Allogeneic HCT in Seattle • Among patients who are alive at 2 years post survival: transplant, what percentage are still alive at – 90% at 5 years 15 years? – 85% at 10 years – A. 50% – 80% at 15 years • Among 5 year DFS, – B. 80% subsequent – C. 20% survival: – D. 100% – 80% at 20 years Socie et al, NEJM 1999 Flowers and Deeg, HJ in Thomas ’ s HCT, 4th Ed., 2009 Bhatia et al, Blood 2007 Martin et al, JCO 2010 Chronic GVHD (ARS) Major events after allogeneic transplant • What is the median onset of chronic GVHD Seattle 1980-2006 after allogeneic transplantation? N=5050 – A. 2 months 100d DFS – B. 12 months All allo Tx – C. 6 months Extensive chronic GVHD – D. 18 months 34% CI = 53% 1-KM 1
2/28/2014 Chronic Graft-versus-Disease (GVHD) Why is Chronic GVHD a Problem? • Most common late complication after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant Occurs in 20 ‐ 70% of patients surviving more than • Median onset 6 months after transplant 100 days (60% incidence in Seattle) (tapering off prophylactic immune Major cause of death despite lower relapse rate; suppression) 40% survival at 8 years Associated with decreased quality of life • 10% diagnosed beyond 1-year after Secondary malignancies are more common in transplant patients with chronic GVHD • Affects multiple organs with inflammatory and fibrotic clinical phenotypes NIH Concensus Criteria for Chronic Biomarker GVHD • In 2005, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16443511 convened an experts conference to develop • Identify an approach for the identification, consensus on criteria for: validation, and application of biomarkers for – Diagnosis and Staging chronic GVHD – Pathology – Biomarkers – Response Measurement – Supportive Care – Design of Clinical Trials http://ccr.ncifcrf.gov/resources/gvhd/ Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:126 ‐ 137 (2006) Design of Clinical Trials Response Criteria http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16635784 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16503494 Biology of Blood and Marrow Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:491 ‐ 505 (2006) Transplantation 12:252 ‐ 266 (2006) 2
2/28/2014 Response Criteria Pathology http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16399567 • Summarizes and proposes measures and criteria • Outlines optimal sampling and tissue preparation for assessing outcomes in clinical trials involving • Minimal criteria for diagnosis of chronic GVHD patients with chronic GVHD • Specific requirements for diagnosis of chronic GVHD • Proposed chronic GVHD ‐ specific Core measures: • Definition of diagnostic categories which reflect the integration of histopathology, clinical, laboratory and – Clinician or patient assigned signs and symptoms radiographic information: – No GVHD – The chronic GVHD symptom scale by Lee et.al. – Possible GVHD – The clinician or patient reported global rating scales – Consistent with GVHD http://www.asbmt.org/GvHDForms – Definite GVHD http://www.asbmt.org/cGvHD_Guidelines Biology of Blood and Marrow Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:252 ‐ 266 (2006) Transplantation 12:31 ‐ 47 (2006) Diagnosis and Staging Diagnosis and Staging http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16338616 • In the past, any manifestation of GVHD that • Standardize the criteria for the diagnosis of chronic was present or continued after day 100 was GVHD arbitrarily defined as chronic GVHD. • Proposes a new clinical scoring system (0 ‐ 3) that describes the extent and severity of chronic GVHD for each organ or site at any given time taking functional impact into account • Proposes new guidelines for global assessment of chronic GVHD severity that are based on the number of organs or sites involved and the degree of involvement of infected organs (mild, moderate, severe) Biology of Blood and Marrow Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) Transplantation 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) Diagnosis and Staging Diagnosis and Staging • Diagnostic signs and symptoms • Diagnosis of chronic GVHD requires the – Refer to those manifestations that establish the presence of presence of at least 1 diagnostic clinical sign chronic GVHD without the need for further testing or evidence of other organ involvement OR • Distinctive signs and symptoms • The presence of at least 1 distinctive – Refer to those manifestations that are not ordinarily found in acute GVHD, but not sufficient enough to establish an manifestation confirmed by pertinent biopsy unequivocal diagnosis of chronic GVHD without further testing or additional organ involvement or other relevant test in the same or other • Other features organ – Rare, controversial or non ‐ specific features of chronic GVHD that can not be used to establish a diagnosis • Distinction from acute GVHD • Common features • Exclusion of other possible diagnoses – Seen in both acute and chronic GVHD Biology of Blood and Marrow Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) Transplantation 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) 3
2/28/2014 Diagnostic versus Distinctive Features Diagnostic versus Distinctive Features Organ or Site Diagnostic (sufficient to Distinctive (seen in chronic Other Features Common Organ or Site Diagnostic (sufficient to Distinctive (seen in chronic Other Features Common establish the diagnosis of GVHD, but insufficient alone * Can be acknowledged as (seen in both Acute and establish the diagnosis of GVHD, but insufficient alone to * Can be acknowledged as part (seen in both Acute and Chronic chronic GVHD) establish a diagnosis of chronic of the chronic GVHD GVHD) chronic GVHD) to establish a diagnosis of part of the chronic GVHD Chronic GVHD) GVHD) symptomatology if the chronic GVHD) symptomatology if the diagnosis is confirmed* diagnosis is confirmed* SKIN Poikiloderma Depigmentation Sweat impairment Erythema EYES New onset dry, gritty, or Photophobia Lichen planus ‐ like features Ichthyosis Maculopapular rash painful eyes ❷ Periorbital Sclerotic features Keratosis pilaris Pruritus Cicatricial conjunctivitis hyperpigmentation Morphea ‐ like features Hypopigmentation Keratoconjunctivitis sicca ❷ Blepharitis (erythema of the Lichen sclerosus ‐ like features Hyperpigmentation Confluent areas of punctate eyelids with edema) NAILS Dystrophy keratopathy Longitudinal ridging, splitting, or GENITALIA Lichen planus ‐ like features Erosions ❶ brittle features Oncycholysis Vaginal scarring or stenosis Fissures ❶ Pterygium unguis Ulcers ❶ Nail loss (usually symmetric; affects most nails) ❶ SCALP & BODY HAIR New onset of scarring or Thinning scalp hair, typically GI TRACT Esophageal web Exocrine pancreatic Anorexia nonscarring scalp alopecia (after patchy, coarse, or dull (not Stricture or stenosis in the insufficiency Nausea recovery from explained by endocrine or other upper to mid third of the Vomiting chemoradiotherapy) causes) esophagus ❶ Diarrhea Scaling, papulosquamous lesions Weight Loss Failure to Thrive MOUTH Lichen ‐ type features Xerostomia Gingivitis Hyperkeratotic plaques Mucocele Mucositis LIVER Total Bili, Alk Phos >2X ULN Restriction of mouth opening Mucosal atrophy Erythema ❶ from sclerosis Pseudomembranes ❶ Pain Ulcers ❶ AST, ALT >2XULN ❶ Filiipovich et al. Biol of Blood and Marrow Filiipovich et al. Biol of Blood and Marrow Transplant 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) Transplant 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) Diagnostic versus Distinctive Features Organ or Site Diagnostic (sufficient to Distinctive (seen in chronic Other Features Common establish the diagnosis of GVHD, but insufficient alone * Can be acknowledged as part of (seen in both Acute • Insert case study to highlight differences chronic GVHD) to establish a diagnosis of the chronic GVHD symptomatology and Chronic GVHD) chronic GVHD) if the diagnosis is confirmed* between distinctive and diagnostic features of LUNG Bronchiolitis obliterans Bronchiolitis obliterans BOOP diagnosed with lung biopsy diagnosed with PFTs and Radiology ❷ chronic GVHD MUSCLES, FASCIA, JOINTS Joint stiffness or contractures Myositis or polymyositis ❷ Edema secondary to sclerosis Muscle cramps Arthralgia or arthritis HEMATOPOIETIC AND Thrombocytopenia IMMUNE Eosinophilia Hypo or hypergammaglobulinemai Autoantibodies (AIHA and ITP) OTHER Pericardial or pleural effusions Ascites Peripheral Neuropathy Nephrotic Syndrome Myasthenia gravis Cardiac conduction abnormality or cardiomyopathy Filiipovich et al. Biol of Blood and Marrow Transplant 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) Category Time of Symptoms Presence of acute Presence of chronic NIH Consensus Tool GVHD features GVHD features ACUTE GVHD Classic acute <100 days YES NO Persistent, >100 days YES NO Recurrent or Late Onset acute CHRONIC GVHD Classic chronic No time limit NO YES Overlap syndrome No time limit YES YES Filiipovich et al. Biol of Blood and Marrow Transplant 11:945 ‐ 955 (2005) 4
Recommend
More recommend