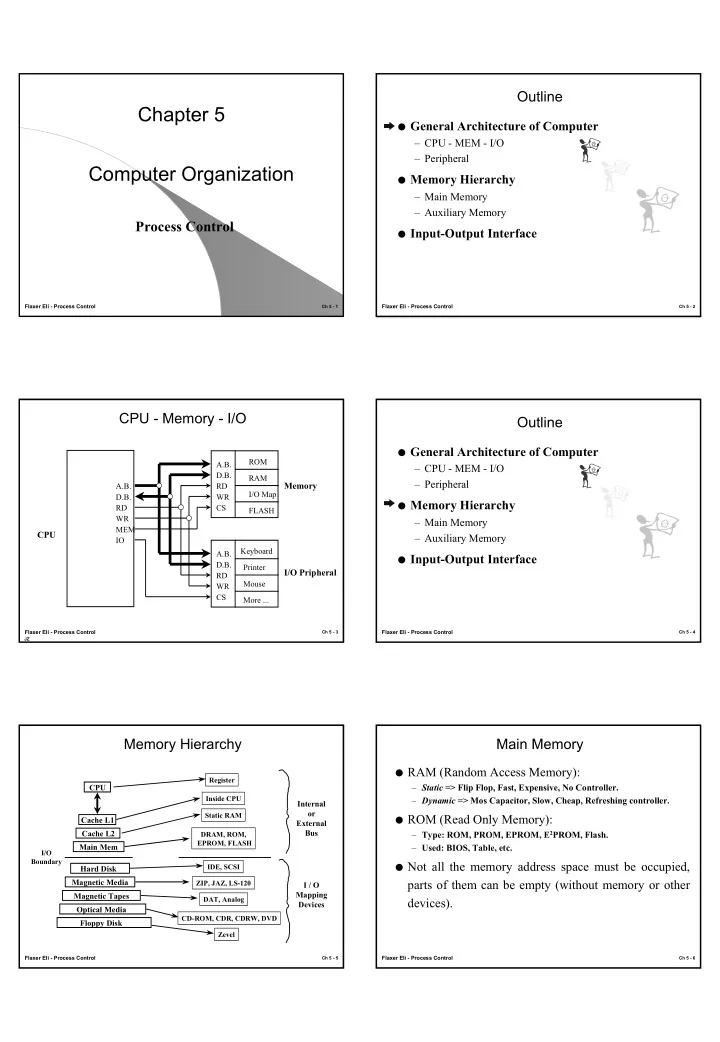

Outline Chapter 5 � General Architecture of Computer – CPU - MEM - I/O – Peripheral Computer Organization � Memory Hierarchy – Main Memory – Auxiliary Memory Process Control � Input-Output Interface Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 1 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 2 CPU - Memory - I/O Outline � General Architecture of Computer ROM A.B. – CPU - MEM - I/O D.B. RAM – Peripheral Memory A.B. RD I/O Map D.B. WR � Memory Hierarchy RD CS FLASH WR – Main Memory MEM CPU – Auxiliary Memory IO Keyboard A.B. � Input-Output Interface D.B. Printer I/O Pripheral RD Mouse WR CS More ... Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 3 Ch 5 - 4 JZ Memory Hierarchy Main Memory � RAM (Random Access Memory): Register – Static => Flip Flop, Fast, Expensive, No Controller. CPU Inside CPU – Dynamic => Mos Capacitor, Slow, Cheap, Refreshing controller. Internal or Static RAM � ROM (Read Only Memory): Cache L1 External Cache L2 Bus DRAM, ROM, – Type: ROM, PROM, EPROM, E 2 PROM, Flash. EPROM, FLASH Main Mem – Used: BIOS, Table, etc. I/O Boundary � Not all the memory address space must be occupied, IDE, SCSI Hard Disk Magnetic Media parts of them can be empty (without memory or other ZIP, JAZ, LS-120 I / O Mapping Magnetic Tapes DAT, Analog devices). Devices Optical Media CD-ROM, CDR, CDRW, DVD Floppy Disk Zevel Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 5 Ch 5 - 6
Memory Address Map RAM & ROM Chips CS RD RAM 0 0 RD CS RD WR Function Data Bus WR WR 1K x 8 Chip Select 0 x x None Tri -State DB(0..7) 1 AB Decoder CS k-Bit AB(10..11) 0 0 None Tri -State 1 Read RAM 2 Data Bus CS RAM 1 RD 0 1 Write From Outside 1 EN RD 2 n x k Write 3 CPU 1K x 8 WR WR 1 0 Read From Memory 1 n-Bit AB AB 1 1 Ilegal Address 1 AB(0..11) CS RAM 2 RD AB(12) WR 1K x 8 Chip Select CS AB CS RD Function Data Bus AB(13..15) k-Bit Read ROM RD CS Data Bus 0 x None Tri -State RAM 3 2 n x k BEGIN END A 12 A 11 A 10 RD 1 0 None Tri -State 1K x 8 RAM 0 0000 H 03FFH 0 0 0 AB(0..9) WR n-Bit AB AB RAM 1 0400 H 07FFH 0 0 1 1 1 Read From Memory Address RAM 2 0800 H 0BFFH 0 1 0 CS ROM RAM 3 0C00H 0FFFH 0 1 1 RD 4K x 8 ROM 1000 H 1FFFH 1 x x AB AB(0..11) Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 7 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 8 Unoccupied Memory Address Address Map Table CS RD RAM 0 BEGIN END A 12 A 11 A 10 0 RD WR WR 1K x 8 DB(0..7) 1 AB Decoder RAM 0 0000 H 03FFH 0 0 0 AB(10..11) 2 CS RAM 1 EN RD 3 RAM 1 0400 H 07FFH 0 0 1 CPU 1K x 8 WR AB AB(0..9) RAM 2 0800 H 0BFFH 0 1 0 AB(0..11) CS AB(12) Reg RD RAM 3 0C00H 0FFFH 0 1 1 AB(13..15) WR 4 x 8 AB(0..1) AB BEGIN END A 12 A 11 A 10 ROM 1000 H 1FFFH 1 x x RAM 0 0000 H 03FFH 0 0 0 CS ROM RAM 1 0400 H 07FFH 0 0 1 RD None 0800 H 0BFFH 0 1 0 4K x 8 AB(0..11) AB Reg 0C00H 0C03H 0 1 1 ROM 1000 H 1FFFH 1 x x Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 9 Ch 5 - 10 Address Map Table Auxiliary Memory � Hard Disk: BEGIN END A 12 A 11 A 10 – IDE => 30G, Fast, Internal. – Scsi => 100G, Ultra Fast, Internal / External. RAM 0 0000 H 03FFH 0 0 0 � TAPE : – DAT : Slow, 100G per cassette . RAM 1 0400 H 07FFH 0 0 1 – Travan : Very Slow, 1G per cassette. � Optics: None 0800 H 0BFFH 0 1 0 – CD, CDR, CDRW => 640M. Reg 0C00H 0C03H 0 1 1 – DVD, DVD-RAM => 5G. � Removable: ROM 1000 H 1FFFH 1 x x – Zip => 100M, 250M. – Jaz => 1G, 2G. – Ls-120 => 120M. – More => Floppy, Flash, ... . Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 11 Ch 5 - 12
Input-Output Interface Outline � I/O interface provide a method for transferring � General Architecture of Computer information between internal storage and external I/O – CPU - MEM - I/O devices. – Peripheral � Memory Hierarchy � To resolve the differences between CPU and peripherals (Mechanism, Transfer Rate, Format, etc) – Main Memory – Auxiliary Memory the system include interface. � Input-Output Interface � In addition, each device may have its own controller that supervise the operation of the particular mechanism in the peripheral. Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 13 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 14 I/O Bus and Interface Input-Output Interface � To communicate with particular device, the processor Data Bus Addr Bus place a devise address on the address bus ( Port Addr ). CPU Control � When the interface detects ins own address, it activates the device that it controls. All others peripherals are disable in Tri-State. Interface Interface Interface Interface � At the same time the processor provides a function code in the control lines. Keyboard CD Hard Printer & or � The data send / received in Bi-directional data bus. Disk Display DVD � Each CPU has special opcode for I/O operation. Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 15 Ch 5 - 16 Physical Memory Accessing Physical Memory Accessing • If the operation system not allow direct accessing to the Assembler READ WRITE hardware, we must use tool kit or lib to map the physical memory to the pointer. • Each compiler has it’s own library Mov DI , AbsAdr Mov DI , AbsAdr Mov Al , [DI] Mov [DI] , Al static unsigned char *kbf1; int pt1; C & C++ READ WRITE int main () { char *AbsAdrPtr = AbsAdr; unsigned char temp; MyData = (*AbsAdrPtr) ; (*AbsAdrPtr) = MyData; MapPhysicalMemory (0x417, 1, &kbf1, &pt1); temp = *kbf1; printf(“%x”, temp); UnMapPhysicalMemory (pt1); } Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 17 Ch 5 - 18
Physical Memory Accessing Input-Output Instruction • ReadFromPhysicalMemory (AbsAdr, Buffer, Number_Of_Byte); Assembler IN OUT • WriteToPhysicalMemory (AbsAdr, Buffer, Number_Of_Byte); BYTE In AL , Op1 Out Op1, AL WORD In AX , Op1 Out Op1, AX DWORD In EAX, Op1 Out Op1, EAX int main () { Op1 = Immd 8 bit Addr or 16 bit address in DX. unsigned char temp; ReadFromPhysicalMemory (0x417, temp, 1); WriteToPhysicalMemory (0x469, 1000, 4); C & C++ IN OUT printf(“%x”, temp); } BYTE char inp (int Address) outp (int Address, char Data) WORD short inpw (int Address) outpw (int Address, short Data) Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 19 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 20 Example: 8254 Input-Output Instruction PASCAL & DELPHI 1.0 DB(0..7) DB 8254 BYTE Data := Port[Address] Port[Address] := Data IOR RD WORD Data := Portw[Address] Portw[Address] := Data IOW WR Timer 0 DELPHI 2.0+ (32 bit) CPU Port Timer 1 AB(2..9) CS Select Not Support Not Support Timer 2 Use inline assembler Use inline assembler Status AB(0) A0 AB(1) A1 Control BASIC Data% = INP(Address%) OUT(Address%, Data%) Base Port Port Space is: Address is: VISUAL BASIC 1024 ports Not Support Not Support 0x40 Use external DLL Use external DLL Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 21 Ch 5 - 22 8254 Addresses 8254 Control Select CS A 1 A 0 RD WR Tri -State 0 x x x x SC1 SC0 RW1 RW0 M2 M1 M0 BCD Timer 0 1 0 0 x x Timer 1 1 0 1 x x SC RW M BCD Timer 2 1 1 0 x x Select Counter Read / Write Mode Bin / BCD Control 1 1 1 0 1 Status 1 1 1 1 0 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 23 Ch 5 - 24
8254 Control Field 8254 Control Field SC - Select Counter M - Mode SC1 SC0 M2 M1 M0 0 0 Select Counter 0 0 0 0 Mode 0 0 0 1 Mode 1 0 1 Select Counter 1 0 1 0 Mode 2 1 0 Select Counter 2 0 1 1 Mode 3 1 1 Read - Back Command 1 0 0 Mode 4 1 0 1 Mode 5 RW - Read Write RW1 RW0 0 0 Counter Latch Command BCD - Binary Code Decimal BCD 0 1 Read / Write LSB 0 Binary Counter 16 Bit 1 0 Read / Write MSB 1 BCD Counter 4 Digit 1 1 Read / Write LSB first & MSB after Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 25 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 26 I/O Programming Example (C) Shift Operations • Set the Timer2 of 8254 to mode 3, Binary counting, and 16 • C language has two shift operations for variable and constant: bit interfacing. Load the counter with 0x1234. >> (shift right) << (shift left). • Shift left operation always insert ‘0’ to the LSB = 0xB6 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0x36=54 0 int main () 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 { unsigned char temp; after temp = 0xB6; outp(0x43, temp) // write control 0x6C=108 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 outp(0x42, 0x34) // write least outp(0x42, 0x12) // write most } Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 27 Ch 5 - 28 Shift Operations Shift Operations • If the type is sign, the MSB is duplicated (sign extended). • Shift right operation insert, to the MSB, value that depended in the type of the variable or the constant. • If the type is unsigned, ‘0’ is insert to the MSB 0x36=54 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 after 0x1B=27 0 0x36=54 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 after 0xB6=-74 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0x1B=27 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 after 0xDB=-37 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 Flaxer Eli - Process Control Flaxer Eli - Process Control Ch 5 - 29 Ch 5 - 30
Recommend
More recommend