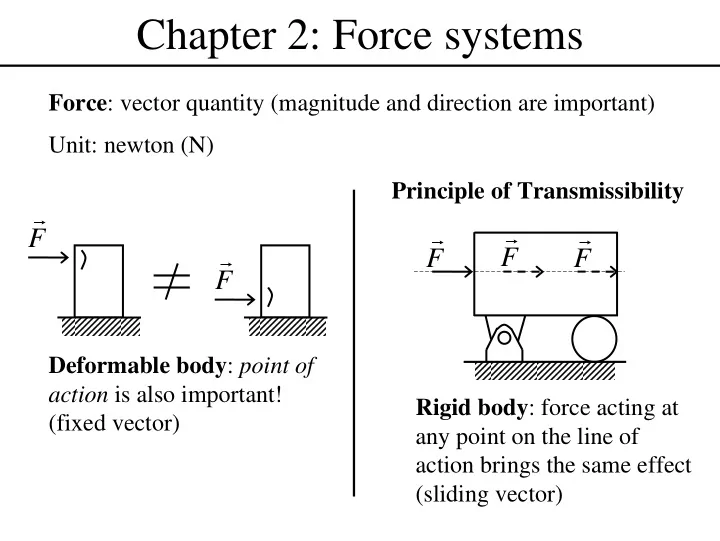

Chapter 2: Force systems Force : vector quantity (magnitude and direction are important) Unit: newton (N) Principle of Transmissibility r r r r F r F F F F Deformable body : point of action is also important! Rigid body : force acting at (fixed vector) any point on the line of action brings the same effect (sliding vector)
External and internal effects r F External r F r F Internal Fixed Depend on body in consideration
Concurrent forces r r F R 2 r r r F R F 2 A 1 r F A 1 r • Concurrent forces : F A Forces that their line of action 1 r intersect at a point (point A ) r R F 2 • Their sum is called resultant R • Line of action of resultant R must pass point A
Vector components and projections b b r F r r b R R r F r 2 F 1 a a r F a r r r r , F 1 , F = vector components F a F = orthogonal projection 2 r b r R R of (along axis a and b ) of (onto axis a and b ) r r r r r r ≠ + = + R F F R F F 1 2 a b
A special case of vector addition r R r r R 1 R 2 r r r r R R 2 2 F F F R R 2 2 2 1 1 F F F 1 1 1 F F F F r r r r F 1 and F 2 are Add F and – F to Magnitude, direction r r parallel produce R 1 and R 2 and line of action of r R can be known
Sample problem (1) Combine the two forces P and T , which act on the fixed structure at B , into a single equivalent force R .
Sample problem (2) Determine the components of the 800- N force F along the oblique axes a and b . Also, determine the projections of F onto the a - and b - axes
Sample problem (3) The tension in cable AC is 8 kN. Determine the required tension T in cable AB such that the net effect of the two cable tension is a downward force at point A . Determine the magnitude R of this downward force.
Rectangular components r r r = + y F F F x y ˆ + = ˆ F F i F j ˆ j r x y r F F y F x = cos( θ F ) θ r F y = sin( θ x F ) ˆ F i x r r r = + 2 2 F F F = F , F vector components of F x y x y − θ = r 1 tan ( / ) F F = y x F , F scalar components of F x y
Reference axis Reference axis: assignment based on convenience r r F F x θ β y θ F x = − F cos θ y F y = − F sin θ x x r F F x = F sin( β − θ ) F x = F cos θ θ y F y = − F cos( β − θ ) F y = − F sin θ
Vector summation r r r = + = + + + ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ R F F ( F i F j ) ( F i F j ) 1 2 1 x 1 y 2 x 2 y + = + + + ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ( ) ( ) R i R j F F i F F j x y 1 x 2 x 1 y 2 y y ∑ = + = R F F F r r x 1 x 2 x x F F F 2 y ∑ 2 1 = + = R F F F r F 1 y y 1 y 2 y y R R y o x F 1 x F 2 x R x
Sample problem (4) If the equal tensions T in the pulley cable are 400 N, express in vector notation the force R exerted on the pulley by the two tensions. Determine the magnitude of R .
Sample problem (5) If the cable tension is 750 N, determine the n- and t- components of this force acting on point A of the bar.
Sample problem (6) The 500-N force F is applied to the vertical pole as shown. (1) Write F in terms of the unit vector i and j and identify both its vector and scalar components. (2) Determine the scalar components of the force vector F along the x'- and y'- axes. (3) Determine the scalar components of F along the x- and y'- axes.
Recommend
More recommend