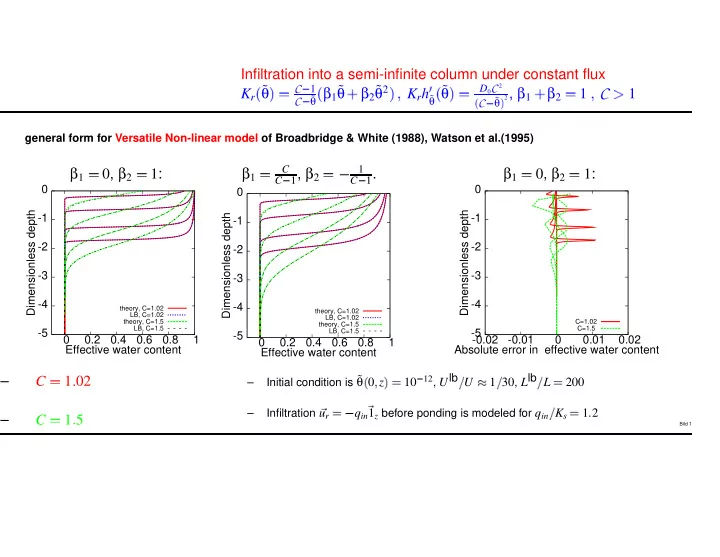

✌ ✔ ☎ ✂ ☞ ✠ ✂ ✄ ✂ ✡ ✂ ✄ ✖ ✎ ✒ ✂ ✕ ✄ ✎ ✂ ✔ ✎ ✒ ✒ ✓ ✂ ✂ ✒ ✑ ☛ ✂ ☛ ✟ ✆ ✆ � � ✞ ✁ ✂ ✄ ✂ ✄ ✁ � ☎ ✁ ✝ Infiltration into a semi-infinite column under constant flux θ β 1 ˜ θ β 2 ˜ θ 2 θ D 0 C 2 2 , β 1 β 2 ˜ ˜ C 1 K r K r h 1 1 C θ θ ˜ ˜ θ ˜ C C general form for Versatile Non-linear model of Broadbridge & White (1988), Watson et al.(1995) β 1 0 , β 2 β 1 1 , β 2 β 1 0 , β 2 C 1 1 : 1 . 1 : C C 0 0 0 Dimensionless depth Dimensionless depth Dimensionless depth -1 -1 -1 -2 -2 -2 -3 -3 -3 -4 -4 -4 theory, C=1.02 theory, C=1.02 LB, C=1.02 LB, C=1.02 theory, C=1.5 C=1.02 theory, C=1.5 LB, C=1.5 C=1.5 -5 LB, C=1.5 -5 -5 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 -0.02 -0.01 0 0.01 0.02 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Effective water content Absolute error in effective water content Effective water content θ 12 , U lb 30 , L lb Initial condition is ˜ – C 1 02 – 0 z 10 U 1 L 200 ✍✏✎ – Infiltration u r q in 1 z before ponding is modeled for q in K s 1 2 – C 1 5 Bild 1
✠ ✂ ✁ ✄ ✁ ✂ ✂ ✠ ✖ ✂ ✎ ✍ ✡ ✡ ✎ � ☞ ✒ ✖ ✎ ✖ ✎ ✡ ☛ � ✡ ☎ ✝ � � ✁ ✁ ✂ ✂ � ✝ � ☎ ✡ � ✁ ✁ ✁ ✄ ✁ ✂ � ✂ ✂ Steady state infiltration with VGM (van Genuchten 1980) and modified VGM (Vogel et al. 2001) models: θ β 0 α 0 h m , β 0 α 0 h s n n m , ˜ h 1 1 – Original model: h h s is α 0 θ ˜ 0 , n 1 and m n as empirical parameters 1 1 unbounded, h s 0 – Modified model: h h s θ ˜ is bounded, h s 0 Without averaging With averaging – Example: Sandy soil, 10 10 Moisture formulation, h_s=0 Moisture form.+Averaging, h_s=0 α 1 , n 3 7 m 5 Darcy, h_s=0 Darcy, h_s=0 9 Moisture formulation, h_s=-9cm Darcy 0 8 8 Vertical coordnate z, [m] Vertical coordnate z, [m] h_s=0 h_s=-3cm h_s=-9cm 7 -0.02 6 6 Pressure head h, [m] 5 -0.04 4 4 3 2 2 -0.06 red : h s 0 1 green: h s 3 cm 0 0 -0.08 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 blue : h s 9 cm Pressure head h, [m] Pressure head h, [m] – Input flux is q in 0 1 K s , K s 0 1 m h , h z L 0 3 4 m . Box has 100 cells. -0.1 0.999 0.9992 0.9994 0.9996 0.9998 1 Effective water content Bild 2
✂ ✂ ✖ � ✎ � ✌ ✁ ☞ ✄ ✖ ✎ ✍ � ✎ ✁ ✂ ✁ ✖ ✄ ✎ ✞ ✂ ✎ ✂ � ✄ � ✂ ✄ ✝ ✁ ✂ ✁ ✄ ✂ ✕ ✁ � ✖ ✖ ✖ ✁ ✎ ✝ � ✁ ✖ ✄ ✎ ✆ ✡ ✞ ✆ ✝ ✞ ✟ ✟ ✟ � ☎ ✁ ✂ � ✁ ☎ � ✁ ✟ ☎ ✄ ✂ ✆ ✍ ✁ � ✆ ✂ ✂ ☞ ✁ ✆ ✞ � ✟ Exact variably saturated non-stationary solution J.-P. Carlier (Cemagref, 2004) following “A class of exact solutions for Richards’ equation”, Barry et al.(1993) a) Definition of retention curve: -0.6 0.3 θ γ B ∂ h theory sub_it=0 ˜ h 1 h K r dh LB sub_it=5 ∞ -0.7 h sub_it=10 0.25 sub_it=50 -0.8 Relative L^2-Error γ h s B ∂ h 1 1 sub_it=1000 K r dh ∞ h - Depth Z, m -0.9 0.2 -1 -1.1 0.15 b) BCM hydraulic conductivity β , -1.2 function: K r h h h s 0.1 -1.3 β θ θ ˜ h s ˜ 1 1 0 then h B -1.4 0.05 -1.5 c) Linear solution within both -1.6 0 -4.5 -4 -3.5 -3 -2.5 -2 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Z Pressure head, m Time, h zones: h h t 0 0 A t tKs 1 with A t 1 W e θ s θ r γ – Exact h t -solution is fixed at top Z 0 6 m and the bottom Z 1 6 m Lambert function W x , – Computations are started at t t 0 0 1 h , h t 0 Z 1 6 m 72 m x W x exp W x . 10 3 h – Picture: t 20 Bild 3
✂ ✂ ✝ � ✂ ✝ � ✁ ✡ ✡ ✄ ✁ ☛ ✁ ✖ ✎ ✎ ✖ � ✝ ✡ � � � and θ Steady state infiltration in Sandy soil using h h formulations: Pressure head formula- tion does not use re- tention curves and has Pressure head formulation Mixed formulation 10 10 no approximation when Pressure formulation, h_s=0 Mixed formulation, h_s=0 Darcy, h_s=0 Darcy 9 9 h h s is unbounded, θ ˜ 8 8 Vertical coordnate z, [m] Vertical coordnate z, [m] 0 . h s 7 7 Mixed formulation does 6 6 not use retention cur- 5 5 4 4 ves in unsaturated zone 3 3 but needs h 1 to ex- θ ˜ 2 2 trapolate them beyond 1 1 air entry value h s . He- 0 0 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 6 Pressure head h, [m] Pressure head h, [m] re, P h 1 10 θ ˜ 24 m . 3566 Pressure head h L is fixed to 3 4 m at the bottom z L 0 . – 0 1 K s . Box has 100 cells. – Input flux is q in Bild 4
✁ ✟ ✂ � � ✆ � � ✁ ✁ � ☎ ✁ ✁ ✡ ✂ ✆ ✄ ✁ � ✡ ☎ ✁ � ☎ ✝ ✁ � ✞ � ✁ ✁ ✁ � ✂ ✂ ✞ � ✂ ✄ ✟ � ✁ ✁ ☎ � ✞ � ✟ ✁ � � ✞ ✁ ✁ ☎ ✁ ☎ ✁ ✁ � ✂ ✁ � � ✆ ✁ � ☎ ✂ ✟ ✞ ✞ ✟ � � � ✄ ✞ ✁ ✁ ✁ ✆ � ✂ � � ✁ ✂ ✁ ✡ � � � � ✁ ✟ ✟ ✡ � � ✟ ☎ ✂ ✡ � ✂ ☎ ✂ ✁ ✁ � � ✆ ✡ � ✂ ✞ � ✟ � ☎ ✆ ✁ ✆ ✁ ✁ ✁ ☎ ✞ ✂ ✁ � ✡ � ✁ � � ✂ ✁ � ✁ ✂ ✁ ✂ ✁ ✁ ☎ ✁ ✁ ✂ � � ✆ � ✆ ✟ ✁ Dispersion relation (D.d’Humières) – Diffusion term: Solution is looked in the form, ν lb ν ν r ν k 2 r k 2 n k k 1 k k ω t , f f 0 exp i k r Ut n 1 where r Optimal diffusion solution ν k , c 2 e – 0 for any s and a is ω i ν k k 2 k k 1 ν k α k β ∑ α k β D αβ 2 k 2 λ opt λ opt Λ 2 λ opt 3 3 e D D k k x k y k z 9 cos θ sin φ sin θ sin φ cos φ . k – Advection term: i ω t and f 0 are the r z exp U lb k 2 r k 2 n k k U 1 u k u k 1 n eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the linear operator r – Optimal advection solution u 0 is BGK Model k 1 1 eq. , � ✆☎ � ✆☎ 1 f eq. eq. λ opt λ opt Λ 2 λ opt λ opt f 3 3 D e D e 9 diag exp k C j Bild 5
Recommend
More recommend