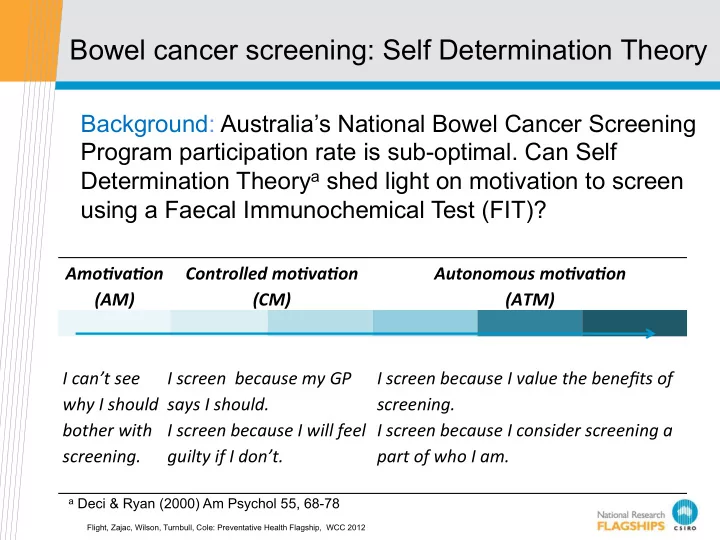

Bowel cancer screening: Self Determination Theory Background: Australia’s National Bowel Cancer Screening Program participation rate is sub-optimal. Can Self Determination Theory a shed light on motivation to screen using a Faecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)? Amo$va$on( Controlled(mo$va$on( Autonomous(mo$va$on( (AM) ! (CM) ! (ATM) ! I"can’t"see" I"screen""because"my"GP" I"screen"because"I"value"the"benefits"of" why"I"should" says"I"should. ! screening. ! bother"with" I"screen"because"I"will"feel" I"screen"because"I"consider"screening"a" screening. ! guilty"if"I"don’t. ! part"of"who"I"am. ! a Deci & Ryan (2000) Am Psychol 55, 68-78 Flight, Zajac, Wilson, Turnbull, Cole: Preventative Health Flagship, WCC 2012
Bowel cancer screening: Self Determination Theory Methods Results • N=1827 recruited from the • Autonomous Motivation (ATM) electoral roll (subsample of larger significantly distinguished study) between those ready to screen at baseline from those not ready • Age between 50 and 74 (AM and CM not sig.) • Dependent variables: (1) • ATM significantly associated with readiness to screen (baseline return of completed FIT (AM and survey); (2) return of FIT CM not sig.) • Independent variables: (1) self • SE initially significant correlate of efficacy (baseline survey); (2) completed FIT scores on types of motivation (AM, CM, ATM) determined from • When ATM entered into endpoint survey administered regression model, SE no longer following return of FIT or 12 an influence weeks after (non participants) Flight, Zajac, Wilson, Turnbull, Cole: Preventative Health Flagship, WCC 2012
Bowel cancer screening: Self Determination Theory Conclusions • All participants agreed to receive a FIT. However: • Those who intended to screen and did screen scored higher on self efficacy than non-participants. • Those who intended to screen and did screen scored significantly higher on ATM than non-participants, but did not differ on AM and CM. • When entered into a regression model (self efficacy 1, ATM 2) the effect of self efficacy on screening behaviour disappeared. • Screening invitations should aim to enhance autonomous motivation eg through motivational interviewing. Flight, Zajac, Wilson, Turnbull, Cole: Preventative Health Flagship, WCC 2012
Recommend
More recommend