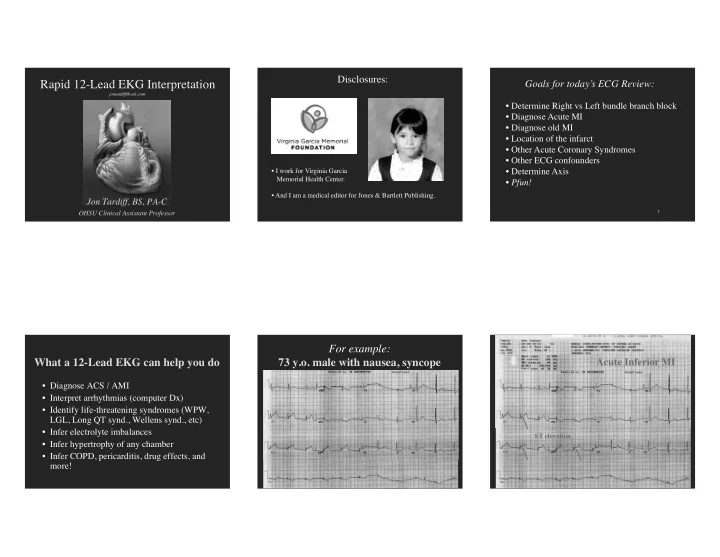
Acute Inferior MI What a 12-Lead EKG can help you do 73 y.o. male - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Disclosures: Rapid 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Goals for todays ECG Review: jontardiff@aol.com Determine Right vs Left bundle branch block Diagnose Acute MI Diagnose old MI Location of the infarct
Disclosures: � Rapid 12-Lead EKG Interpretation � Goals for today’s ECG Review: � jontardiff@aol.com � • Determine Right vs Left bundle branch block � • Diagnose Acute MI � • Diagnose old MI � • Location of the infarct � • Other Acute Coronary Syndromes � • Other ECG confounders � • I work for Virginia Garcia � • Determine Axis � Memorial Health Center. � • Pfun! � • And I am a medical editor for Jones & Bartlett Publishing. � Jon Tardiff, BS, PA-C � 3 � OHSU Clinical Assistant Professor � For example: Acute Inferior MI � What a 12-Lead EKG can help you do � 73 y.o. male with nausea, syncope � • Diagnose ACS / AMI � • Interpret arrhythmias (computer Dx) � • Identify life-threatening syndromes (WPW, LGL, Long QT synd., Wellens synd., etc) � • Infer electrolyte imbalances � ST elevation � • Infer hypertrophy of any chamber � • Infer COPD, pericarditis, drug effects, and more! � 5 5 � 6 � 6
another example… � What rhythm? (look at V1 for P waves) � Atrial fl utter (w/septal MI?) � The fl utter waves are invisible in Lead II � 9 � 9 WPW Graphic � Wolff-Parkinson-White synd. � WPW with Atrial Fib � Same pt, converted to SR � • short PR � • wide QRS � • delta wave � 10 � 10 1 10 12 � 12 12 2 2
Confounder: Left Bundle Branch Block � Limitations of a 12-Lead ECG � Impending AMI with normal ECG! � • Truly useful only ~40% of the time � • Each ECG is only a 10 sec. snapshot � • Serial ECGs are necessary, especially for ACS � • Other labs help corroborate ECG fi ndings (cardiac markers, Cx X-ray) � • Confounders must be ruled out (dissecting aneurysm, pericarditis, WPW, LBBB, digoxin, RVH) � 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 � 14 4 4 15 � 15 15 15 1 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 5 5 Confounder: Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome � “ECG Pearls” � • Lead II is the easiest lead to read / most intuitive � 13 hrs later — Acute Anterior MI � • But Lead V1 is our single best lead. � • Lead V3 is best for QT interval measurement � • “A Q in III is free.” (isolated Q in L III) � • 80% of reading an ECG is fi nding the P wave! � Elevated ST segments � • The other half is knowing where the + electrode is. ☺ � Pt is a 4 y.o. child w/ one episode of tachycardia and shortness of breath. WPW mimicking MI ( false Q waves in Lead II, III, AVF, V1, & V3). Also mimicking LBBB. � 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 � 16 1 6 6
Normal 12-Lead ECG � ECG Lead Placement � & � Limb Leads � Electrophysiology Review � � I (standard � II leads) � III - � ± � + � 19 � 20 � Conduction System � Lead II � Rapid Int Rapid Interpretation Tips � nterpretati ati tion ti ti ti ti ti ti ti i i i i o Tip on on on on on on on on on on on on on on on n n T s Dr. Willem Einthoven � P wave axis � …upright in L II � II � R � T � P � U � R � Q � S � R wave axis � …upright in L II � SA Node AV Node His Bundle BBs Purkinje Fibers � 22 � 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 2 2 2 23 � 23 � 24 � Q � S �
Intervals � QRS Morphology in Lead II � Leads I, II, III � II � I III II PR � QRS � QT � II � PR Interval: 120 – 200 mSec (3 – 5 boxes) � QRS width: 60 – 120 mSec (1 ½ – 3 boxes) � QT/QTc interval: 400 mSec (10 boxes) � 25 � 26 � 27 � 27 � Normal Sinus Rhythm � Triplicate Method: � 6-second : � 6 seconds Limb (frontal plane) Leads � � 300, 150, 100, � Count PQRST in a 6- second strip & multiply x 10 � 75, 60, 50 � I � Easy, & more accurate (standard � Quick, easy, sufficient � II leads) � III 300 150 100 75 60 6 seconds � aVR � aVL (augmented leads) � aVF � What is the heart rate? Horizontal axis is time (mS); vertical axis is electrical energy (mV) � 28 � 29 � 30 �
6 Frontal Plane Leads Normal 12-Lead ECG � (limb leads) � Axis � I Leads � - � I � III II II � III � aVR* � L aVL � F R aVF � 32 � 33 � Limb (frontal Chest (precordial) plane) Leads � Leads � � I � V1 (standard (anterior � II � V2 leads) leads) � III � V3 � aVR � V4 � aVL � V5 (lateral � aVF � V6 leads) 34 � 34 (augmented leads) 35 � 36 �
Normal 12-Lead ECG � V Lead Cutaway � V Lead Progression � Rapid Interpretation Tips � Lots of ways to read EKGs… � Rapid Interpretation Tips � • Identify the rhythm. If supraventricular* , � • QRSs wide or narrow? � • Sinus rhythm or not? � If no LBBB, � • Regular or irregular? � • If not, is it atrial fi brillation? � • Fast or slow? � • BBB? � Step-by-step method for reading a 12-Lead � • P waves? � • MI? � � If present, � • Rule out other confounders: WPW, pericarditis, LVH, digoxin effect � Symptoms: � • Identify location of infarct, and consider appropriate • Syncope is bradycardia, heart blocks, or VT � treatments: MONA, PCI [or fi brinolytic], nitrate • Rapid heart beat is AF, SVT, or VT � infusion, heparin infusion, GP IIb, IIIa inhibitor, beta- blocker, clopidogrel, statin, etc. � 41 �
Rapid Interpretation Tips � Normal 12-Lead ECG � Supraventricular rhythms � Rapid Interpretation Tips � • Identify the rhythm. If supraventricular, � • Sinus rhythm � If no LBBB, � • Atrial fi brillation � • Junctional rhythm � � If present, � • PSVT / AVNRT � • Atrial tachycardia � • Rule out other confounders: WPW, pericarditis, LVH, digoxin effect � • Atrial fl utter � • Identify location of infarct, and consider appropriate • Wandering atrial pacemaker � treatments: MONA, PCI [or fi brinolytic], nitrate • MAT � infusion, heparin infusion, GP IIb, IIIa inhibitor, beta- blocker, clopidogrel, statin, etc. � Bundle Branch Blocks Bundle Branch Blocks The Problem with Bundle (QRS > 0.12 sec.) Two QRSs Branch Blocks � Blocked (right-sided lead) (left-sided lead) Healthy bundle � ventricle � V1 R’ • Desynchronized contraction of the ventricles � notch I • Reduced cardiac output � r • Worsened heart failure � S • LBBB confounds the EKG interpretation � Left BBB and makes it harder to fi nd ACS � Right BBB (L I, V5, V6: (V1, V2, MCL1: upright QRS V1 R’ notch slur I I rsR’ pattern) with a notch) r 47 � 48 � 48 48 48 48 48 48 48 48 48 48 4 8 S
LBBB � Practice: Bundle Branch Block � RBBB � V 5 V 6 � V 1 & V 2 � ( & I, aVL) � 51 � Which Bundle Branch is Blocked? � Which Bundle Branch is Blocked? � 1 � 1 � 2 � Right Bundle Branch Block (Lead V1) � LBBB 12-Lead � RBBB � RBBB �
Where is the Pathology? � Right Bundle Branch Block � 2 � Left Bundle Branch Block � LBBB 12-Lead � (L I, V5, V6) � Where is the Pathology? � Left Bundle Branch Block � Axis Determination � 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 58 5 58 58 58 � 8 59 �
Why We Care About Axis Deviations � Axis Deviation � How to calculate Axis � Horizontal heart (0°): obesity, 3 rd � Easiest: the computer does it for you! � trimester pregnancy. Ascites � The axis shifts towards hypertrophy � Vertical heart (90°): slender build � & away from infarction � Easy : fi nd the tallest R wave � (if tallest is Lead II = normal axis ) � Left Axis Deviation : LBBB, � Anterior MI, Inferior MI, Left � anterior hemiblock, LVH � Even easier : (if Lead II is upright = � normal axis � Right Axis Deviation : Anterior MI, � 63 � Lateral MI, RBBB, COPD, RVH, � Left posterior hemiblock � Funnest : Thumbs up / Thumbs down � Extreme RAD : Ectopic rhythm � 61 � 62 � (VT), MI � 3 � 1 1 � Practice: Axis � Axis Axis Practice � Ax A is Pra is is is is is is is is is is s Pra s s s s ractice ra ra ra ra ra r cti ra ra ra ra ra ra ra ra ra a a Calculating Axis: Thumbs Up / Down Method � Normal Axis � I � I � Lead I —Your Left thumb � Lead aVF —Your Right thumb � F � F � 64 � 65 � 6 66 66 � 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 66 6
4 � 4 � 5 � Left Axis Deviation � I � I � F � F � 67 � 68 � 69 � 5 � 6 � 6 � Right Axis Deviation � Extreme Right Axis Deviation � 70 70 70 � 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 0 0 0 0 71 � 72 � 72 72 72 72 72 72 7 72
New 12-Lead ECG Format � Rapid Interpretation Tips � New 12-Lead ECG Format � New � Rapid Interpretation Tips � • Identify the rhythm. If supraventricular, � • Rule out left bundle branch block. If no LBBB, � II � aVL � • Check for: ST elevation, or ST depression with T aVL � II � wave inversion, and/or pathologic Q waves . � aVF � � If present, � I � aVF � I � • Rule out other confounders: WPW, pericarditis, LVH, digoxin effect � Old � -aVR � III � -aVR � III � • Identify location of infarct, and consider appropriate treatments: MONA, PCI [or fi brinolytic], nitrate infusion, heparin infusion, GP IIb, IIIa inhibitor, beta- blocker, clopidogrel, statin, etc. � 73 � ST elevation, ST depression, T wave inversion, pathologic Q waves � STEMI � Normal � Ischemia � Injury � Infarction � 77 �
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.























