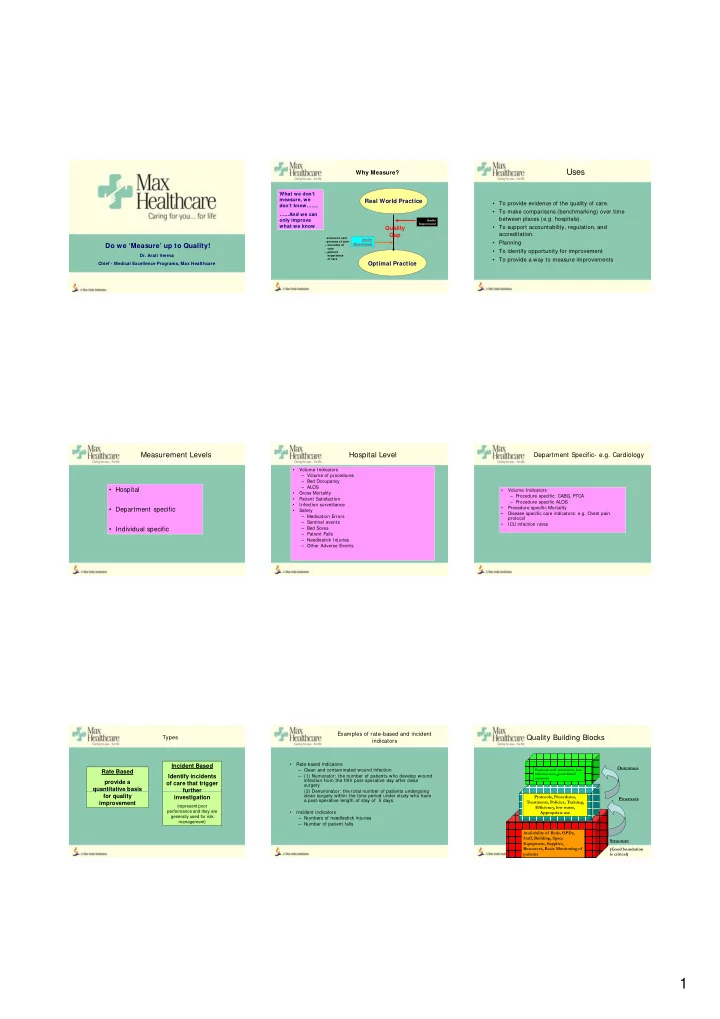

Uses Why Measure? What we don’t measure, we Real World Practice • To provide evidence of the quality of care. don’t know……. • To make comparisons (benchmarking) over time ……And we can between places (e.g. hospitals). only improve Quality Improvement what we know what we know • • To support accountability regulation and To support accountability, regulation, and Quality Q lit accreditation. Gap - access to care Quality - process of care • Planning Do we ‘Measure’ up to Quality! Measurement – outcome of care • To identify opportunity for improvement – patient Dr. Arati Verma experience • To provide a way to measure improvements of care Optimal Practice Chief - Medical Excellence Programs, Max Healthcare Measurement Levels Hospital Level Department Specific- e.g. Cardiology • Volume Indicators – Volume of procedures – Bed Occupancy – ALOS • Hospital • Volume Indicators • Gross Mortality – Procedure specific: CABG, PTCA • Patient Satisfaction – Procedure specific ALOS • Infection surveillance • Department specific • Department specific • Procedure specific Mortality Procedure specific Mortality • Safety S f t • Disease specific care indicators: e.g. Chest pain – Medication Errors protocol – Sentinel events • ICU infection rates • Individual specific – Bed Sores – Patient Falls – Needlestick Injuries – Other Adverse Events Examples of rate-based and incident Types Quality Building Blocks indicators • Rate-based indicators Incident Based Outcomes – Clean and contaminated wound infection Patient & staff satisfaction, Low Rate Based infection rates, good clinical Identify incidents – (1) Numerator: the number of patients who develop wound outcomes infection from the fifth post-operative day after clean provide a of care that trigger surgery q quantitative basis further further – (2) Denominator: the total number of patients undergoing (2) Denominator: the total number of patients undergoing for quality clean surgery within the time period under study who have Protocols, Procedures, investigation Processes a post-operative length of stay of 5 days. improvement Treatments, Policies, Training, (represent poor Efficiency, low waste, performance and they are • Incident indicators Appropriate use generally used for risk – Numbers of needlestick injuries management) – Number of patient falls Availability of Beds, OPDs, Staff, Building, Space Structure Equipment, Supplies, Resources, Basic Monitoring of (Good foundation patients is critical) 1
A new indicator now in use Sample Patient suddenly collapses in Corridor • Appropriateness of Care Structure Process Outcome – Antibiotic use • Availability of • Response time • % Failure to medication in within 3 minutes Resuscitate – Overuse of Investigations I Responder Code Blue crash cart • Algorithm • Length of stay Alerts Code BLS Started Team Reach Patient – Overstay in hospitals BLS Blue by 1 Designated Transferred to • % of Doctors in % of Doctors in followed followed post Survival post Survival Continued till Continued till Responder R d Location and L i d Emergency – Underuse of Specialists Code Blue Emergency Dept • Documentation • % Discharged to Take over Dept/ICU Team arrives Treatment who are ACLS – Number of MRIs ordered for particular condition compliance Home qualified • Total Code Blue vs number showing positive findings Mortality – Number of appendicectomies done vs number showing positive histopathology Risk adjustment Factors determining Outcome of Care Factors determining Outcome of Care • The patient: • The Illness • The Treatment • The Organization – Demographics: Age, Sex, – Severity • Risk adjustment may be most important for Height (prevention, diagnostics, – Prognosis – Quality Management and – Lifestyle: Smoking, dietary care, rehab, therapy): outcome indicator s. review – Co morbidity habits, alcohol, physical – Competence – Use of Clinical Guidelines activity, weight activity, weight – Technical equipment T h i l i t • In most cases, multiple factors contribute to a – Psychosocial Factors: Social – Safe Practices – Evidence based Clinical Status, Living conditions, – Efficiency practice patient’s survival and health outcomes. Education – Accuracy – Compliance – Effective Defining Thresholds: Standards Getting started How to get started? • Get key functional persons together • 4 Parts: • Brain storm : • Decide on what is the – Identify which processes are important for patient • Component: Measurable aspect of care: e.g. Create Your Own numerator/denominator, sample size, Create Your Own Quality Dashboard Quality Dashboard care/both service and clinical in your hospital. timeliness frequency of data, who will collect. – Research and benchmark from internet • • List desirable targets: List desirable targets: – Some are required for accreditation • Yardstick: Desired quality level: 1 minute • Create your own dashboard • Focus on access, structure, process and outcome "Not everything that • Review regularly and initiate QI projects "Not everything that • Target: Degree to which criterion should be met: can be counted can be counted 100% • Selection: simple, valid, reliable, easily counts, and not counts, and not everything that counts everything that counts measurable process points that impact can be counted." can be counted." - Albert Einstein - Albert Einstein quality/safety of patient care. • Exceptions: Valid reasons for non compliance? (1879-1955) (1879-1955) • The vital few rather than the desirable many 2
Indicators Examples Surgical Mortality Rate Emergency: Relationship to Institutes with lower mortality rates reflect good outcomes of Quality care • Ambulance Response Time – You want to measure mortality rate in surgical • Consultant Response Time Definition Number of patient deaths in the surgical units per 100 department. • Response To Code Blue discharges. – What is the relevance? • Availability of drugs in Ambulance/Crash Numerator Total number of deaths in operated patients in a month X 100 – Can this be measured? Can this be measured? carts carts Denominator Total number of operated patients discharged per month OPD – Define the numerator and denominator • Time taken from registration (including deaths) – How many times, how often and by whom should to Dr consult starting Dimension Safety, Quality this be measured? Data collection Incidental findings • OPD protocols • Appointments timing (clinic start time) Data source MRD • Wearing White Coats Responsibility MRD In charge • Documentation Analysis frequency Monthly Indicators Indicators Indicators IPD Pharmacy Diagnostics • Nurse call bell response time • Delivery to external • Errors in information for Test preparation • Pre operative evaluation customers • Timeliness of Reports Delivery completion • % of Times Substitutes delivered (OPD & IPD) (OPD & IPD) • Timeliness of Consultant rounds • Time to deliver to Depts • Number of Reporting errors • Requisition Errors • Errors in delivery to Depts • Timeliness of post discharge pending • Prescription/transcription errors (wrong medicines) reports of patients • Discharge process timeliness • Waiting time at pharmacy counter Critical success factors Indicators Acute MI % Compliance • Morbidity & Mortality 100.00 100.00 • Transparency 100.00 95.65 95.45 • Hospital Mortality Rate 91.67 87.50 90.00 86.36 • Mutual trust within clinicians and staff • Readmissions 24 hours after discharge 80.00 • Unbiased 73.91 • Post Operative Wound infection rate 70.00 • Indicator should be: Reliable and valid • Infections in 72 hours (for Afebrile Infections in 72 hours (for Afebrile 60.00 • Culture of continuous improvement patient admissions) 50.00 Series1 • Openness to change • Return to theatre rate 40.00 • No Blame games • Return to ICU rate 30.00 • Must show improvement over time • Death within 24 hours of elective 20.00 • Review indicators and targets for current relevance surgery (upto ASA grade 2 patients) 10.00 0.00 Aspirin at Arvl Aspirin IPD Beta Blockers ACE/ARBs IPD Risk ASA at B-blockers at ACE/ARBs at IPD Straification Discharge discharge Discharge 3
Did this ppt have a similar effect on you! 4
Recommend
More recommend