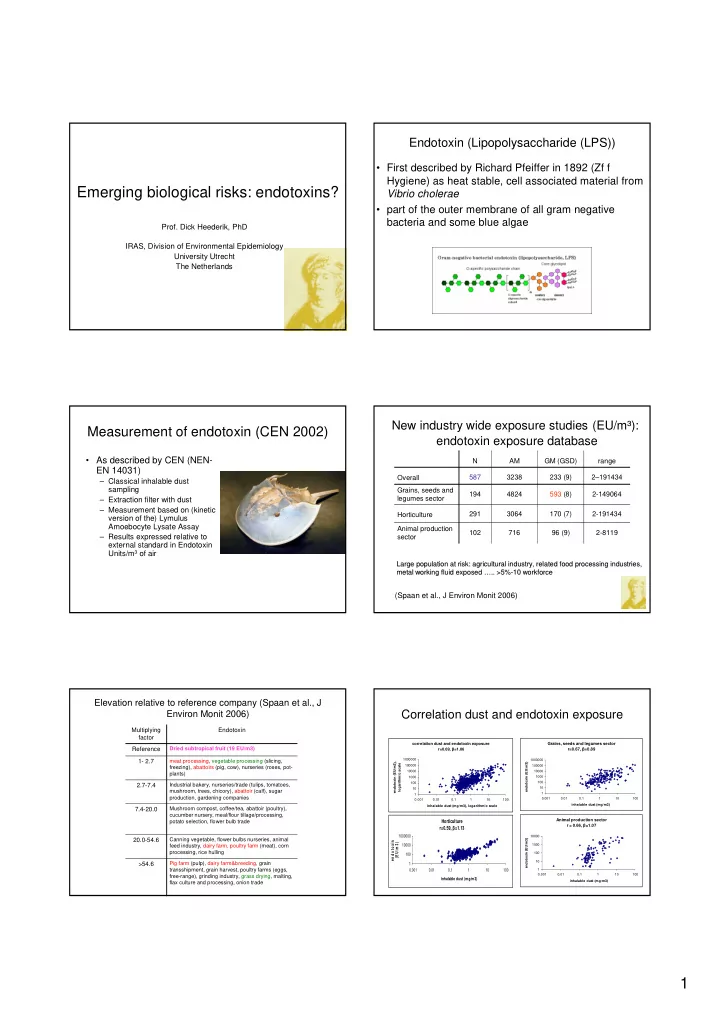

Endotoxin (Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)) • First described by Richard Pfeiffer in 1892 (Zf f Hygiene) as heat stable, cell associated material from Emerging biological risks: endotoxins? Vibrio cholerae • part of the outer membrane of all gram negative bacteria and some blue algae Prof. Dick Heederik, PhD IRAS, Division of Environmental Epidemiology University Utrecht The Netherlands New industry wide exposure studies (EU/m³): Measurement of endotoxin (CEN 2002) endotoxin exposure database • As described by CEN (NEN- N AM GM (GSD) range EN 14031) 587 3238 233 (9) 2–191434 Overall – Classical inhalable dust sampling Grains, seeds and 194 4824 593 (8) 2-149064 legumes sector – Extraction filter with dust – Measurement based on (kinetic 291 3064 170 (7) 2-191434 Horticulture version of the) Lymulus Amoebocyte Lysate Assay Animal production 102 716 96 (9) 2-8119 – Results expressed relative to sector external standard in Endotoxin Units/m 3 of air Large Large population population at risk: at risk: agricultural agricultural industry industry, , related related food food processing industries, processing industries, metal metal working working fluid fluid exposed exposed … ….. >5% .. >5%- -10 10 workforce workforce (Spaan et al., J Environ Monit 2006) Elevation relative to reference company (Spaan et al., J Environ Monit 2006) Correlation dust and endotoxin exposure Multiplying Endotoxin factor Grains, seeds and legumes sector correlation dust and endotoxin exposure Dried subtropical fruit (19 EU/m3) Reference r=0.69, β =1.06 r=0.67, β =0.89 meat processing, vegetable processing (slicing, 1000000 1000000 1- 2.7 endotoxin (EU/m3), endotoxin (EU/m3) logarithmic scale 100000 100000 freezing), abattoirs (pig, cow), nurseries (roses, pot- 10000 10000 plants) 1000 1000 100 100 2.7-7.4 Industrial bakery, nurseries/trade (tulips, tomatoes, 10 10 mushroom, trees, chicory), abattoir (calf), sugar 1 1 production, gardening companies 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 inhalable dust (mg/m3) inhalable dust (mg/m3), logarithmic scale 7.4-20.0 Mushroom compost, coffee/tea, abattoir (poultry), cucumber nursery, meal/flour tillage/processing, Animal production sector Horticulture potato selection, flower bulb trade r = 0.66, β =1.07 r=0.59, β =1.13 1000000 10000 Canning vegetable, flower bulbs nurseries, animal 20.0-54.6 e n d o to x in endotoxin (EU/m3) (E U /m 3 ) 10000 1000 feed industry, dairy farm, poultry farm (meat), corn processing, rice hulling 100 100 10 >54.6 Pig farm (pulp), dairy farm&breeding, grain 1 transshipment, grain harvest, poultry farms (eggs, 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 free-range), grinding industry, grass drying, malting, inhalable dust (mg/m3) inhalable dust (mg/m3) flax culture and processing, onion trade 1
Early evidence on health effects Review of health effects (up to 1997 www.gr.nl) • Cotton production • Experimental animal studies • Experimental studies in humans • Neal et al. JAMA 1942 (injection and inhalation pure suggested Enterobacter endotoxin, inhalation of dust agglomerans might play a role containing endotoxin (cotton, pig in the development of stables) byssinosis • A series of large scale • Rylander et al. was among the observational epidemiologic first to mention endotoxin in studies in agricultural workers and other occupational groups: relation to byssinosis (Chest – Grain processing 1986) – (pig) farming – Composting • Since than, exposure and – Metal working fluids, glass fiber effects have been described in production, etc. a range of industries Acute respiratory changes in cotton dust Health effects exposed individuals: card room studies • Acute: • Experimental study in the – Systemic and respiratory symptoms (dry cough, shortness of US in humans (Castellan breath, fever, shivering, joint pain) ICOH: ODTS 1000 EU/m 3 et al., 1987) (Rylander, 1997) • NOEL for acute lung – (Acute) lung function changes ICOH 100 EU/m 3 – Inflammatory response (neutrophile, cytokines) function changes around 9 ng/m 3 • Chronic: – Accelerated lung function decline (COPD?) • Formed the basis of the proposed exposure • Protective effects: standard in the – Atopy and allergy? Netherlands 50 EU/m 3 – Lung cancer? standard of 200 EU/m 3 adapted Atopy, and hay fever in farmers’ children (Braun-Fahrländer et al., 2002) Interindividual variability in response Endotoxin exposure during first year and current endotoxin exposure were associated with reduced atopy prevelance in children from farming and non-farming families Kline et al. 1999. ARRCCM. 2
occupational endotoxin exposure protects Endotoxin, respiratory symptoms and BHR against respiratory sensitization ast adult age (Smit et al., 2007 in preparation) Bronchial responsiveness to metacholine (%) 100 60 80 Lower respiratory symptoms (%) 50 60 40 30 40 20 20 10 0 10 100 1000 10000 0 10 100 1000 10000 Modeled endotoxin exposure (EU/m 3 ) Modeled endotoxin exposure (EU/m 3 ) Change in FEV 1 > 15% Change in FEV 1 >20% All participants aged 18-65 (n = 878) 95% SE bands 95% SE bands, change in FEV 1 >15% 95% SE bands, change in FEV1 >20% Portengen et al., JACI 2005 Endotoxin, atopy (with and without farm Association of lung cancer with cumulative exposure to endotoxin: 20 year latency childhood)(Smit et al., in preparation) Cum-exp Cases RR* 95%CI Subcohort 80 35 (EU-yrs) 30 208 1090 0.8 0.6-1.0 0 60 Atopic sensitisation (%) 25 Hay fever (%) 122 543 1.0 >0-1274 reference 20 40 15 81 408 0.7 0.5-0.9 1275-2041 10 20 75 347 0.7 0.5-0.9 2041-2082 5 0 0 10 100 1000 10000 57 309 0.5 0.4-0.8 2083-4042 10 100 1000 10000 Modeled endotoxin exposure (EU/m3) Modeled endotoxin exposure (EU/m 3 ) 59 338 0.5 0.4-0.7 4043-138177 All participants aged 18-65 (n= 878) No farm childhood (n = 235) 95% SE bands Farm childhood (n= 194) 95% SE bands, no farm childhood *Hazard ratio, adjusted for age, smoking 95% SE bands, farm childhood Source: Astrakianakis G, et al. JNCI (2007 in press) Variability issues Variability issues 12 kabivitrum 1988 against whittaker 1991 • Variability within and between kabivitrum 1988 against kabivitrum 1993 10 kabivitrum 1993 against whittaker 1993 x = y laboratories LAL assessment – Assay type: KLARE and other 8 • Changes over time seem repeated analysis kinetic versions (Milton et al., 6 limited (supplier, lot, etc.) 1992; Thorne et al., 1997) • Most information on 4 – Storage stability of samples laboratories with different 2 (Douwes et al., 1995; Milton et protocols (Reynolds et al., 0 • Variability in endotoxin al., 1997) 2002, 2005; Chun et al., 2002) -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 – Filter media (Douwes et al., between workers and over endotoxin concentration with kabivitrum based assay 1995; Thorne et al., 1997; • Performance improves when time larger than for Milton et al., 1997) protocols are harmonized chemical agents! – “Inhibition” and “enhancement” (Chun et al., 2002 and Linsel (Hollander et al., 1993) et al., 2003) – Extraction medium (Tween • Need to allow for this in optimal) (Douwes et al., 1995; • Major steps in harmonization the exposure assessment Thorne et al., 2003; USA can now be made (Spaan et ASTM protocol) strategy al., 2007; Wouters et al., 2007) 3
In conclusion Other issues Fig. 1a: TNF-a productie in WBA - exp.1 • No doubt about the role of endotoxin as cause of respiratory disease • Information from a limited number of 700 industries • Quantitative evidence has become stronger, as well as insight in Lolium-1 mechanisms Festuca-1 600 Wheat-1 • Exposure to a complex mixture Cauliflower Red beet 500 • Potential protective effects with regard to atopic responses: two sides of LPS cytokine (pg/mL) the coin? • extrapolation from one industry to 400 another? • Introduction of CEN protocol on EU level needed so reduce interlab 300 variability • Evidence remarkably consistent 200 across industries • High variability in endotoxin levels requires specific measurement strategy for biological agents 100 • Endotoxin often most potent 0 • Standard setting? SCOEL? constituent (in vitro evidence) 0.1 1 10 100 zaad extract (microliter/test) 4
Recommend
More recommend