
Viruses
What is a virus?
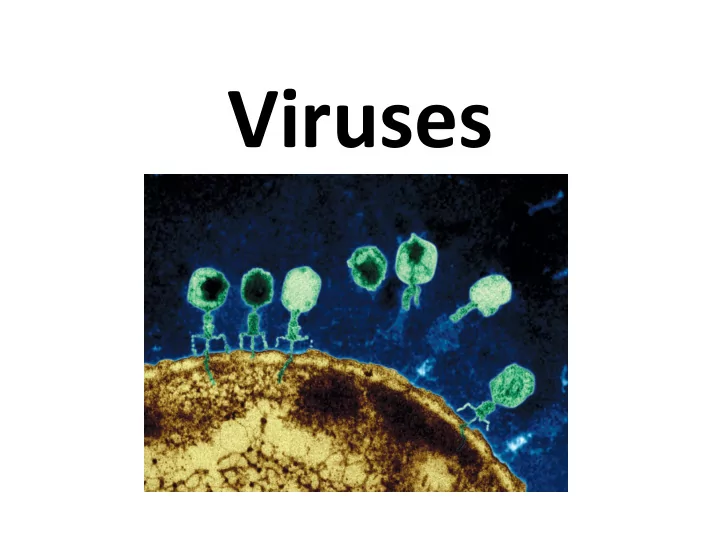
What is a virus? • A small infectious agent that reproduces only within a host cell ( obligate intracellular parasites ) • Infect all life forms, including bacteria • Lack metabolic enzymes and equipment for making proteins (i.e. ribosomes) • Infect cells of only a limited variety of hosts ( host range of the virus )
Cell Specificity • Viruses identify host cells by a “lock and key” fit between viral surface proteins and specific receptor molecules on the outside of cells
Structure of a Virus
Structure of a Virus • Composed of a nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA) and a protein coat ( capsid ) • Some viruses are also enveloped with a material composed of lipids and proteins
RNA or DNA? • The majority of viruses have RNA genomes • Plant viruses frequently have single-stranded RNA genomes • Bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) tend to have double-stranded DNA genomes
Virus Groups DNA Viruses RNA Viruses Retroviruses Chickenpox, Cold, influenza, HIV, human T- herpes, rabies, ebola, lymphotropic hepatitis B polio virus (HTLV-1)
How do viruses reproduce?
Lytic Cycle • Virus replicates immediately via a component assembly model allowing one virus to produce many viral progeny simultaneously Five steps: • Attachment • Penetration • Replication • Assembly • Release (lysis of host cell)
Lytic Cycle of Reproduction
Lysogenic Cycle • Virus integrates its genome into the host cell genome (DNA) • Results in a latent (lysogenic) infection • May result in new properties for the host such as increased pathogenicity in bacteria • Environmental conditions then trigger virus to initiate the lytic cycle
Lysogenic Cycle of Reproduction
Viruses and Genetic Variation • Viruses transmit DNA or RNA when they infect a host cell and introduce genetic variation • Examples: 1. Transduction in bacteria – type of horizontal gene transfer 2. Transposons in DNA – mobile genetic elements, viruses may move DNA within genomes and between individuals
Viruses and Evolution Fast Track • Replication is highly efficient • RNA viruses lack replication error-checking mechanisms, higher rates of mutations • Related viruses can combine/recombine information if they infect the same host cell
Evolution of Drug Resistant HIV • 3TC is an HIV drug that interferes with viral genome replication
HIV Virus
HIV (Retrovirus) • Retrovirus – alternate flow of information from RNA to DNA using reverse transcriptase • Demonstrates rapid evolution of a virus – Accumulates many mutations during replication – Reproduces quickly – one virus to billions of viral progeny in one day
Recommend
More recommend