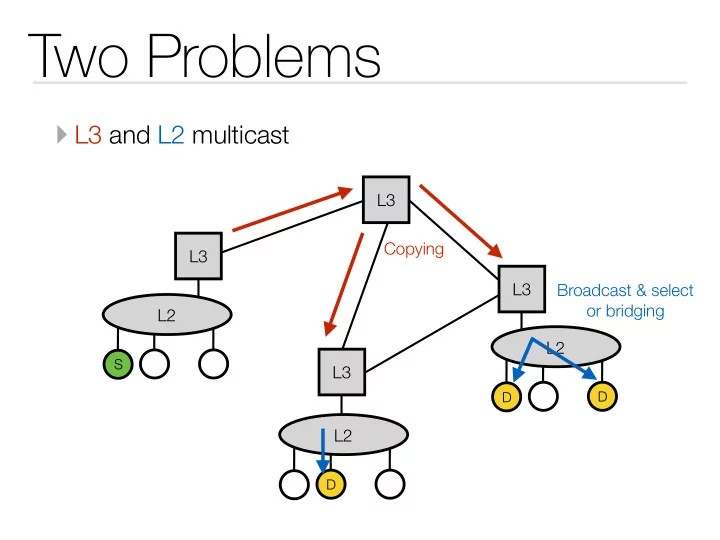

Two Problems ‣ L3 and L2 multicast L3 Copying L3 L3 Broadcast & select or bridging L2 L2 S L3 D D L2 D
Multicast Membership Discovery ‣ IGMP - Internet Group Management Protocol - Version 1 - Version 2 - group leave message - Version 3 - source specific multicast (SSM) ‣ Messages - Host Membership Query (MAC broadcast to 224.0.0.1) - Host Membership Report ‣ IGMP Snooping
Multicast Router Discovery ‣ IPv6: IP -> ICMPv6 header -> MRD message - ICMPv6 messages 151 ( Multicast Router Advertisement ), 152 ( Multicast Router Solicitation ) and 153 ( Multicast Router Termination ). ‣ IPv4: IP -> IGMP header -> MRD message - IGMP messages 0x30 ( Multicast Router Advertisement ), 0x31 ( Multicast Router Solicitation ) and 0x32 ( Multicast Router Termination ). ‣ All-snoopers multicast addresses 224.0.0.106 and FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:6A ‣ IPv4 TTL / IPv6 Hop Limit set to 1
DVMRP ‣ Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol - use a distance vector routing protocol to establish unicast routing between multicast routers connected via tunnels - use reverse path forwarding to flood multicast traffic - PRUNE - tell neighbor that you are not interested in multicast traffic from a particular group & and a source - creates soft state - GRAFT - notify router of a change of situation (renewed interest in a group/source)
OSPF (review) ‣ Open Shortest Path First - link state routing algorithm R R - two-level hierarchy Area 0 R R R R - user-defined link weights R ‣ Version history: R R Area 1 Area N Area 2 - OSPF (1989) - OSPFv2 (1998) - OSPFv3 (2008, IPv6)
MOSPF ‣ Multicast OSPF - on demand multicast routing - routers discover local multicast membership - group membership is flooded within an area - multicast traffic is forwarded along the spanning tree from the source (equal cost multi-path problem) - border routers are by default members of all multicast groups
CBT ‣ Core-Based Trees - receiver-initiated join sent towards the core node - state (multicast routes) created along the way - Issue: core location
PIM ‣ Protocol Independent Multicast - … “independent” of the underlying unicast protocols ‣ Two modes proposed (one size does not fit all) - Dense Mode (DM) • similar to DVMRP (flood and prune) - Sparse Mode (SM) • similar to Core Based Trees ‣ Applications - PIM-SM: IPTV
PIM-SM ‣ Designated Router (DR) - each source/destination has one ‣ Rendez Vous Point (RP) - does most of the copying work D S RP DR D Register DR D Data
Recommend
More recommend