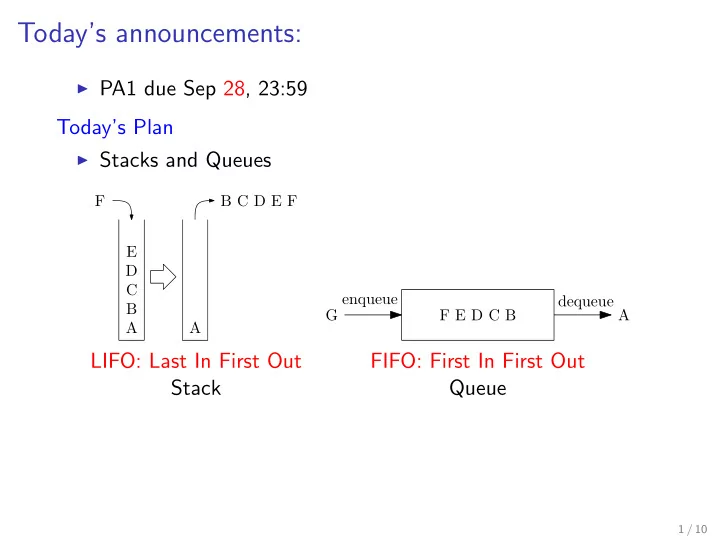

Today’s announcements: ◮ PA1 due Sep 28, 23:59 Today’s Plan ◮ Stacks and Queues F B C D E F E D C enqueue dequeue B G F E D C B A A A LIFO: Last In First Out FIFO: First In First Out Stack Queue 1 / 10
Stack: Array implementation S size − 1 0 5 a b c d e top = 5 class Stack{ void Stack<LIT>:: public: push(const LIT & e) { Stack(); if( isFull() ) resize(); void push(const LIT & e); S[top] = e; LIT pop(); top++; bool isEmpty() const; } private: LIT * S; LIT Stack<LIT>::pop() { int size; assert(!isEmpty()); int top; top--; }; return S[top]; } Runtimes? 2 / 10
Stack: Array implementation resize Resize If array S is full, create a larger array and copy existing data into it. a b c d e S a b c d e new S How much time does it take to resize from size x to size y ? How big should the new array be? ◮ The original size PLUS a constant? ◮ The original size TIMES a constant? ◮ Something else??? 3 / 10
Resize: Original PLUS a constant Original size = c Increase size by + c when full How much time to perform n pushes into an empty stack? Number of resizes = i th resize cost = total resize cost = 4 / 10
Resize: Original TIMES a constant Original size = c Increase size by × c when full How much time to perform n pushes into an empty stack? Number of resizes = i th resize cost = total resize cost = 5 / 10
Stack Summary Linked list implementation Constant time push and pop Array implementation Constant time pop Constant time push (until full) Cost over n pushes is O ( n ) (average O (1) per push) Why use an array? 6 / 10
Queue Abstract Data Type enqueue, dequeue, isEmpty, ... template<class LIT> enqueue(1) class Queue{ enqueue(2) public: enqueue(3) Queue(); dequeue() // {~Queue(), copy, op=}? dequeue() void enqueue(const LIT & e); enqueue(4) LIT dequeue(); dequeue() bool isEmpty() const; enqueue(5) private: dequeue() ??? dequeue() }; Why a queue? ◮ Hold jobs for a printer ◮ Store packets on network routers ◮ Make waitlists fair ◮ Depth first search 7 / 10
Queue: Linked list implementation c e ∅ b d f Which pointer is front and which is back ? LIT Queue<LIT>::dequeue() { class Queue{ assert(!isEmpty()); public: LIT ret = ->data; Queue(); Node *p = ; void enqueue(const LIT & e); = ->next; LIT dequeue(); delete p; bool isEmpty() const; return ret; private: } struct Node { LIT data; void Queue<LIT>:: Node * next;}; enqueue(const LIT & e) { Node * front, * back; if (isEmpty()) int size; front = back = new Node(e); }; else = ->next=new Node(e); Runtimes? } 8 / 10
Queue: Circular array implementation Q 0 7 12 size − 1 a b c d e front = 7 back = 12 LIT Queue<LIT>::dequeue() { class Queue{ LIT e = Q[front]; public: front = (front + 1) % size; Queue(); return e; void enqueue(const LIT & e); } LIT dequeue(); void Queue<LIT>:: bool isEmpty() const; enqueue(const LIT & e) { private: if( isFull() ) resize(); LIT * Q; Q[back] = e; int size; back = (back + 1) % size; int front, back; } }; bool Queue<LIT>::isFull() const { Runtimes? return( front == (back + 1) % size ); } 9 / 10
Queue: Array implementation resize Resize If array Q is full, create a larger array and copy existing data into it. f b r a o c n k t = = 0 2 3 7 f g a b c d e 0 15 Where to copy? 10 / 10
Recommend
More recommend