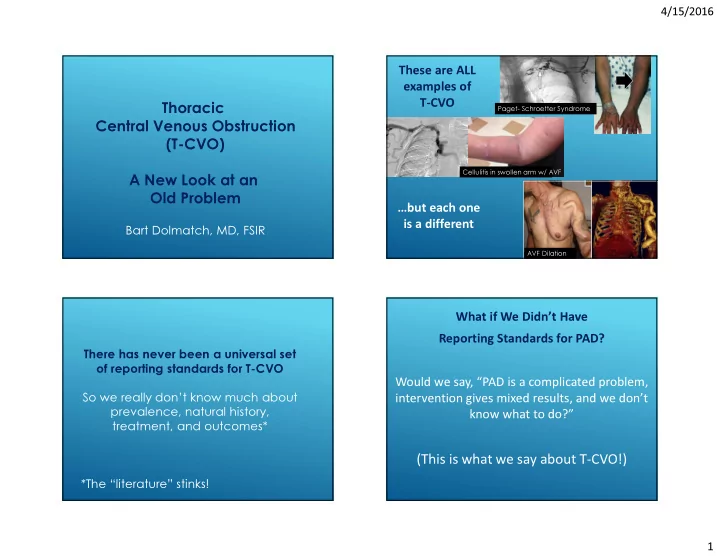

4/15/2016 These are ALL examples of T-CVO Thoracic Paget- Schroetter Syndrome Central Venous Obstruction (T-CVO) Cellulitis in swollen arm w/ AVF A New Look at an Old Problem …but each one is a different Bart Dolmatch, MD, FSIR AVF Dilation What if We Didn’t Have Reporting Standards for PAD? There has never been a universal set of reporting standards for T-CVO Would we say, “PAD is a complicated problem, So we really don’t know much about intervention gives mixed results, and we don’t prevalence, natural history, know what to do?” treatment, and outcomes* (This is what we say about T-CVO!) *The “literature” stinks! 1
4/15/2016 PAD ANATOMIC CLASSIFICATION PAD REPORTING SYSTEMS For SYMPTOMS Why are there are NO Reporting Standards Birth of the Central Vein work Group for Thoracic CVO? (CVWG) Representatives from Interventional Radiology Vascular Surgery Transplant Surgery Nephrology Hematology/Oncology Cardiology Pediatrics Clinical Anatomy 20 members (+/-) 14 Conference Calls – 2 yrs 2
4/15/2016 Members and/or Officers from… Do we all Know Thoracic Central Vein Anatomy? Where does the Subclavian Vein begin? � Soc. Interventional Radiology � Soc. Vascular Surgery � Am. College of Surgeons � Vascular Access Soc. of the Americas � Am. Soc. of Diagnostic and Interv. Nephrologists 1 st rib � Am. Soc. of Pediatric Hematologists and Oncologists � Am. Heart Assoc. � …and many other org’s and societies Thoracic “Central Veins” * Central IJV’s start here SCV SCV starts starts here here Is the Internal Jugular Vein a “Central Vein?” The « central venous» segment of the Internal …and the suprahepatic IVC) Jugular Vein starts at the superior margin of 1st rib 3
4/15/2016 Anatomy of Thoracic CVO “Anatomically” Important Features of All T-CVO’s Type 1a 1. How “obstructed?” Stenosis: Up to 99% luminal narrowing Type 1b Occlusion: 100% obstruction 2. Venous flow or AV access flow? Type 2a 3. “Type” of Obstruction? Type 2b Symptoms Type 3 1. Swelling (Yes/No) Type 4 2. Pain (Yes/No) 3. Onset of dyspnea (Yes/No) 4. Onset of CNS symptoms (Yes/No) Headache, Dizziness, Altered vision, Altered hearing, Seizure, Other (specify) Type 5 Type 6 4
4/15/2016 Signs Duration of Symptoms 1. Swelling – measure and record in mm’s Unilateral a. Reported in # of days (not weeks or months) Bilateral/head-neck b. 2. Skin changes: 1-14 days (Acute) Skin discoloration of the affected arm a. 15-28 days (Sub-acute) b. Lymphatic blistering or weeping Stasis ulcers c. >28 days (Chronic) Infection (cellulitis, abscess, or purulent drainage) d. Non-healing wounds or incisions e. 3. Venous findings: a. Ectatic venous collaterals (exam and/or imaging) b. Venous thrombosis (exam and/or imaging) c. Phlebitis (exam) Performance Status Due to T-CVO 3 Functional Limitations 0. Asymptomatic : No change in performance Problems with cannulation of an upper body 1. I. Symptomatic : No change in performance hemodialysis access II. Symptomatic : Impaired ; some restriction in physical Inability to place venous access (venous catheter or 2. exercise, self-care and/or performance of some daily AV access) at an intended site. activities but not disabled T-CVO that necessitates recanalization or 3. III. Symptomatic : Disabled ; cannot exercise, and capable of only limited self-care and daily activities intervention by any method (e.g., guide wire recanalization, angioplasty, stent placement, or surgery) IV. Symptomatic: Incapacitated ; incapable of self-care and daily activities 5
4/15/2016 T-CVO Reporting Highlights � Define Anatomy Paget- Schroetter Syndrome � Stenosis, occlusion Occlusion � Anatomy of Obstruction Unilateral with Venous Flow � Symptoms (4) Type 1b Symptoms: Left Arm Swelling, Pain (no dyspnea or � Signs (3) CNS) Signs: Swelling, Plethora (no venous findings) � Duration R Arm 102mm L Arm 128mm � Performance Status Duration: 2 Days (Acute) Performance Status: III. Symptomatic : Disabled ; cannot � Functional Limitation exercise, and capable of only limited self-care and daily activities Functional Limitation: None Status of T-CVO Reporting Standards Cellulitis in swollen arm w/ AVF 1. Endorsed by the Society of Interventional Radiology as a formal Reporting Standards Project Occlusion Draft manuscript nearly completed 2. Unilateral with AV access flow 1. Co-publication by JVIR and JVS Type 4 Symptoms: Right Arm Swelling, Pain (no dyspnea or CNS) 2. Many other groups are interested in “endorsing” this work. Signs: Swelling, Erythema, cellulitis (no venous findings) 3. Publication planned before summer 2016 R Arm 134mm L Arm 112mm Further work has begun on lesions, collaterals, 3. Duration: 20 Days (Sub Acute) etiologies. Performance Status: III. Symptomatic : Disabled ; cannot Nomenclature of T-CVO for EHR and Global Lexicon 4. exercise, and capable of only limited self-care and daily activities Functional Limitation: Cannot cannulate AVF 6
4/15/2016 Does this T-CVO make you smile? Catheter Related CVO 7
Recommend
More recommend