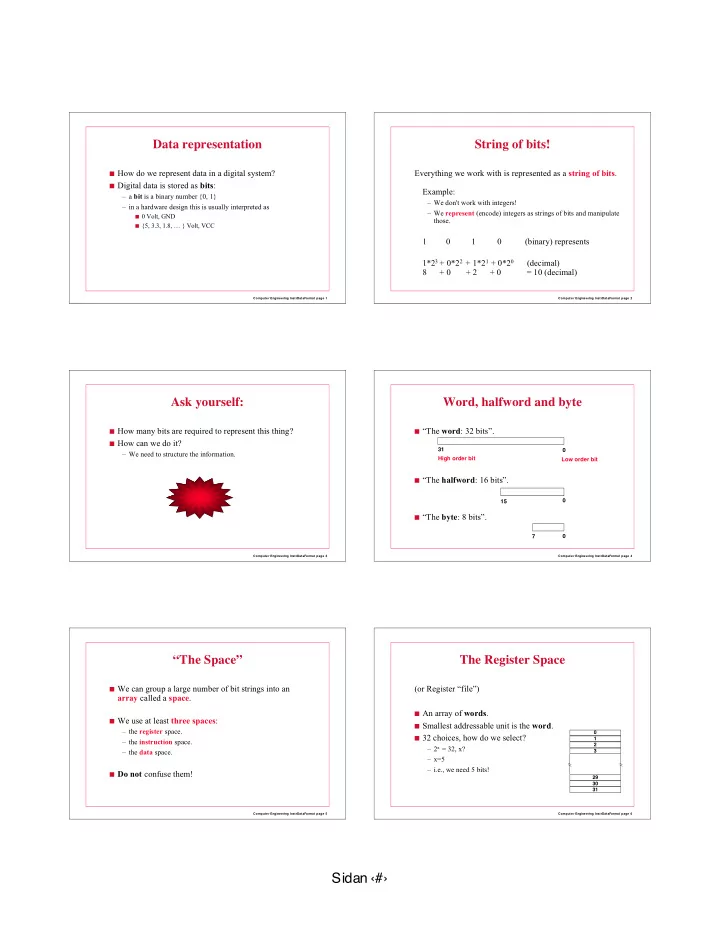

Data representation String of bits! ■ How do we represent data in a digital system? Everything we work with is represented as a string of bits . ■ Digital data is stored as bits : Example: – a bit is a binary number {0, 1} – We don't work with integers! – in a hardware design this is usually interpreted as – We represent (encode) integers as strings of bits and manipulate ■ 0 Volt, GND those. ■ {5, 3.3, 1.8, … } Volt, VCC 1 0 1 0 (binary) represents 1*2 3 + 0*2 2 + 1*2 1 + 0*2 0 (decimal) 8 + 0 + 2 + 0 = 10 (decimal) Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 1 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 2 Ask yourself: Word, halfword and byte ■ How many bits are required to represent this thing? ■ “The word : 32 bits”. ■ How can we do it? 31 0 – We need to structure the information. High order bit Low order bit ■ “The halfword : 16 bits”. 15 0 ■ “The byte : 8 bits”. 7 0 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 3 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 4 “The Space” The Register Space ■ We can group a large number of bit strings into an (or Register “file”) array called a space . ■ An array of words . ■ We use at least three spaces : ■ Smallest addressable unit is the word . – the register space. 0 ■ 32 choices, how do we select? 1 – the instruction space. 2 – 2 x = 32, x? – the data space. 3 – x=5 – i.e., we need 5 bits! ■ Do not confuse them! 29 30 31 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 5 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 6 Sidan ‹#›
Address The Instruction space ■ To work with a space we must be able to address the (or instruction memory) elements of the space. ■ An array of bytes. ■ Each space may have a different address method. ■ Smallest addressable unit is a byte , but the smallest accessible unit is a word . ■ 2 32 bytes gives 2 30 accessible words. Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 7 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 8 What's that mean? But: ■ An instruction address is 32 bits long. ■ Only every fourth address is legal. ■ Same as a word . ■ The ones whose last two bits are “00”. ■ An instruction address fits into a word! ■ We can access 2 30 instructions. Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 9 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 10 Instruction memory 1 Instruction memory 2 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 12 13 14 15 ■ Address “4”: 0000........00100 ■ Address "3": 0000........00011 ■ The hardware will complain! ■ Hardware accesses an entire 32-bit word . ■ This is called an “ alignment error ”. ■ The address was not “ word aligned ”. Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 11 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 12 Sidan ‹#›
Byte order Instruction memory 3 0 1 2 3 Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 ■ Big endian 4 5 6 7 Addr 0 Addr 1 Addr 2 Addr 3 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Byte 3 Byte 2 Byte 1 Byte 0 ■ Little endian Addr 0 Addr 1 Addr 2 Addr 3 ■ An instruction is represented by 32 bits. ■ There are two “instruction formats”. (Not the whole truth, but don't worry about it) Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 13 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 14 Instruction formats “Data space” 6 bits 5 5 5 ■ 2 32 bytes, byte addressable, byte accessible. Format 1 (reg) Opcode rs rt rd ■ A data address fits into 32 bits. 6 bits 5 5 16 Format 2 (imm) Opcode rs rt Immediate ■ Halfword accesses must be halfword aligned; (low order bit = 0). Remember: – Never immediate field together with rd -field. ■ Word accesses must be word aligned; – Immediate field is only 16 bits! (low order 2 bits = 0). Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 15 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 16 Review - How many bits?? Review - How many bits?? ■ Instruction address ? ■ Instruction address 32, word aligned ■ Instruction ? ■ Instruction 32 ? 16 – Immediate field – Immediate field ? 5 – Register address – Register address ■ Register ? ■ Register 32 ■ Data address ? ■ Data address 32, byte aligned ■ Data ? ■ Data 8 (byte) 16 (halfword) 32 (word) Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 17 Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 18 Sidan ‹#›
Questions? Feedback from the lectures: Per.Lindgren@ltu.se Computer Engineering InstrDataFormat page 19 Sidan ‹#›
Recommend
More recommend