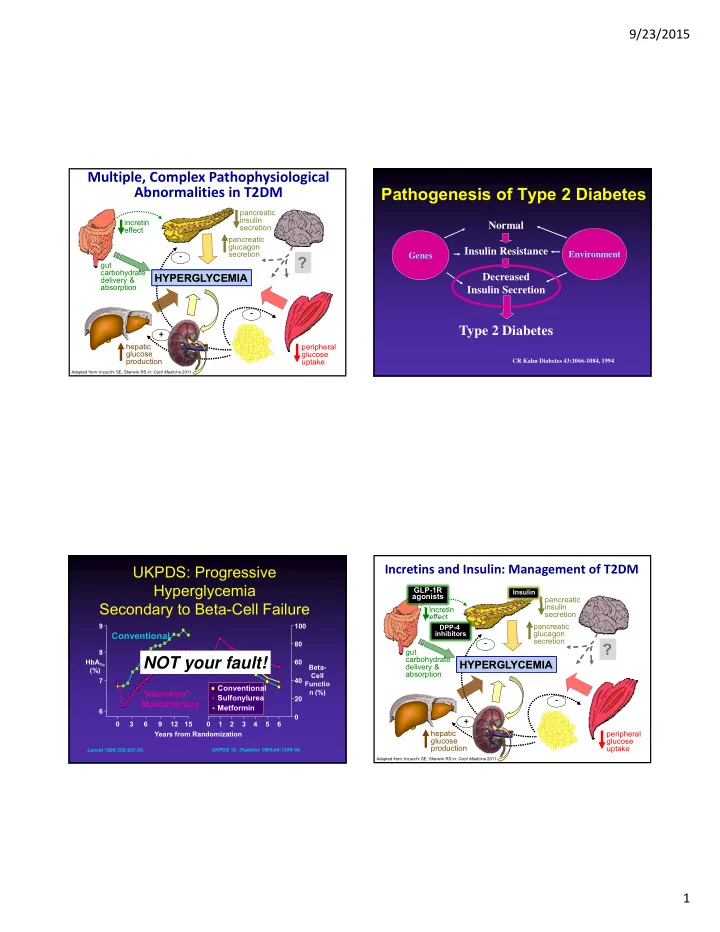

9/23/2015 Multiple, Complex Pathophysiological Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Abnormalities in T2DM pancreatic insulin incretin Normal secretion effect pancreatic glucagon Insulin Resistance secretion Environment ‐ Genes ? gut carbohydrate HYPERGLYCEMIA HYPERGLYCEMIA Decreased delivery & absorption Insulin Secretion ‐ Type 2 Diabetes + hepatic peripheral glucose glucose production uptake CR Kahn Diabetes 43:1066-1084, 1994 Adapted from: Inzucchi SE, Sherwin RS in: Cecil Medicine 2011 Incretins and Insulin: Management of T2DM UKPDS: Progressive Hyperglycemia GLP-1R Insulin agonists pancreatic Secondary to Beta-Cell Failure insulin incretin secretion effect 9 100 pancreatic DPP-4 glucagon Conventional inhibitors secretion ‐ 80 ? gut 8 carbohydrate NOT your fault! HbA 1c 60 HYPERGLYCEMIA HYPERGLYCEMIA Beta- delivery & (%) absorption Cell 7 40 Functio Conventional “Intensive” n (%) Sulfonylurea 20 ‐ Monotherapy Metformin 6 0 + 0 3 6 9 12 15 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 hepatic Years from Randomization peripheral glucose glucose production uptake 13 Lancet 1998;352:837-53. UKPDS 16. Diabetes 1995;44:1249-58. Adapted from: Inzucchi SE, Sherwin RS in: Cecil Medicine 2011 1
9/23/2015 The Holy Grail is to mimic Physiologic Serum Insulin Insulin Therapy in Type 2 DM Secretion Profile Doesn’t Take home points: seem that 75 hard…. Breakfast Lunch Dinner • Insulin controls blood glucose Plasma • Insulin is not a penalty 50 Insulin ( U/mL) • Using basal insulin is simple and 25 safe • Complex regimens are demanding 0 4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 28:00 32:00 for the patient and the provider Time Polonsky KS et al, N Engl J Med 1996. Many insulin regimens are effective Ideal Basal/Bolus Insulin Absorption Pattern: Multiple daily injections or insulin pump Breakfast Lunch Supper Breakfast Lunch Dinner Plasma Insulin Plasma Insulin 75 Immediate Insulin Breakfast Lunch Dinner 50% Prandial Insulin 50% Glucose NPH Bolus Insulin Plasma Basal Insulin 50% Glargine or Detemir Insulin 50% 50 4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 4:00 4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 4:00 ( U/mL) Time Time Breakfast Lunch Dinner Breakfast Lunch Dinner Plasma Insulin Plasma Insulin 25 Prandial Insulin 50% 50% NPH NPH 50% 50% 0 4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 4:00 4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 4:00 4:00 8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 4:00 8:00 Time Time SMBG is based on regimen Time Skyler J, Kelley’s Textbook of Internal Medicine 2000. 2
9/23/2015 Is there another way? Glucagon Like Peptide receptor agonists GLP1 RA https://www.google.com/search?q=insulin+pump&biw=1440&bih=752&source Pancreatic Islet Morphology: Insufficient Insulin and Elevated Glucagon Normal Glucose Tolerance and in T2DM ( Insulin/Glucagon Ratio) T2DM CHO meal 400 mg/dL 300 NGT T2DM 200 Glucose 100 β -Cells 0 NGT 150 (insulin) U/mL T2DM 100 Insulin 50 α -Cells 0 150 (glucagon) pg/mL Glucagon 125 100 75 -60 0 60 120 180 240 Time (min) T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus; NGT = normal glucose tolerance; CHO=carbohydrate T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus Adapted from Rhodes CJ. S cience. 2005; 307:380–384. Adapted from Muller WA, et al. N Engl J Med . 1970;283:109–115. 3
9/23/2015 GLP-1 Modulates Numerous GLP-1 and DPP4 Functions in Humans The Incretin Effect in Healthy Subjects GLP-1: Secreted upon Oral Glucose the ingestion of food Intravenous (IV) Glucose Promotes satiety and * reduces appetite 200 2.0 * Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) * C-peptide (nmol/L) Alpha cells: 1.5 * Incretin Effect Postprandial * * glucagon secretion 100 1.0 Liver: * Glucagon reduces 0.5 Beta cells: hepatic glucose output Enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion 0 0.0 Stomach: Helps regulate 0 60 120 180 0 60 120 180 gastric emptying Time (min) Time (min) N = 6; Mean (SE); * P 0.05 Data from Flint A, et al. J Clin Invest . 1998;101:515-520; Data from Larsson H, et al . Acta Physiol Scand. 1997;160:413-422 Data from Nauck MA, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab . 1986;63:492-498 Data from Nauck MA, et al. Diabetologia . 1996;39:1546-1553; Data from Drucker DJ. Diabete s. 1998;47:159-169 GLP-1 ↓ This is overwhelming ↓ Mrs Jones is here for a 30 minute visit 4
9/23/2015 Lifestyle: Relationship of walking to mortality among US adults with Always first line diabetes DESIGN: Prospective cohort study SUBJECTS: 2896 adults 1990 and 1991 National Health Interview Survey RESULTS: Mortality Inactive 2 hours/wk 3-4 hours/wk All Cause Ref 1.0 39% 54% CV Ref 1.0 34% 53% CONCLUSIONS: Walking was associated with lower mortality across a diverse spectrum of adults with diabetes. One death per year may be preventable for every 61 people who could be persuaded to walk at least 2 h/wk. Arch Intern Med. 2003 Jun 23;163(12):1440-7 Approach to the management Patient Centered: of hyperglycemia HbA1c more less 7% stringent stringent PATIENT / DISEASE FEATURES Approach to the Management of Hyperglycemia Risks potentially associated low high with hypoglycemia and other drug adverse effects HbA1c Disease duration more less newly diagnosed long-standing 7% stringent stringent Risks Usually not modifiable potentially Life expectancy long short associated with Low High hypoglycemia, Important comorbidities other drug absent few / mild severe adverse effects Established vascular absent few / mild severe complications Patient attitude and expected treatment efforts highly motivated, adherent, less motivated, non-adherent, Potentially excellent self-care capacities poor self-care capacities modifiable Resources and support Figure 1. Modula on of the intensiveness Readily available limited system Diabetes Care 2012;35:1364–1379 of glucose lowering therapy in T2DM Courtesy of S Inzucchi Diabetologia 2012;55:1577–1596 Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149; Diabetologia 2015;10.1077/s00125-014-3460-0 Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149; Diabetologia 2015;10.1077/s00125-014-3460-0 5
9/23/2015 Approach to the Management of Hyperglycemia Approach to the Management of Hyperglycemia HbA1c HbA1c less less more more 7% 7% stringent stringent stringent stringent Disease Life Newly diagnosed Long-standing Long Short duration expectancy Figure 1. Modula on of the intensiveness Figure 1. Modula on of the intensiveness Diabetes Care 2012;35:1364–1379 Diabetes Care 2012;35:1364–1379 of glucose lowering therapy in T2DM of glucose lowering therapy in T2DM Diabetologia 2012;55:1577–1596 Diabetologia 2012;55:1577–1596 Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149; Diabetologia 2015;10.1077/s00125-014-3460-0 Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149; Diabetologia 2015;10.1077/s00125-014-3460-0 Approach to the Management of Hyperglycemia Approach to the Management of Hyperglycemia HbA1c HbA1c more less more less 7% 7% stringent stringent stringent stringent Established Important vascular Absent Severe Absent Severe comorbidities Few / Mild Few / Mild complications Figure 1. Modula on of the intensiveness Figure 1. Modula on of the intensiveness Diabetes Care 2012;35:1364–1379 Diabetes Care 2012;35:1364–1379 of glucose lowering therapy in T2DM of glucose lowering therapy in T2DM Diabetologia 2012;55:1577–1596 Diabetologia 2012;55:1577–1596 Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149; Diabetologia 2015;10.1077/s00125-014-3460-0 Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149; Diabetologia 2015;10.1077/s00125-014-3460-0 6
Recommend
More recommend