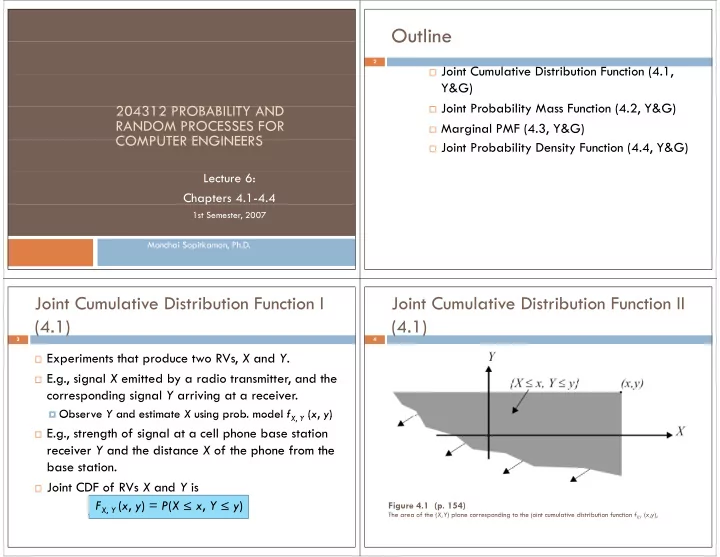

Outline Outline 2 � Joint Cumulative Distribution Function (4.1, � Joint Cumulative Distribution Function (4.1, Y&G) � Joint Probability Mass Function (4.2, Y&G) � Joint Probabilit Mass F nction (4 2 Y&G) 204312 PROBABILITY AND 204312 PROBABILITY AND RANDOM PROCESSES FOR � Marginal PMF (4.3, Y&G) COMPUTER ENGINEERS COMPUTER ENGINEERS � Joint Probability Density Function (4.4, Y&G) Lecture 6: Chapters 4.1-4.4 p 1st Semester, 2007 Monchai Sopitkamon, Ph.D. Joint Cumulative Distribution Function I Joint Cumulative Distribution Function II (4.1) (4.1) 3 4 � Experiments that produce two RVs, X and Y . � E.g., signal X emitted by a radio transmitter, and the g , g y , corresponding signal Y arriving at a receiver. � Observe Y and estimate X using prob. model f X Y ( x , y ) � Observe Y and estimate X using prob. model f X , Y ( x , y ) � E.g., strength of signal at a cell phone base station receiver Y and the distance X of the phone from the receiver Y and the distance X of the phone from the base station. � Joint CDF of RVs X and Y is F X , Y ( x , y ) = P ( X ≤ x , Y ≤ y ) Figure 4.1 (p. 154) The area of the ( X Y ) plane corresponding to the joint cumulative distribution function f The area of the ( X,Y ) plane corresponding to the joint cumulative distribution function f XY ( x , y ), ( x y )
Joint Cumulative Distribution Function III Joint Probability Mass Function I (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function I (4.2) (4.1) 5 6 � Joint prob. mass function of discrete RVs X and Y is: f f � For any pair of RVs X and Y = = = F ( x , y ) P ( X x , Y y ) � 0 ≤ F X , Y ( x , y ) ≤ 1 X , Y X , Y � { X = x , Y = y} is an event in an experiment where � F X ( x ) = P ( X ≤ x , Y ≤ ∞ ) = F X , Y ( x , ∞ ) there is a set of observations that leads to both X = � F Y ( y ) = P ( X ≤ ∞ , Y ≤ y ) = F X , Y ( ∞ , y ) � F ( y ) = P ( X ≤ ∞ Y ≤ y ) = F ( ∞ y ) x and Y = y. � F X , Y ( ∞ , ∞ ) = P ( X ≤ ∞ , Y ≤ ∞ ) =1 � To find P X , Y ( x , y ), we sum the probabilities of all X , Y � F X , Y ( − ∞ , y ) = F X , Y ( x, − ∞ ) = 0 outcomes of the experiment for which X = x and Y = y. � If x ≤ x 1 and y ≤ y 1 , then F X , Y ( x , y ) ≤ F X , Y ( x 1 , y 1 ) , , � Three ways to represent a joint PMF: a list, a matrix, and a graph. Joint Probability Mass Function II (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function II (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function III (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function III (4.2) 7 8 � Ex.4.1: Two-IC Test � P ( S ) = 1, where S = sample space of the experiment Test two ICs one after the other. Possible outcomes are ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑ = accepted ( a ) and rejected ( r ). Assume all Ics are P ( x , y ) 1 � Or X , Y ∈ ∈ x S y S acceptable with prob. 0.9 and outcomes of successive X Y � P � P X , Y ( x , y ) ≥ 0 for all pairs x , y ( x y ) ≥ 0 for all pairs x y tests are independent. X counts the number of � For discrete RVs X and Y and any set B in the X , Y acceptable IC and Y counts the number of successful plane, the prob. of the event {( X , Y ) ∈ B } is: tests before a reject. b f j l th b f th t {( X Y ) B } i ∑ ∑ = ( ( ) ) ( ( , , ) ) P B P x y y X X , Y Y ∈ B ( x , y )
Joint Probability Mass Function IV (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function IV (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function V (4.2) Joint Probability Mass Function V (4.2) 9 10 � Ex.4.2: Find the prob. of the event B that X = Y B ∩ S X , Y = {(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2)} , Therefore, P ( B ) = P X , Y (0, 0) + P X , Y (1, 1) + P X , Y (2, 2) = 0.01 + 0.09 + 0.81 0 0 0 09 0 = 0.91 Figure 4.2 (p. 157) Subsets B of the ( X,Y ) plane. Points ( X,Y ) ∈ S X,Y are marked by bullets. S b B f h ( X Y ) l P i ( X Y ) S k d b b ll Marginal PMF I (4.3) Marginal PMF I (4.3) Marginal PMF II (4.3) Marginal PMF II (4.3) 11 12 � Consider just one of the RVs (e.g., Y ) and ignore the � Ex.4.3: Find the marginal PMFs for the RVs X and Y . other one (e.g., X ). P X , Y ( x , y ) y = 0 y = 1 y = 2 x = 0 0.01 0 0 � For discrete RVs X and Y with joint PMF P X , Y ( x , y ), x = 1 0.09 0.09 0 ∑ ∑ marginal PMF of X : marginal PMF of X : = = F F ( ( x x ) ) P P ( ( x x , y y ) ) , x = 2 0 0 0.81 X X , Y ∈ y S y 2 2 = ∑ ∑ = ∑ ∑ = = ∑ ∑ P ( 0 ) P ( 0 , y ) 0 . 01 P ( 1 ) P ( 1 , y ) 0 . 18 marginal PMF of Y : marginal PMF of Y : = X X , , Y X X , , Y F F ( ( y y ) ) P P ( ( x x , y y ) ) . = = Y X , Y y 0 y 0 ∈ x S = ∑ X 2 = = ≠ P ( 2 ) P ( 2 , y ) 0 . 81 P ( x ) 0 x 0 , 1 , 2 X X , Y X = = y y 0 0 = ∑ = ∑ 2 2 = = P ( 0 ) P ( x , 0 ) 0 . 10 P ( 1 ) P ( x , 1 ) 0 . 09 Y X , Y Y X , Y = = x 0 x 0 = ∑ 2 = = ≠ P ( 2 ) P ( x , 2 ) 0 . 81 ( ) 0 0 , 1 , 2 P y y Y X , Y Y = x 0
Marginal PMF III (4.3) Marginal PMF III (4.3) Joint Probability Density Function I (4.4) Joint Probability Density Function I (4.4) 13 14 � Ex.4.3 (cont.): � The joint PDF of the continuous RVs X and Y is a function f X,Y ( x , y ) with the property P X , Y ( x , y ) y = 0 y = 1 y = 2 P X ( x ) x = 0 0.01 0 0 0.01 ∫ ∫ x y = F ( x , y ) f ( u , v ) dvdu x = 1 0.09 0.09 0 0.18 X , Y X , Y − ∞ − ∞ x = 2 0 0 0.81 0.81 � The joint PDF f X,Y ( x , y ) measures prob. per unit P Y ( y ) 0.10 0.09 0.81 area, whereas the PDF f X ( x ) measures prob. per X unit length. = = ⎧ ⎧ 0 . 01 0 0 . 1 0 x y ⎪ ⎪ = = ⎪ ⎪ � f X Y ( x , y ) is a derivative of the CDF: � f X,Y ( x , y ) is a derivative of the CDF: 0 . 18 x 1 0 . 09 y 1 = = ⎨ ⎨ ⎨ ⎨ P P ( ( x x ) ) P P ( ( y y ) ) = = X Y 0 . 81 x 2 0 . 81 y 2 ⎪ ⎪ ∂ 2 ⎪ ⎪ F ( x , y ) ⎩ ⎩ 0 otherwise 0 otherwise = X , Y ( , ) f x y ∂ ∂ x ∂ ∂ X , , Y y Joint Probability Density Function II Joint Probability Density Function III (4.4) (4.4) 15 16 � Properties of the joint PDF f X,Y ( x , y ): � Ex.4.4: RVs X and Y have joint PDF ⎧ ≤ ≤ ≤ ≤ � f X,Y ( x , y ) ≥ 0 for all ( x , y ) c 0 x 5 , 0 y 3 , = = , ⎨ ⎨ f f ( ( x x , y y ) ) X , Y ∞ ∞ ⎩ � . ∫ ∫ 0 otherwise. = f ( x , y ) 1 X , Y − ∞ − ∞ Find the constant c and P ( A ) = P (2 ≤ X <3, 1 ≤ Y <3). � An event A corresponds to a region of the X , Y � An event A corresponds to a region of the X , Y From the fact that the integral of the joint PDF over the plane with the prob. of A being the double integral sample space is 1: = ∫ ∫ = ∫ ∫ of f X,Y ( x , y ) over the region of the X , Y plane of f ( x y ) over the region of the X Y plane 5 3 = = 1 1 c c dy dy dx dx 15 15 c c 0 0 corresponding to A . Therefore, Therefore, c = 1/15 c 1/15 � The prob. that the continuous RVs ( X , Y ) are in A is: Th b th t th ti RV ( X Y ) i A i = ∫ ∫ 1 ∫∫ = 3 3 = P ( A ) f ( x , y ) dx dy P ( A ) dv du 2 / 15 X , Y 2 1 15 15 A
Joint Probability Density Function IV Joint Probability Density Function IV (4.4) (4.4) 17 18 � Ex.4.5: Find the joint CDF F X,Y ( x , y ) when X and Y � Ex.4.5: Find the joint CDF F X,Y ( x , y ) when X and Y have joint PDF have joint PDF ≤ ≤ ≤ ≤ ≤ ≤ ⎧ ⎧ 2 0 y x 1 , 2 0 y x 1 , = = = = ⎨ ⎨ ⎨ ⎨ f f ( ( x x , y y ) ) f f ( ( x x , y y ) ) X , Y X , Y ⎩ ⎩ 0 otherwise. 0 otherwise. f X,Y ( x , y ) = 2 F X,Y ( x , y ) = 0 F X,Y ( x , y ) = 1 Joint Probability Density Function IV Joint Probability Density Function IV (4.4) (4.4) 19 20 � Ex.4.5: Find the joint CDF F X,Y ( x , y ) when X and Y � Ex.4.5: Find the joint CDF F X,Y ( x , y ) when X and Y have joint PDF ≤ ≤ ≤ have joint PDF ≤ ≤ ≤ ⎧ ⎧ 2 0 y x 1 , 2 0 y x 1 , = = = = ⎨ ⎨ ⎨ ⎨ ( ( , ) ) ( ( , ) ) f f x x y y f f x x y y X , Y X , Y ⎩ 0 otherwise. ⎩ 0 otherwise. = ∫ ∫ = ∫ ∫ y x ∫ ∫ x x ∫ ∫ = − = 2 2 F ( x , y ) 2 du dv x F ( x , y ) 2 du dv 2 xy y X , , Y X , , Y 0 0 v v 0 0 v v
Recommend
More recommend