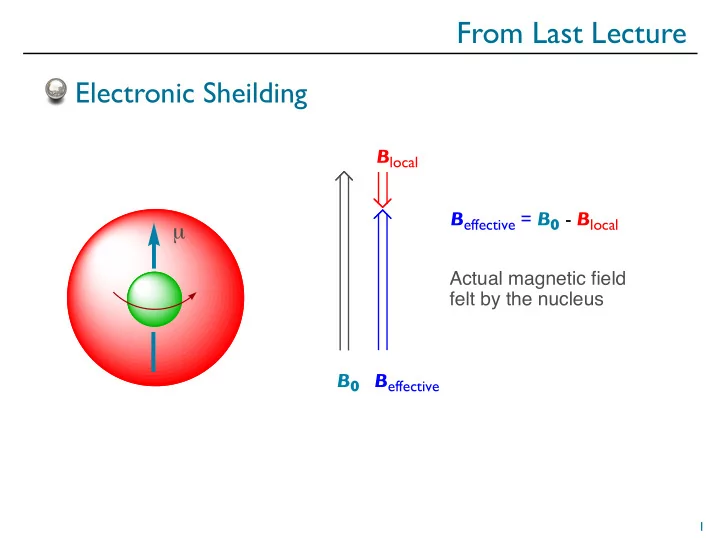

From Last Lecture Electronic Sheilding B local B effective = B 0 - B local µ Actual magnetic field felt by the nucleus B 0 B effective 1
From Last Lecture δ = ppm = Chemical Shift from TMS (Hz) Spectrometer Frequency (MHz) 100 Hz = 1.0 ppm 100 MHz 300 Hz = 1.0 ppm 100 MHz NMR 300 MHz 300 MHz NMR Reference TMS 1.0 ppm 0 2
From Last Lecture Difficult - Carbon 13 only 1.1% of all carbon. Number of different carbons Functional Group Regions 13 C NMR O C C R OR C C O O C C R NR 2 R R C O C N C X 200 150 100 50 0 ppm δ 3
From Last Lecture Symmetry in molecules can make carbons “Chemically Equivalent” Cl O C H 3 C CH 3 Br same electronic environment 4
Substitution of Carbon The intensity of the peaks roughly correlates with the number of hydrogens on the carbon. 5
C13 NMR Regions 13 C NMR O C C R OR C C O O C C R NR 2 R R C O C N C X 200 150 100 50 0 p δ 6
Bromooctanol Br HO 7
Bromooctanal H Br O 8
Alanine Me-Ester HCl O OCH 3 H 3 C NH 3 Cl 9
Alaninol OH H 3 C NH 2 10
Alaninol - phthalimide OH O H 3 C N O 11
DEPT -C13 OH A - normal C13 B - CH carbons only C - Odd # up (CH3 and CH) Even # down (CH2) 12
Example from 13.7 Cl KOH ethanol or 13
A Real Example O O O O NH NH NH OR N O N N O O O O H 2 , Pd/C H 2 , Pd/C O O O O NH NH NH OR N O In the alkane region N there would O O N O O only be 4 peaks due to In the alkane region there would be 6 symmetry different peaks 14
The Answer Is . . . O NH N O O O O NH N O 15
Proton NMR Number of chemically different hydrogens Relative Ratios of protons (peak size) How many neighboring hydrogens Chemical shifts and functional groups 16
Proton Equivalency Diastereotopic Homotopic H H H H C CH 3 C H 3 C C H 3 C CH 3 H Cl replace H's - Enantiotopic diastereomers replace H's - same X H H X H H H X X H C CH 3 C CH 3 C CH 3 H 3 C C H 3 C C H 3 C C C C H 2 H Cl H Cl H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C CH 3 replace H's - enantiomers X H H X C CH 3 C CH 3 H 3 C C H 3 C C H 2 H 2 17
Proton NMR Scale Range 0-10 ppm 1 H NMR H H H H H C H H C C H H OH H C O H H C O H H C X 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 ppm δ 18
Methyl Acetate O C CH 3 H 3 C O Area under peak corresponds to the number of H’s for that resonance 19
Recommend
More recommend