
DATA RECOVERY Reconstructed Values 400 ON ENCRYPTED DATABASES 350 WITH 300 k-NEAREST NEIGHBOR 250 QUERY LEAKAGE 200 EVGENIOS M. KORNAROPOULOS 150 CHARALAMPOS PAPAMANTHOU ROBERTO TAMASSIA 100 50 0 0 100 200 300 400 Full version: https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/719
INTRO WHO CARES ABOUT k-NN? COLUMN-ORIENTED DBMS
INTRO WHO CARES ABOUT k-NN? COLUMN-ORIENTED DBMS OBJECT-RELATIONAL DBMS
INTRO WHO CARES ABOUT k-NN? COLUMN-ORIENTED DBMS OBJECT-RELATIONAL DBMS CLOUD SERVICES
SETUP k-NEAREST NEIGHBORS Records: 2
SETUP k-NEAREST NEIGHBORS Records: q 2
SETUP k-NEAREST NEIGHBORS Records: q 2
SETUP VORONOI DIAGRAMS 3
SETUP VORONOI DIAGRAMS 3
SETUP VORONOI DIAGRAMS 3
SETUP VORONOI DIAGRAMS Voronoi Diagram Voronoi Edges Voronoi Segment Response 3
SETUP ENCRYPTED SEARCH Server Client Responses Tokens PRF K ( ) = t ) = t 0 PRF K ( ) = t 00 PRF K ( PRF K ( ) = t 4
SETUP ENCRYPTED SEARCH Server Client Responses Tokens PRF K ( ) = t ) = t 0 PRF K ( ) = t 00 PRF K ( PRF K ( ) = t Search Pattern Access Pattern Leakage 4 Leakage
OUR CONTRIBUTIONS OVERVIEW k-NN EXACT RECONSTRUCTION ORDERED RESPONSES: Possible when all encrypted queries are issued UNORDERED RESPONSES: Impossible due to many reconstructions k-NN APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION ORDERED RESPONSES: Approximate reconstruction when not all encrypted queries are issued UNORDERED RESPONSES: Even with many reconstructions approximate with bounded error 5
OUR CONTRIBUTIONS OVERVIEW k-NN EXACT RECONSTRUCTION ORDERED RESPONSES: Possible when all encrypted queries are issued UNORDERED RESPONSES: Impossible due to many reconstructions k-NN APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION ORDERED RESPONSES: Approximate reconstruction when not all encrypted queries are issued UNORDERED RESPONSES: Even with many reconstructions approximate with bounded error 5
UNORDERED RESPONSES ASSUMPTIONS OF THE ATTACK BOUNDARIES: Known boundaries α and β STATIC: No updates in the database UNIFORMITY: Queries are generated uniformly at random from [ α , β ] 6
UNORDERED RESPONSES Impossible to achieve Exact Reconstruction EXACT RECONSTRUCTION Best Case Scenario { s 3 , s 4 } { s 0 , s 1 } { s 1 , s 2 } { s 2 , s 3 } { s 4 , s 5 } for the Adversary β α 7
UNORDERED RESPONSES Impossible to achieve Exact Reconstruction EXACT RECONSTRUCTION Best Case Scenario { s 3 , s 4 } { s 0 , s 1 } { s 1 , s 2 } { s 2 , s 3 } { s 4 , s 5 } for the Adversary β α Valid Reconstruction DB 1 7
UNORDERED RESPONSES Impossible to achieve Exact Reconstruction EXACT RECONSTRUCTION Best Case Scenario { s 3 , s 4 } { s 0 , s 1 } { s 1 , s 2 } { s 2 , s 3 } { s 4 , s 5 } for the Adversary β α Valid Reconstruction DB 1 Valid Reconstruction DB 2 7
UNORDERED RESPONSES Impossible to achieve Exact Reconstruction EXACT RECONSTRUCTION Best Case Scenario { s 3 , s 4 } { s 0 , s 1 } { s 1 , s 2 } { s 2 , s 3 } { s 4 , s 5 } for the Adversary β α Valid Reconstruction DB 1 Valid Reconstruction DB 2 7
UNORDERED RESPONSES Impossible to achieve Exact Reconstruction EXACT RECONSTRUCTION Best Case Scenario { s 3 , s 4 } { s 0 , s 1 } { s 1 , s 2 } { s 2 , s 3 } { s 4 , s 5 } for the Adversary β α Valid Reconstruction DB 1 Valid Reconstruction DB 2 Many reconstructions that explain the Voronoi Diagram Vor(DB 1 )=Vor(DB 2 )=… 7
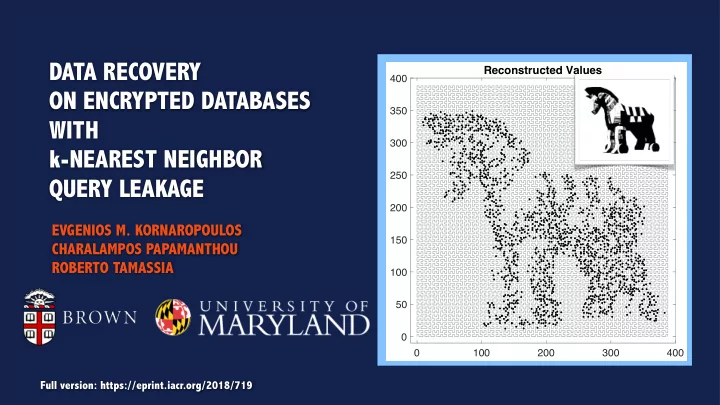
Since there are reconstructions and the MANY IMPOSSIBLE exact recovery is , the encrypted values must be safe…
Since there are reconstructions and the MANY IMPOSSIBLE exact recovery is , the encrypted values must be safe… Answer: We can still compute an reconstruction that is to the encrypted DB VERY CLOSE
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION In case all queries are issued: The length of each Voronoi segments Uniform Query Distribution: Estimate via Concentration Bounds on Multinomials 8
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION In case all queries are issued: The length of each Voronoi segments Goal: Characterize the set of all valid reconstructions that explain the Voronoi Diagram 8
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION In case all queries are issued: The length of each Voronoi segments Goal: Characterize the set of all valid reconstructions that explain the Voronoi Diagram What’s Next: Intuitive characterization = rigorous reconstruction guarantees 8
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 4 = 2 b 2 , 4 − v 2 = 2 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 4 = 2 b 2 , 4 − v 2 = 2 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 4 = 2 b 2 , 4 − v 2 = 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 4 = 2 b 2 , 4 − v 2 = 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 6 = 2 b 4 , 6 − v 4 = 2 b 4 , 6 − 2 b 2 , 4 + b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 8 = 2 b 6 , 8 − v 6 = 2 b 6 , 8 − 2 b 4 , 6 + 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 Half of the as a function of unknown ξ 0 v i 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 1 = b 1 , 3 − ξ 1 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 3 = b 1 , 3 + ξ 1 v 4 = 2 b 2 , 4 − v 2 = 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 5 = 2 b 3 , 5 − v 3 = 2 b 3 , 5 − b 1 , 3 − ξ 1 v 6 = 2 b 4 , 6 − v 4 = 2 b 4 , 6 − 2 b 2 , 4 + b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 7 = 2 b 5 , 7 − v 5 = 2 b 5 , 7 − 2 b 3 , 5 + b 1 , 3 + ξ 1 v 8 = 2 b 6 , 8 − v 6 = 2 b 6 , 8 − 2 b 4 , 6 + 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 9 = 2 b 7 , 9 − v 7 = 2 b 7 , 9 − 2 b 5 , 7 + 2 b 3 , 5 − b 1 , 3 − ξ 1 Other half of the as a function of unknown ξ 1 Half of the as a function of unknown ξ 0 v i v i 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Use geometry of bisectors to define unknowns v 0 = b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 1 = b 1 , 3 − ξ 1 v 2 = b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 3 = b 1 , 3 + ξ 1 v 4 = 2 b 2 , 4 − v 2 = 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 5 = 2 b 3 , 5 − v 3 = 2 b 3 , 5 − b 1 , 3 − ξ 1 v 6 = 2 b 4 , 6 − v 4 = 2 b 4 , 6 − 2 b 2 , 4 + b 0 , 2 + ξ 0 v 7 = 2 b 5 , 7 − v 5 = 2 b 5 , 7 − 2 b 3 , 5 + b 1 , 3 + ξ 1 v 8 = 2 b 6 , 8 − v 6 = 2 b 6 , 8 − 2 b 4 , 6 + 2 b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 − ξ 0 v 9 = 2 b 7 , 9 − v 7 = 2 b 7 , 9 − 2 b 5 , 7 + 2 b 3 , 5 − b 1 , 3 − ξ 1 Other half of the as a function of unknown ξ 1 Half of the as a function of unknown ξ 0 v i v i Reduced the space of reconstructions from n-dimensions to 2-dimensions 9
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Ordering Constraints: v 0 < v 1 ⇒ − 10
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Geometric Characterization Ordering Constraints: v 0 < v 1 ⇒ − ξ 0 + ξ 1 < c 0 , 1 , where c 0 , 1 = ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) ξ 1 ξ 0 10
UNORDERED RESPONSES * APPROXIMATE RECONSTRUCTION Modeling All Reconstructions: Geometric Characterization Ordering Constraints: v 0 < v 1 ⇒ − ξ 0 + ξ 1 < c 0 , 1 , where c 0 , 1 = ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) v 1 < v 2 ⇒ − ξ 0 − ξ 1 < c 1 , 2 , where c 1 , 2 = − ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) ξ 1 v 2 < v 3 ⇒ ξ 0 − ξ 1 < c 2 , 3 , where c 2 , 3 = ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) v 3 < v 4 ⇒ ξ 0 + ξ 1 < c 3 , 4 , where c 3 , 4 = ( b 2 , 4 − b 1 , 3 ) + ( b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 ) v 4 < v 5 ⇒ − ξ 0 + ξ 1 < c 4 , 5 , where c 4 , 5 = 2( b 3 , 5 − b 2 , 4 ) − ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) v 5 < v 6 ⇒ − ξ 0 − ξ 1 < c 5 , 6 , where c 5 , 6 = 2( b 4 , 6 − b 3 , 5 ) − ( b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 ) − ( b 2 , 4 − b 1 , 3 ) v 6 < v 7 ⇒ ξ 0 − ξ 1 < c 6 , 7 , where c 6 , 7 = 2( b 5 , 7 − b 4 , 6 ) − 2( b 3 , 5 − b 2 , 4 ) + ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) v 7 < v 8 ⇒ ξ 0 + ξ 1 < c 7 , 8 , where c 7 , 8 = 2( b 6 , 8 − b 5 , 7 ) − 2( b 4 , 6 − b 3 , 5 ) + ( b 2 , 4 − b 1 , 3 ) + ( b 2 , 4 − b 0 , 2 ) ξ 0 v 8 < v 9 ⇒ − ξ 0 + ξ 1 < c 8 , 9 , where c 8 , 9 = 2( b 7 , 9 − b 6 , 8 ) − 2( b 5 , 7 − b 4 , 6 ) + 2( b 3 , 5 − b 2 , 4 ) − ( b 1 , 3 − b 0 , 2 ) 10
Recommend
More recommend