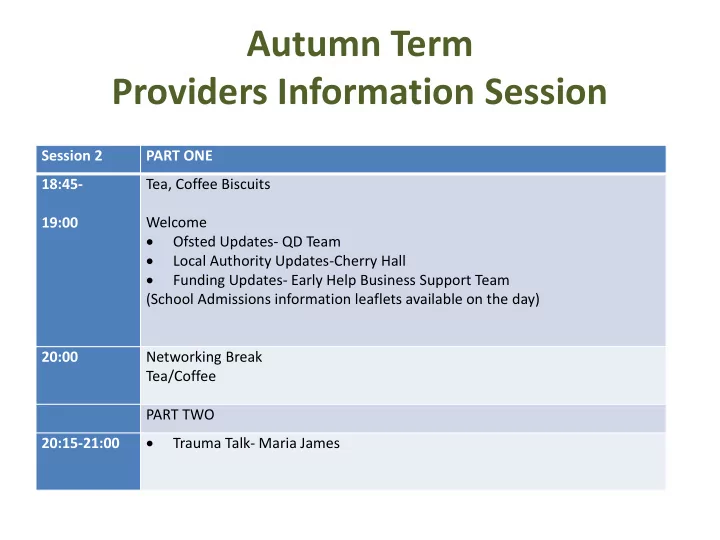

Autumn Term Providers Information Session Session 2 PART ONE 18:45- Tea, Coffee Biscuits 19:00 Welcome • Ofsted Updates- QD Team • Local Authority Updates-Cherry Hall • Funding Updates- Early Help Business Support Team (School Admissions information leaflets available on the day) 20:00 Networking Break Tea/Coffee PART TWO • Trauma Talk- Maria James 20:15-21:00
QD Team • Alison Hallissey • Sue Gardner • Marion Wright • Danielle Jones QD.Team@bracknell-forest.gov.uk Ofsted Updates
Ofsted Education Inspection Framework September 19 Quality of Education the expectation is that all learners will receive a high-quality, ambitious quality of education
Cultural capital • Cultural capital is about preparing children with the knowledge and skills for what comes next; important in early years because what children learn in those vital first years of life will stay with them forever. • It is about giving children the best possible start to their early education, particularly the most disadvantaged
Planning • Plan activities, provocations and lines of enquiry with intent to enhance vocabulary, build curiosity and engage children with a sense of awe and wonder Broaden children’s knowledge- • offer experiences that extend, stretch and challenge them, to benefit them both in the present and future.
The 3 ‘I’s • Intent What do the children need to learn, know or be able to do to succeed in life (cultural capital) • Implementation How you deliver your plans • Impact How do you know if what you planned was successful
Learning Walk Inspectors will complete a learning walk around the premises with the provider or their representative early on in the inspection. This provides an opportunity for leaders to explain how they organise the early years provision, including the aims and rationale for their EYFS curriculum
School care and holiday provision The inspector will talk to practitioners about: how practitioners create the play environment How they seek children's views and engage them in planning of activities Talk about performance management and professional development Evaluate a sample of policies and procedures and relevant documentation Where possible, seek the views of parents
Awe and Wonder Children need an inspirational environment that changes and includes quirky objects and things that lie outside the ordinary. They need to hear words that are strange and alluring, hear stories that open up new worlds of imagination and wonder; they need drama and songs, adventure and the great outdoors “Think like a child to be like a child.”
50 Things to do before I’m 5 E.G: Play pooh sticks • Fly a kite • • Roll down a hill Hide in a pile of autumn leaves • • Have a snail race Go crabbing • Visit a museum • • Hear a musician play an instrument
PVI experiences • Old School Day Nursery • The Pines Pre School • Updates from EIF meeting with Ofsted • The DfE are seeking your views on proposed changes to the EYFS statutory framework. Please see link below should you wish to respond: • https://consult.education.gov.uk/early-years-quality- outcomes/early-years-foundation-stage- reforms/supporting_documents/EYFS%20reforms%20consu ltation.pdf https://www.slideshare.net/ofstednews •
Cherry Hall Locality Manager cherry.hall@bracknell-forest.gov.uk Local Authority Updates
Early Help Support Team 01344 351555 EHBS@bracknell-forest.gov.uk
Free Entitlement Funding Quiz Please discuss your answers within your groups for 8 minutes (1 minute per question).
Question 1 - If a child’s birth date is 1 September they can start claiming free entitlement funding from:
Question 2 - A child turns 3 on 1 March 2020, they have a 30 hour code with a valid from date 6 April 2020, they start claiming extended hours from:
Question 3 - Parents must pay the difference between the hourly rate paid by Bracknell Forest to the childcare provider, and the childcare providers published hourly rate: False
• Question 4 - Parents can expect to pay for lunches if children stay in childcare all day: True
Question 5 - The free entitlements can be delivered over 52 weeks of the year: True If your setting is open 52 weeks of the year you can stretch funding over 52 weeks. However if your setting closes for bank holidays and INSET days these must be deducted.
Question 6 - To claim free entitlement funding, all childcare providers need to do is submit a headcount task on the provider portal: False
Question 7 - If a parent provides their NI number and date of birth on the Parent Declaration form this should be entered on the provider portal: False
Question 8 - Bracknell Forest Council can extend the deadline if I forget to submit my headcount task: False
If you have any specific free entitlement funding questions following on from the quiz please contact us directly or attend the next provider portal session: Date – Tuesday 3 December Time – 7 – 9 pm Venue – Bracknell Open Learning Centre The dates are published, in advance, on our website:
Comfort break
Introduction to trauma Maria James Early Help Parenting Lead
Definition 1 of psychological trauma • Trauma is an exceptional experience in which powerful and dangerous stimuli overwhelm the child’s capacity to regulate emotions. • This is also the case for adolescents and adults
Definition 2 of psychological trauma Trauma is the unique individual experience of an event or enduring conditions in which the individual’s ability to integrate his/her emotional experience is overwhelmed and the individual experiences (either objectively or subjectively) a threat to his/her life, bodily integrity, or that of a caregiver or family. (Pearlman, L.A, and Saavitne K.W, 1995
Emotional regulation and trauma Both these definitions tell us that: • It’s not the event itself , it’s our reaction to the event that makes it traumatic. • The event becomes traumatic when we are overwhelmed and cannot regulate ourselves.
Types of trauma There are 2 types of trauma: Type 1 trauma: • A one off single event • Overwhelming • Out of the blue
Examples of Type 1 trauma • Life threatening environmental disasters, floods, earthquakes, hurricanes, tsunamis. • Unexpected death of a family member or friend. • Diagnosis of a life threatening illness. • Accidents or crashes involving injury or death. • Crime: rape, kidnap, assault • Combat
Big T events Shapiro calls Type 1 traumas “Big T events” One off event that overwhelm our ordinary capacity to cope.
Type 2 traumas The content of type 2 trauma events can be different for an adult than a child, but for both children and adults Type 2 trauma is characterised by repeated traumatic events Type 2 traumas are known as “small t events”
Examples of type 2 trauma For the child: • Being ignored when upset or distressed • Not getting needs met and being criticised for having needs • Trauma of seeing others being abused • Having no one who is in tune or can relate to them
Cumulative effect • Cumulative effect of small “t” experiences can be as traumatic as a Big T experience. • Often can be harder to treat as it is not one event to be recalled. • It can be seen by the person as part of a “normal experience” but is chronic and complex.
What is Developmental trauma? Developmental trauma is a term used to describe the impact of early, repeated abuse, neglect, separation and adverse experiences that happens within the child’s important relationships. Children with complex trauma histories are often diagnosed with conditions such as ADHD, oppositional defiance disorder, conduct disorders, anxiety disorders, learning difficulties, autistic spectrum disorder.
ACEs (Adverse Childhood Experiences) ACEs is used generically to refer to overlapping sets of traumatic and adverse childhood experiences and home environment factors that substantially increase a child’s risk for serious, lifelong medical and mental illness. ACEs are common but their effects are cumulative and create increased risk for poor outcomes.
ACEs (Adverse Childhood Experiences) • Physical abuse • Sexual abuse Emotional abuse • Physical neglect • • Emotional neglect • Mother treated violently Household substance abuse • Household mental illness • • Parental separation and divorce • Incarcerated household member
Recommend
More recommend