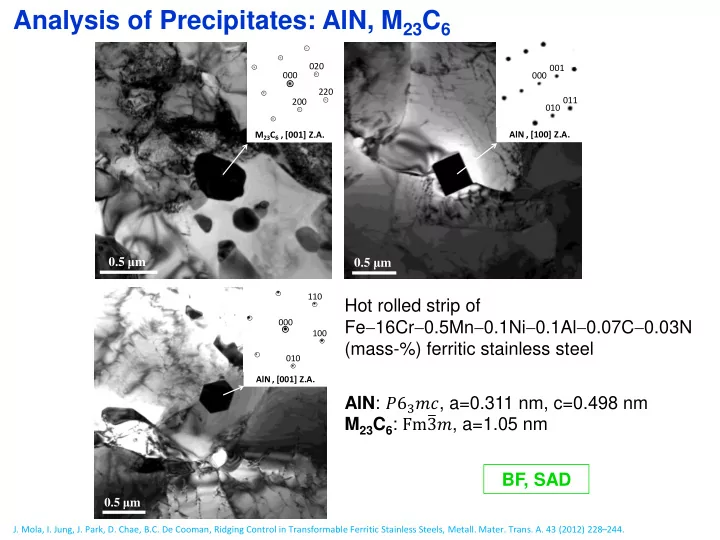

Analysis of Precipitates: AlN, M 23 C 6 020 000 001 000 220 011 200 010 M 23 C 6 , [001] Z.A. AlN , [100] Z.A. 0.5 μ m 0.5 μ m 110 Hot rolled strip of Fe 16Cr 0.5Mn 0.1Ni 0.1Al 0.07C 0.03N 000 100 (mass-%) ferritic stainless steel 010 AlN , [001] Z.A. AlN : 𝑄6 3 𝑛𝑑 , a=0.311 nm, c=0.498 nm M 23 C 6 : Fmത 3𝑛 , a=1.05 nm BF, SAD 0.5 μ m J. Mola, I. Jung, J. Park, D. Chae, B.C. De Cooman, Ridging Control in Transformable Ferritic Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 43 (2012) 228 – 244.
Analysis of Precipitates: Twinned M 23 C 6 Twinned M 23 C 6 precipitates in a 16%Cr ferritic stainless steel 311 ZA of M 23 C 6 113 ZA of M23C6 BF, DF, SAD 113 ZA of M23C6 311 ZA of M 23 C 6 2-4-2 422 2-2-4 422 2-2-4 422 02-2 220 2-4-2 422 0-22 220 2 1 / n m 2 1 / n m J. Mola, Ridging Resistance and Formability in the AISI 430 Transformable Ferritic Stainless Steel, doctoral dissertation, POSTECH, South Korea, 2012.
Analysis of Precipitates: AlN, M 23 C 6 STEM images and EDS analysis of AlN and M 23 C 6 precipitates in a hot rolled strip of Fe 16Cr 0.5Mn 0.1Ni 0.1Al 0.07C 0.03N (mass-%) ferritic stainless steel M 23 C 6 STEM, EDS AlN AlN J. Mola, I. Jung, J. Park, D. Chae, B.C. De Cooman, Ridging Control in Transformable Ferritic Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 43 (2012) 228 – 244.
Analysis of Precipitates: M 2 N M 2 N precipitates in a 16%Cr ferritic stainless steel 35-1 Z.A. of bcc // 112 Z.A. of hcp -10-3 bcc 1-1-2 bcc 3-2-1 bcc axis : [3,5,-1] 2-11 bcc Orientation Relationship M 2 N : 𝑄6 3 /𝑛𝑛𝑑 , a=0.274 nm, c=0.444 nm (110) bcc // (001) hcp BF, SAD <111> bcc // <110> hcp J. Mola, Ridging Resistance and Formability in the AISI 430 Transformable Ferritic Stainless Steel, doctoral dissertation, POSTECH, South Korea, 2012.
Analysis of Precipitates: M 2 N Elongated M 2 N precipitates in a 16%Cr ferritic stainless steel Orientation Relationship (110) bcc // (001) hcp <111> bcc // <110> hcp -11-1 hcp 110 bcc -1-10 bcc -01-1 hcp -100 hcp BF, SAD J. Mola, Ridging Resistance and Formability in the AISI 430 Transformable Ferritic Stainless Steel, doctoral dissertation, POSTECH, South Korea, 2012.
Analysis of Precipitates: M 7 C 3 Faulted M 7 C 3 carbides in an Fe 17Cr 6Mn 3Ni 4Al 0.45C duplex stainless steel Faulted BF, SAD R. Rahimi, B.C. De Cooman, H. Biermann, J. Mola, Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-alloyed Fe – Cr – Ni – Mn – C stainless steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 618 (2014) 46 – 55. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2014.09.001.
Analysis of Precipitates: M 3 C DF1 Orthorhombic M 3 C ( ): a= 0.509 nm Dark field imaging of a tempered b= 0.674 nm Fe 13Cr 0.3C martensitic c= 0.452 nm stainless steel using two different cementite reflections BF SAD pattern of martensite and two cementite ( θ ) variants DF2 Z.A.: [0-11] //[001] 1 //[001] 2 -200 -2-40 1 240 2 200 2 -200 1 0-20 1 020 2 011 0.5 m -220 1 -220 2 Q. Huang, B.C. De Cooman, H. Biermann, J. Mola, Influence of Martensite Fraction on the Stabilization of Austenite in Bagaryatski O.R.: Austenitic – Martensitic Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. {112} // {010} <01-1> // <001> 47 (2016) 1947 – 1959. J. Mola, B.C. De Cooman, Quenching and Partitioning (Q&P) Processing of Martensitic Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. BF, DF, SAD 44 (2013) 946 – 967.
Analysis of Precipitates: B2 BF, SAD B2 0 ത 1 1 Z.A. Fe 17Cr 6Mn 9Ni 7Al 0.46C ferritic stainless steel (A) 011 111 100 A B Ferrite 0 ത 1 1 Z.A. 211 (B) 011 Only weak 200 B2 reflections 0.3 μ m B2-(Ni,Fe)Al intermetallics exhibiting a cube-on-cube O.R. with the ferritic matrix R. Rahimi, P. Pekker, H. Biermann, O. Volkova, B.C. De Cooman, J. Mola, Volumetric changes associated with B2-(Ni,Fe)Al dissolution in an Al-alloyed ferritic steel, Mater. Des. 111 (2016) 640 – 645. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.033.
Analysis of Precipitates: VN a) VN precipitates in an Fe 15Cr 6Mn 3Ni 0.65V 0.5Si 0.11C 0.24N austenitic stainless steel HRTEM, SAD 20 nm SAD pattern of c) SAD pattern of (c) e) 004 c) 222 113 002 111 30 nm M. Wendler, B. Reichel, R. Eckner, O. Fabrichnaya, L. Krüger, A. Weiß, J. Mola, Effect of Vanadium Nitride Precipitation on Martensitic Transformation and Mechanical Properties of CrMnNi Cast Austenitic Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 47 (2016) 139 – 151.
Recrystallization / Precipitation TEM montage of ferrite and Cr carbides and nitrides in an Fe 16Cr 0.4Mn 0.1Ni 0.04C 0.04N ferritic stainless steel Annealing time: 30 s + 30 s BF 0.4 µm J. Mola, E. Seo, I. Jung, B.C.De Cooman, J. Park, Cold rolling of α+ α′ dual-phase microstructure in transformable ferritic stainless steel, in: Proceedings of 7th Eur. Stainl. Steel Conf. Sci. Mark., Como, Italy, 2011.
Recrystallization / Precipitation BF 1 µm TEM montage of ferrite and Cr carbides and nitrides in an Fe 16Cr 0.4Mn 0.1Ni 0.04C 0.04N ferritic stainless steel Annealing time: 30 min J. Mola, E. Seo, I. Jung, B.C.De Cooman, J. Park, Cold rolling of α+ α′ dual-phase microstructure in transformable ferritic stainless steel, in: Proceedings of 7th Eur. Stainl. Steel Conf. Sci. Mark., Como, Italy, 2011.
Recrystallization of Martensite and Ferrite Difference in the recrystallization behavior of ferrite and martensite in a cold-rolled Fe 16Cr 0.4Mn 0.1Ni 0.04C 0.04N ferritic-martensitic stainless steel (a) Rex. α Recovered Annealing conditions: 0.5 µm 0.5 µm rapid heating to 750 ° C and DF BF (d) (e) In-lath Twin immediate precipitates boundary cooling precipitates αʹ Twin BF, DF boundary precipitates 0.2 µm J. Mola, B.C. De Cooman, J. Park, Recrystallization behavior of α′ martensite in transformable ferritic stainless steels, in: Proceedings of 7th Eur. Stainl. Steel Conf. Sci. Mark., Como, Italy, 2011.
Recrystallization of Martensite Bulging Recrystallization of Due to the high density of lath boundary precipitates, bulging of recrystallized regions into recovered martensite preferentially occurs in the longitudinal directions of laths. BF Fe 16Cr 0.4Mn 0.1Ni 0.04C 0.04N dual-phase stainless steel Rex. annealing conditions: 15 s 830 ° C J. Mola, B.C. De Cooman, J. Park, Recrystallization behavior of α′ martensite in transformable ferritic stainless steels, in: Proceedings of 7th Eur. Stainl. Steel Conf. Sci. Mark., Como, Italy, 2011.
Recrystallization of Martensite Bulging Recrystallization of Due to the high density of lath boundary precipitates, bulging of recrystallized regions into recovered martensite preferentially occurs in the longitudinal directions of laths. 1 µm BF Fe 16Cr 0.4Mn 0.1Ni 0.04C 0.04N dual-phase stainless steel Rex. annealing conditions: 15 s 830 ° C J. Mola, B.C. De Cooman, J. Park, Recrystallization behavior of α′ martensite in transformable ferritic stainless steels, in: Proceedings of 7th Eur. Stainl. Steel Conf. Sci. Mark., Como, Italy, 2011.
Stacking Faults Stabilization of austenite in an Fe 16Cr 0.4Mn 0.1Ni 0.04C 0.04N transformable stainless steel obtained by Q&P processing bcc bcc Twin boundary BF 002 tw -111 tw -111 -11-1 -111 tw 000 00-2 bcc 1 µm J. Mola, B.C. De Cooman, Quenching and partitioning processing of transformable ferritic stainless steels, Scr. Mater. 65 (2011) 834 – 837.
Deformation-Induced Martensite αʹ -martensite formation at intersections of ε -martensite plates in Fe 14.3Cr 5.5Mn 5.5Ni 0.5Si 0.37N 0.02C austenitic stainless steel DF1, ε+α BF ε V1 BF DF1 ε V2 DF2 DF3 0.1 m DF3, α DF2, ε ത 3 ത ത ത ത 3 ത Z.A. γ ത ത ε α BF, DF, SAD J. Mola, M. Wendler, A. Weiß, B. Reichel, G. Wolf, B.C. De Cooman, Segregation-Induced Enhancement of Low-Temperature Tensile Ductility in a Cast High-Nitrogen Austenitic Stainless Steel Exhibiting Deformation-Induced α′ Martensite Formation, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 46 (2015) 1450 – 1454.
Region 1: γ + ε Deformation-Induced Martensite Strain-induced γ ε αʹ transformation route in an Fe 7Mn 0.1C medium Mn steel 2 1/ nm 2 1/ nm BF, SAD Region 2: γ + αʹ + ε 2 1 2 1/ nm 2 1/ nm B.C. De Cooman, P. Gibbs, S. Lee, D.K. Matlock, Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis of Yielding in Ultrafine-Grained Medium Mn Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 44 (2013) 2563 – 2572.
Spontaneous Martensite Fe − Cr− Mo−0. C−0.4N stainless steel after partial transformation to spontaneous (athermal ) α -martensite α Fe− Cr− Mo−0. C−0.4N BF α 0.2 µm J. Mola, Considerations in the design of formable austenitic stainless steels based on deformation-induced processes, in Austenitic Stainless Steels - New Aspects, Eds. W. Borek, T. Tański , Z. Brytan, InTechOpen, Typesetting stage.
Recommend
More recommend