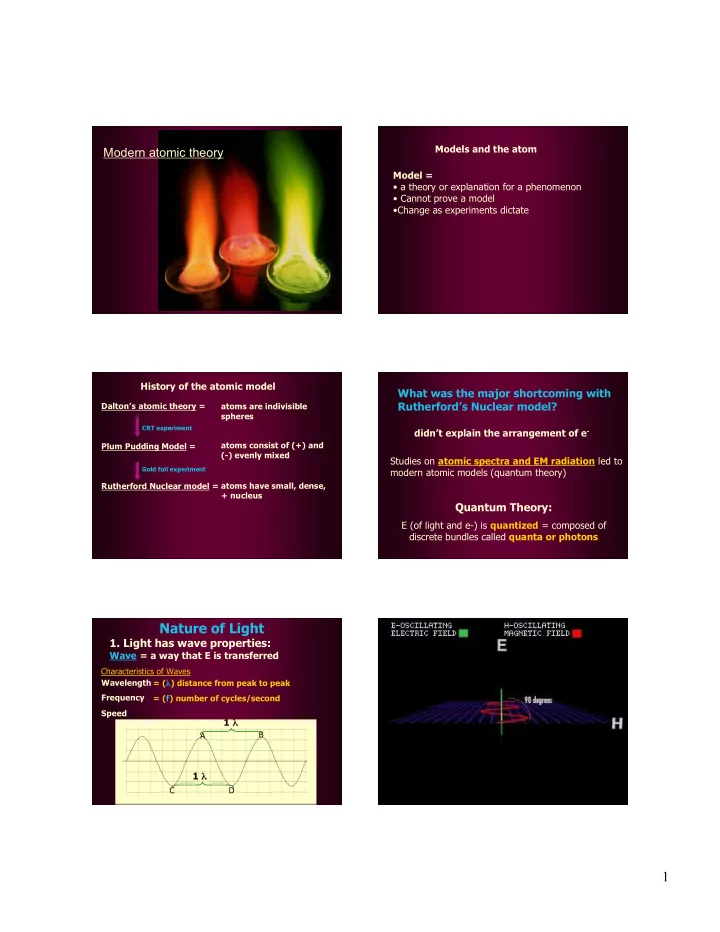

Models and the atom Modern atomic theory Model = • a theory or explanation for a phenomenon • Cannot prove a model •Change as experiments dictate History of the atomic model What was the major shortcoming with Rutherford’s Nuclear model? Dalton’s atomic theory = atoms are indivisible spheres CRT experiment didn’t explain the arrangement of e - Plum Pudding Model = atoms consist of (+) and (-) evenly mixed Studies on atomic spectra and EM radiation led to Gold foil experiment modern atomic models (quantum theory) Rutherford Nuclear model = atoms have small, dense, + nucleus Quantum Theory: E (of light and e-) is quantized = composed of discrete bundles called quanta or photons Nature of Light 1. Light has wave properties: Wave = a way that E is transferred Characteristics of Waves Wavelength = ( λ ) distance from peak to peak Frequency = (f) number of cycles/second Speed 1 λ B A 1 λ C D 1
2. Light has particle properties: Light is a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Photoelectric effect •Evidence that EM energy is quantized Highest E Lowest E •Irradiating a metal surface with light causes e - to be ejected Micro radio γ rays x rays UV IR wave • Frequency of light must be above some threshold Visible light Vacuum light tube metal longest λ λ indirectly proportional to energy e - Highest freq. Frequency directly proportional to energy V explanation: 1 photon of certain E causes Freq and λ are indirectly related emission of a single e - Spectra Analysis •EM energy has properties of both: 1) Continuous spectrum = •Waves • contains all colors from red to violet •Particles photons with discrete E •When passed through prism, see streak of color, not bands •Electrons also have both particle and wave properties 2) Bright line (Atomic) spectrum = Line spectra of elements •contains only certain discrete λ •When passed through prism, see series of lines H Hg • excited atoms emit discrete spectra Ne What is the significance of a line spectrum? •atoms can only give off certain E light •e - can only possess certain amounts of E •Gives clues to how e - are arranged 2
Bohr Model of the Atom: •first quantum model of atom (e - has a discrete quantity of E) This emitted E can be used to identify an • e - arranged in concentric shells around nucleus ( = orbits ) element. •if E absorbed: 1) e - jumps from inner to an outer shell (unstable state) 2) then e - falls from outer to inner shell (more stable) 3) E released as photon of light photon photon of light of light Excited state= Ground state= Ground state Higher E state Lowest E state + + + n = 1 n = 1 n = 1 n = 2 n = 2 n = 2 n = 3 n = 3 n = 3 3
Recommend
More recommend