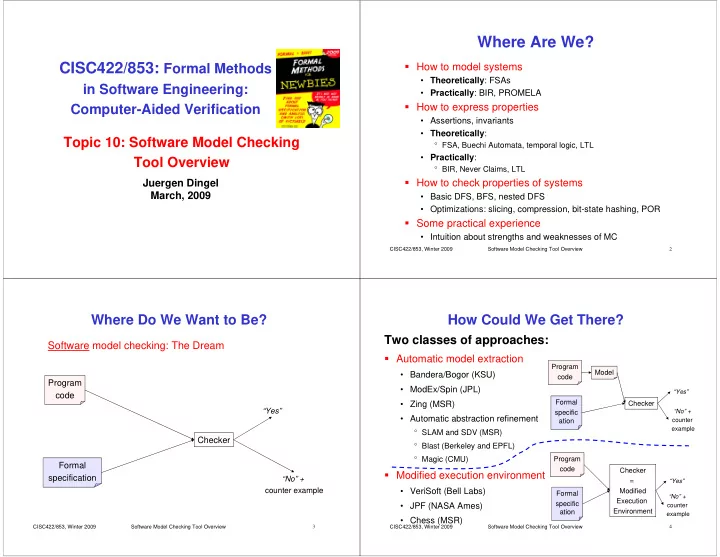

Where Are We? � How to model systems CISC422/853: Formal Methods • Theoretically : FSAs in Software Engineering: • Practically : BIR, PROMELA � How to express properties Computer-Aided Verification • Assertions, invariants • Theoretically : Topic 10: Software Model Checking ° FSA, Buechi Automata, temporal logic, LTL • Practically : Tool Overview ° BIR, Never Claims, LTL � How to check properties of systems Juergen Dingel March, 2009 • Basic DFS, BFS, nested DFS • Optimizations: slicing, compression, bit-state hashing, POR � Some practical experience • Intuition about strengths and weaknesses of MC CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 2 Where Do We Want to Be? How Could We Get There? Two classes of approaches: Software model checking: The Dream � Automatic model extraction Program Model • Bandera/Bogor (KSU) code Program • ModEx/Spin (JPL) “Yes” code Formal • Zing (MSR) Checker “Yes” “No” + specific • Automatic abstraction refinement ation counter example ° SLAM and SDV (MSR) Checker ° Blast (Berkeley and EPFL) ° Magic (CMU) Program Formal code Checker � Modified execution environment specification “No” + = “Yes” counter example • VeriSoft (Bell Labs) Modified Formal “No” + Execution specific • JPF (NASA Ames) counter Environment ation example • Chess (MSR) CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 3 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 4
Bandera/Bogor Bandera/Bogor (Cont’d) � bandera.projects.cis.ksu.edu � SW MC framework for Java developed at KSU � Since Bandera 1.0 (alpha): • Code, papers, FAQ, Forum • All of Java • Use Bogor (instead of Spin, SMV, …) Optimizer • slicing • data abstraction BIR Java Jimple BIR Bogor Front end constructor � Current research: • How to deal with native code, libraries, distributed code? • Distributed model checking CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 5 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 6 Automatic Abstraction Refinement ModEx (FeaVer) / Spin (AAR) � Problem: How to find appropriate abstraction? � SW MC for distributed systems written in C � Answer: Use counter example to iteratively compute � Developed by G. Holzmann at Bell Labs (now JPL) abstraction: since 1998 (0) start with most aggressive overabstraction P 0 of P � Use user-defined look-up tables to translate C into (1) if P i satisfies property, then done PROMELA (2) if P i doesn’t satisfy property (w/ counter example cex), then � cm.bell-labs.com/cm/cs/what/modex/ ° check if cex feasible in P (i.e., if cex is not a “false negative”) • Code ° if yes, then done (P does not satisfy property, output cex) • User guide ° if no, then • Examples q use cex to refine P i into program P i+1 that cannot exhibit cex q set i to i+1 and goto 1. • Papers CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 7 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 8
Automatic Abstraction Refinement SLAM, Blast and Magic (Cont’d) � Used by � Analyze C programs � Predicate abstraction for abstraction refinement • SLAM/SDV (MSR) • Blast (Berkeley and EPFL) � SLAM/SDV (MSR) • Magic (CMU) • research.microsoft.com/slam � Pros: ° Papers • Appropriate abstraction computed automatically http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/devtools/tools/SDV.mspx • � Blast (Berkeley and EPFL) � Cons: • www-cad.eecs.berkeley.edu/~rupak/blast/ • So far, only been applied to sequential programs ° Code (in Eclipse), user manual, papers � Magic (CMU) • www-2.cs.cmu.edu/~chaki/magic ° Code, user manual, papers CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 9 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 10 Problems With SW MC Through SW MC Through Modified Execution Translation Environment � What if run-time environment of your language knew 1. Need translation in both directions ⇒ about code model ⇓ • non-determinism counter example ⇐ counter example • exhaustive exploration (in code terms) (in model terms) • formal specifications • optimizations? 2. Correctness of analysis hinges on correctness of � You’d get translation • VeriSoft (C/C++) 3. Some MC languages (e.g., SMV, Spin) not well suited • JPF2 (Java) to represent modern, OO code Program code Checker • Chess (MSR) • In Bandera, Java was initially translated into PROMELA = “Yes” • Bogor was developed to solve this problem Modified Formal “No” + Execution specific counter Environment ation example CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 11 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 12
VeriSoft VeriSoft (Cont’d) � Processes communicate through communication objects � SW MC for concurrent C/C++ programs • Semaphores, channels, or shared memory � Developed by Patrice Godefroid at Bell Labs in 1996 � Visible action: � Analysis: • Read or write access to communication object • Directly on (only slightly modified) source code � VeriSoft exhaustively enumerates all possible sequences ⇒ no translation necessary of visible actions a concurrent program can perform up to • Uses VeriSoft scheduler which replaces standard C scheduler a user-defined depth � Supports: • Checks for ° Deadlocks, livelocks, divergences, and assertion violations • Support for non-deterministic choice: VS_toss(n) ° Simplifies implementation of test harnesses CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 13 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 14 VeriSoft (Cont’d) VeriSoft: AC Example � Analysis uses • State-less DFS: no seen set Wow! Wow! ⇒ less memory, but looping possible Temperature Door ⇒ DFS bounded by user-defined depth parameter Sensor Sensor � Optimizations: AC_Controller • Partial order reduction assume(b) assume(b) • Search space pruning: abort(b) in Bogor in Bogor AC • Abstraction through: placement of visible actions � GUI allows: “Is the AC always on, when • display of computation tree up to depth • door is closed and • inspection of variable values at every node in tree • room is hot?” • display of violating states • guided execution CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 15 CISC422/853, Winter 2009 Software Model Checking Tool Overview 16
Recommend
More recommend