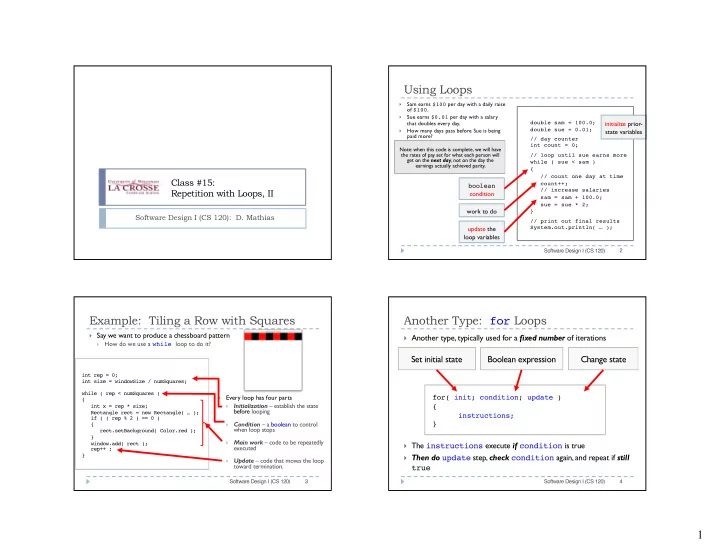

Using Loops } Sam earns $100 per day with a daily raise of $100 . Sue earns $0.01 per day with a salary } initialize prior- that doubles every day. double sam = 100.0; double sue = 0.01; How many days pass before Sue is being state variables } paid more? // day counter int count = 0; Note: when this code is complete, we will have the rates of pay set for what each person will // loop until sue earns more get on the next day , not on the day the while ( sue < sam ) earnings actually achieved parity. { // count one day at time Class #15: count++; boolean Repetition with Loops, II // increase salaries condition sam = sam + 100.0; sue = sue * 2; work to do } Software Design I (CS 120): D. Mathias // print out final results update the System.out.println( … ); loop variables 2 Software Design I (CS 120) Example: Tiling a Row with Squares Another Type: for Loops } Say we want to produce a chessboard pattern } Another type, typically used for a fixed number of iterations How do we use a while loop to do it? } Set initial state Boolean expression Change state int rep = 0; int size = windowSize / numSquares; while ( rep < numSquares ) Every loop has four parts for( init; condition; update ) } { Initialization – establish the state int x = rep * size; { } before looping Rectangle rect = new Rectangle( … ); instructions; if ( ( rep % 2 ) == 0 ) Condition – a boolean to control } { } when loop stops rect.setBackground( Color.red ); } Main work – code to be repeatedly } } The instructions execute if condition is true window.add( rect ); executed rep++ ; } Then do update step, check condition again, and repeat if still } Update – code that moves the loop } toward termination. true 3 4 Software Design I (CS 120) Software Design I (CS 120) 1
Another Type: for Loops Tiling with a for Loop } A simple loop to add all the integers from 1 to 100 } Again, we produce our row of tiles, using for Code may execute 0 or more times } Set initial state Boolean expression Change state for ( int col = 0; col < numSquares; col++ ) { int x = col * size; int sum = 0; Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(…); Loop declaration – this time, the } if ( col % 2 == 0 ) for( int i = 1; i <= 100; i++ ) initialization of loop variable, { condition , and progress all happen { rect.setBackground( Color.red ); on the same line, at the start sum = sum + i; } window.add( rect ); Main work – code to be repeatedly } System.out.println( sum ); } executed } Important: the variable int col here is local to the loop! As with if-else statements, we cannot use that variable after the loop body is complete (out of scope). 5 6 Software Design I (CS 120) Software Design I (CS 120) Local Variables in Loops Local Variables in Loops } A variable declared inside a code block {…} is local to that block, } A variable declared inside a code block {…} is local to that block, whether the block is an entire class , a method , or a control whether the block is an entire class , a method , or a control structure ( if, else, for, while, do, etc. ) structure ( if, else, for, while, do, etc. ) int n1 = 0; int n2 = 0; This will work properly now int fib = 1; This won’t for ( int i = 1; i <= 10; i++ ) int n1 = 0; All variables are i is local to loop work! { int n2 = 0; now available n1 = n2; int fib = 1; n2 = fib; outside of loop fib = n1 + n2; int i = 0; } System.out.print( i + “ “ + n1 + “ “ + n2 + “ “ + fib ); for ( i = 1; i <= 10; i++ ) int n2 = 0; { int fib = 1; n1 = n2; Neither for ( int i = 1; i <= 10; i++ ) n2 = fib; { will this! int n1 = n2; i and n1 are both local to loop fib = n1 + n2; n2 = fib; } fib = n1 + n2; System.out.print( i + “ “ + fib ); } System.out.print( i + “ “ + n1 + “ “ + n2 + “ “ + fib ); 7 8 Software Design I (CS 120) Software Design I (CS 120) 2
More Examples of for Loops } There are many ways to get the same effect Consider printing out all integers between 5 and 10 } for( int n = 1; n <= 6; n++ ) System.out.println( n + 4 ); for( int n = 0; n < 6; n++ ) System.out.println( n + 5 ); for( int n = 5; n <= 10; n++ ) System.out.println( n ); Print all odd numbers from 1 to 100 : } for( int n = 1; n <= 100; n = n + 2 ) System.out.println( n ); 9 Software Design I (CS 120) 3
Recommend
More recommend