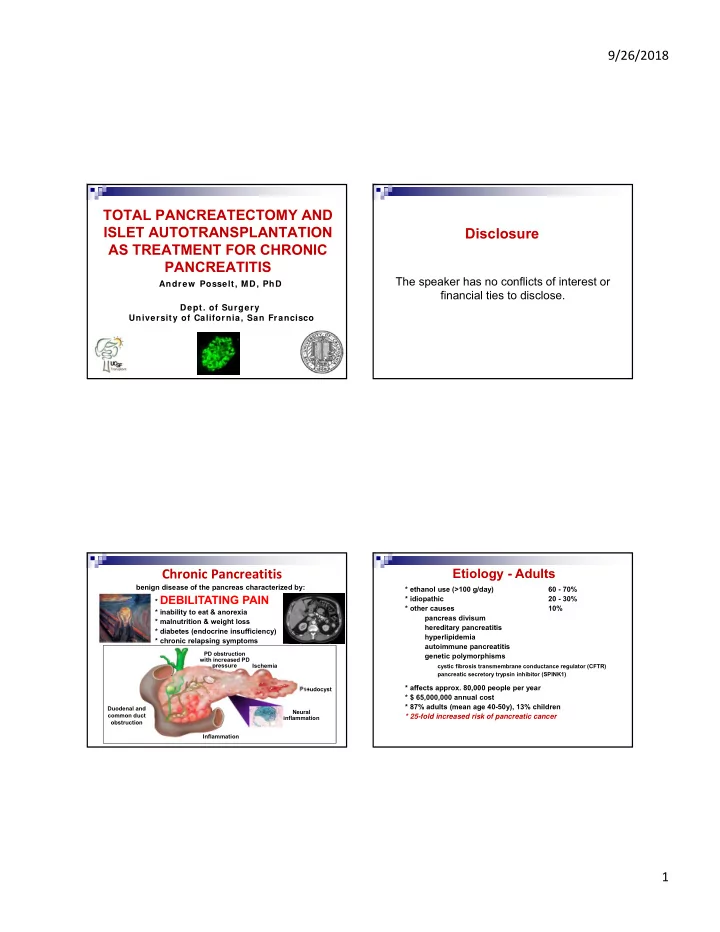

9/26/2018 TOTAL PANCREATECTOMY AND ISLET AUTOTRANSPLANTATION Disclosure AS TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC PANCREATITIS The speaker has no conflicts of interest or Andrew Posselt, MD, PhD financial ties to disclose. Dept. of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Etiology - Adults Chronic Pancreatitis A benign disease of the pancreas characterized by: * ethanol use (>100 g/day) 60 - 70% * DEBILITATING PAIN * idiopathic 20 - 30% * other causes 10% * inability to eat & anorexia pancreas divisum * malnutrition & weight loss hereditary pancreatitis * diabetes (endocrine insufficiency) hyperlipidemia * chronic relapsing symptoms autoimmune pancreatitis PD obstruction genetic polymorphisms with increased PD pressure Ischemia cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor (SPINK1) * affects approx. 80,000 people per year Pseudocyst * $ 65,000,000 annual cost * 87% adults (mean age 40-50y), 13% children Duodenal and Neural common duct * 25-fold increased risk of pancreatic cancer inflammation obstruction Inflammation 1
9/26/2018 Etiology - Children Time to Onset of Diabetes Mellitus 67% Diabetes 33% Insulin requirement * Mean age: 14 y (35% 5-12 y, 65% 13-19 y) 50% at 10 years after symptom onset, 80% at 25 years * 44% male, 56% female Many continue to be c‐peptide positive * 7-8 y Abdominal pain * 5-6 y Dx of CP * 1-2 y Narcotic use Schwarzenberg et al., JPeds 2015 Malka et al., Gastroenterol 2000 Treatment Options Indications for TP-IAT • Narcotic pain meds, enzyme replacement Painful chronic pancreatitis or disabling acute relapsing • Endoscopic therapies pancreatitis refractory to medical/endoscopic therapy - sphincterotomy, stents, dilations Narcotic dependence and/or significantly impaired quality of life • Celiac plexus ablation Imaging/EUS evidence of CP (MRI, MRCP, CT, ERCP) OR relapsing acute pancreatitis (>3 episodes over 6 mos) OR - chemical, surgical hereditary pancreatitis w/ Sx • Surgical decompression (Puestow, Frey, Beger) or Non-diabetic OR C-peptide positive diabetes partial resection (Whipple, distal) Patient and family accept (and can manage) risk of diabetes and - NOT effective in most pts need for lifelong pancreatic enzyme replacement • Total Pancreatectomy - Very effective in most pts, but results in Contraindications: brittle diabetes • Active alcohol use (documented abstinence for >6mos) • Illegal drug use • Islet Autotransplant restores endocrine • Pancreatic cancer (maybe not IPMN) function after TP (TP/IAT) • Advanced liver, lung, heart disease • Relative – absent C-peptide 2
9/26/2018 Timing TP/IAT Cases by State: 1977- 2013 W A: 0 ME Earlier is better! MT ND 2 0 4 OR MN VT:0 VT:0 VT 1 409 N I D SD NY H NH:0 NH:0 Prior to development of central sensitization and opioid-induced W I MI MI M 10 7 2 16 A MA:3 MA:3 W Y 16 17 1 hyperalgesia which can lead to pain recurrence RI :1 RI :1 I A PA: 13 CA NV NE 5 CT:0 CT:0 N OH 50 1 1 J M I L I N 132 D NJ:8 NJ:8 UT D E CO 15 15 0 W DE:0 DE:0 Optimization of islet yield/function 5 KS MO V 1 VA: 8 8 KY: 3 MD:3 6 DC: 0 Prior to invasive surgical procedures (partial resection, ductal drainage) NC: 4 AZ O TN: 9 Prior to glucose intolerance/diabetes NM 3 SC: 61 K AR 1 2 33 MS AL Number of Patients Early in course of disease to minimize fibrosis 91 GA GA 1 4 4 TX TX LA 15+ Younger children (fewer post-op complications and higher islet yields) 15 13 3 11-15 AK FL 0 6-10 11 1-5 0 0 HI Pediatric TP/IAT Cases by State: 1977- 2016 Multi-Disciplinary Team Is A MUST! 27: 5-12 yrs Gastroenterology Nursing 48: 13-19 yrs MN ICU Team Endocrinology 75 PA 10 CA OH 14 9-18 yrs 14 Patient 4-16 yrs Pain Management Psychiatry 14-18 yrs Islet Manufacture Surgery Social Work 3
9/26/2018 UCSF Inpatient Care Algorithm The Procedure Day 1 Day 4-5 PCA PCA transition to short acting elixir Oral pain meds IV Anti-emetics TF at goal NG out/GT to gravity, NPO Bowel Regimen Insulin drip Start Lantus, D/C insulin drip Ambulate to chair Start Diabetic education Consult Endocrine, Pain Svcs Day 6 Day 2 ADAT PCA Start TF education/Discharge class Start TF/enzymes Bowel Regimen IV Anti-emetics Continue plan, eval for complications Insulin drip Ambulate x1 Day 7-8 Order PT/OT Eval & Treat Supplement education prn Continue plan, eval for complications Day 3 PCA transition basal to long-acting Consider transfer to Home/Rehab when following are met: TF/enzymes IV Anti-emetics TF stable Adequate water intake to prevent IV depletion/dehydration Insulin drip Patient’s OWN islets Diabetes stable, not requiring daily titration of Diabetes Ambulate x3 No risk of rejection therapy No immunosuppression No surgical concerns Narcotic dose stable, < 3 extra IV doses/day TP-IAT at UMN Pain Relief In patients with CP whose pain persists after Endoscopic Duct Drainage (EDD) procedures, TP-IAT can… 409 pts total Provide pain relief in the majority of patients 53 children (5-18y) Give the chance to wean off narcotics Preserve insulin secretion in most Improve quality of life Effort is needed to identify in advance the few patients whose life will not be made better by TP-IAT 1.2% in-hospital mortality; 89% (adult) and 98% (child) 5-y survival 90% C-peptide pos., 33% partial function 30% insulin independent at 3 y (25% adults, 55% children) Pain improved in 85% adults, 94% children (67% pain-free) 15.9% had complications requiring reoperation (bleeding, anastomotic leaks) Sutherland et al., JACS 2012 4
9/26/2018 Durability of Pain Control QOL by SF-36 Assessment Genetic/Hereditary Nonhereditary Pancreatitis pain Pain severity QOL: Improved in 80%; Same in 15%; Worse in 5% 98% preferred diabetes to former pain 87% said pancreatitis was worse than diabetes 98% would have procedure again School Attendance and Days of Islet Function and Insulin Independence Impaired Activity 25-40% insulin independent in most large cohorts Most insulin dependent patients have graft function Low insulin needs P<0.005 + C-peptide (nearly 90%) P<0.001 Benefit of islets, even if on insulin Stable glycemic control Avoid “brittle” (labile) diabetes Absent hypoglycemic episodes Sutherland et al., Transplantation 2008 Sutherland et al., Transplantation 2008 Ahmad et al., JACS 2005 Ahmad et al., JACS 2005 Webb et al., Pancreas 2008 Webb et al., Pancreas 2008 5
9/26/2018 Durability of Islet Function TP-IAT Particularly Effective in Children with CP Insulin Requirements HbA1c Narcotic Use Insulin Independence ** Ped Adult Adult Ped VERY FEW pts developed diabetes-related complications Wilson, et al., Ann Surg 2014 Who Becomes Insulin Independent? Insulin Independence and IEQ/Kg Predictors: 90% Islet number (mass/yield) 80% 100% function, 70% independent with >5000 IE/kg 83% function, 30% independent with 2501-5000 IE/kg 70% 59% function, 15% independent with <2500 IE/ kg 60% <2500 Prior surgery 50% 2500‐5000 Lower yield after surgical drainage/distal pancreatectomy 40% >5000 Age 30% Allo Pediatric patients have high rates of insulin independence 20% Other characteristics 10% duration of disease, islet quality, insulin resistance 0% 6 months 12 months 24 months 36 months Sutherland et al., Transplantation 2008 Sutherland et al., Transplantation 2008 Ahmad et al., JACS 2005 Ahmad et al., JACS 2005 Webb et al., Pancreas 2008 Webb et al., Pancreas 2008 6
9/26/2018 High Likelihood of Insulin Islet Autotransplants Function Independence in Young Children Better Than Allotransplants 14000 Fewer islets needed needed (2500IE/kg vs. >7500IE/kg) 12000 Most function >2yrs, approx 80% >3-4yrs; 70% >10yrs 10000 No ‘late’ failures IE/kg 8000 6000 4000 - Brain death 2000 - Increased CIT 0 - Immunosuppression 0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 Can’t be due - Alloimmunity Age at Transplant (years) to hepatic site - Autoimmunity Insulin Dependent Minimal Insulin Insulin Independent - No precursors in highly purified preps Children 5‐18 years of age: 44% ever achieve insulin independence 85% of children <10 years of age have documented insulin independence Insurance Coverage is a Problem! UCSF Experience • 32 adults since 2013 (8-10/y since 2016) All carriers cover TP, but only some cover AIT • 14 children (10 since 2015) AIT adds approx. $27,000-30,000 to overall cost. • 12 isolations for pts at UCLA OR time not significantly prolonged since isolation is • Referrals from CA, NV, AL, AZ, CO, NY, TX, WA, Kaiser performed during biliary and intestinal reconstruction, and infusion takes approx. 20 mins. • Mean hospital stay: 16d (10-60d) Overall LOS, hospitalization costs not significantly • Readmissions: 2 within 30d, 3 within 6 mos increased • Complications: bleeding (2), SBO (2), N/V (1) QOL dramatically increased with AIT even if • Mean IEQ/kg: 5700+2000 (a),7,400+176,000 (p) independence is not achieved, but most pts cant raise • Insulin independence: 60% adults, 87% peds adequate funds to cover procedure. • Pain control: 60% adults off meds, 40% weaning 100% peds off meds 7
Recommend
More recommend