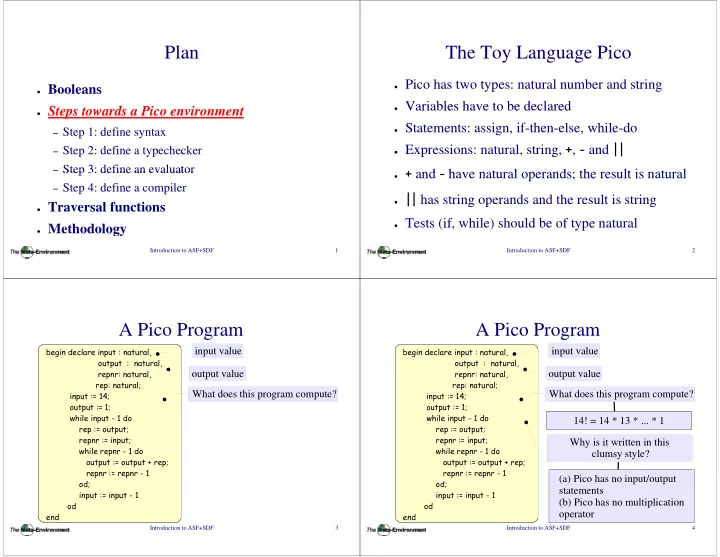

Pla an The Toy Lan nguage Pico ● Pico has two types: natu ural number and string ● Booleans ● Variables have to be dec Variables have to be dec clared clared ● Steps towards a Pico en S d Pi nvironment i ● Statements: assign, if-th hen-else, while-do – Step 1: define syntax ring, + , - and || ● Expressions: natural, str – Step 2: define a typechec cker ● + and - have natural ope + and – Step 3: define an evaluat Step 3: define an evaluat tor tor ha e nat ral ope erands; the res lt is nat ral erands; the result is natural – Step 4: define a compile er ● || has string operands a || g p and the result is string ● Traversal functions T l f ti ● Tests (if, while) should be of type natural ● Methodology Introduction to ASF+SDF 1 Introduction to ASF+SDF 2 A Pico P Program A Pico P Program begin declare input : natural begin declare input : natural, begin declare input : natural begin declare input : natural, input value input value input value input value output : natural, output : natural, repnr: natural, repnr: natural, output value output value rep: natural; rep: natural; rep: natural; rep: natural; input := 14; What does this program compute? input := 14; What does this program compute? output := 1; output := 1; while input - 1 do while input 1 do while input 1 do while input - 1 do 14! 14! = 14 * 13 * ... * 1 14 * 13 * * 1 rep := output; rep := output; repnr := input; repnr := input; Why is it written in this while repnr - 1 do hil 1 d while repnr - 1 do hil 1 d clumsy style? l l output := output + rep; output := output + rep; repnr := repnr - 1 repnr := repnr - 1 (a) Pico has no input/output ( ) p p od; d od; d statements input := input - 1 input := input - 1 (b) Pico has no multiplication od od operator operator end d end d Introduction to ASF+SDF 3 Introduction to ASF+SDF 4
Pla an Step 1: Define syntax for Pico ● Booleans basic/NatCon basic/Str rCon languages/pico/syntax/Types ● Steps towards a Pico e S d Pi nvironment i – Step 1: define syntax languages/pico/ languages/pico/ syntax/Pico syntax/Pico – Step 2: define a typechec cker – Step 3: define an evaluat Step 3: define an evaluat tor tor basic/Whitespace languages/pico/syntax/Identifiers – Step 4: define a compile er ● Traversal functions T l f ti ● Methodology Introduction to ASF+SDF 5 Introduction to ASF+SDF 6 Pico-sy Pico sy yntax 2 yntax, 2 Pico-sy yntax , 1 Syntax rules for statements m module languages/pico/syntax/Pico g g /p / y / PICO-ID ":=" EXP -> STATEMENT imports "if" EXP "then" {STATEMENT ";"}* languages/pico/syntax/Identifiers "else" {STATEMENT ";"}* "fi" -> STATEMENT languages/pico/syntax/Types languages/pico/syntax/Types Sorts and syntax rules Sorts and syntax rules "while" EXP "do" {STATEMENT ";"}* "od“ “ -> STATEMENT basic/NatCon for program and basic/StrCon declarations exports exports sorts PROGRAM DECLS ID-TYPE STATEMENT T EXP List of zero or context-free start-symbols context free start symbols more statements PROGRAM separated by ; * zero or more context-free syntax "begin" DECLS {STATEMENT ";"}* "end" begin DECLS {STATEMENT ; } end > PROGRAM -> PROGRAM + one or more + "declare" {ID-TYPE ","}* ";" -> DECLS PICO-ID ":" TYPE -> ID-TYPE Introduction to ASF+SDF 7 Introduction to ASF+SDF 8
Pico-sy yntax , 3 Ident tifiers module languages/pico/syntax/Identif d l l / i / t /Id tif fi fiers Syntax rules for expressions Syntax rules for expressions Repeat zero ( * ) or one exports PICO-ID -> EXP The sort NatCon is imported NatCon -> EXP sorts PICO-ID ( + ) or more times ( ) from basic/NatCon from basic/NatCon StrCon -> EXP StrCon -> EXP EXP "+" EXP -> EXP {left} EXP "-" EXP -> EXP {left} The sort StrCon is imported lexical syntax EXP "||" EXP -> EXP {left} [a-z] [a-z0-9]* -> PICO-ID [a z] [a z0 9] > PICO ID from basic/StrCon from basic/StrCon "(" EXP ")" > EXP {b "(" EXP ")" -> EXP {bracket} k t} A character class: PICO-ID starts with a lowercase letter lexical restrictions context-free priorities The three operators are EXP "||" EXP -> EXP > EXP "||" EXP > EXP > PICO ID / [ PICO-ID -/- [a-z0-9] 0 9] l ft left-associative i ti EXP "-" EXP -> EXP > EXP "+" EXP -> EXP The priorities of the three p ion: is aaa three, two or one identifier? A l A lexical restricti i l t i ti i i th t id tifi ? operators, a disambiguation -/- can be used to construct: 1 - (2 + 3) , or o define longest match (1 - 2) + 3 ?? (1 - 2) + 3 ?? Introduction to ASF+SDF 9 Introduction to ASF+SDF 10 Pico-T Types Pico: factor rial program begin declare input : n begin declare input : n natural natural, module languages/pico/syntax/Types output : natural, The sort of possible types in a Pico repnr: n natural, exports exports rep: nat rep: nat ural; ural; program program input := 14; sorts TYPE The constants natural and string output := 1; context-free syntax represent types as can be declared in represent types as can be declared in while input 1 d while input - 1 d do do "natural" -> TYPE rep := output t; Pico program "string" -> TYPE repnr := inpu ut; "nil-type" -> TYPE yp while repnr - while repnr - 1 do 1 do The constant nil-type is used for output := o output + rep; repnr := re epnr - 1 handling error cases od; d; input := input t - 1 od end d Introduction to ASF+SDF 11 Introduction to ASF+SDF 12
Syntax for Pi ico: summary Intermezzo: Symbols (1) ● The modules languages s/pico/syntax/ Pico An elementary symbol is: defines (together with th defines (together with th he imported modules) the he imported modules) the – Literal: “abc” l “ b ” Li syntax for the Pico langu uage mes: INT – Sort (non-terminal) nam ● This syntax can be used Thi t b d t d d to – Character classes: [a-z] : : one of a , b , ..., z ● ~ : complement of charac – Generate a parser that ca an parse Pico programs p cter class. – Generate a syntax-direct ted editor for Pico programs ● / : difference of two char racter classes. ● /\ : intersection of two ch /\ : intersection of two ch – Generate a parser that ca p an parse equations containing p q g haracter classes haracter classes. fragments of Pico progra ams ● \/ : union of two charact er classes. Introduction to ASF+SDF 13 Introduction to ASF+SDF 14 Intermezzo: Symbols (2) Intermezzo: produ uctions (functions) A complex symbol is: A complex symbol is: ● General form of a produ uction (function): – Repetition: – S1 S2 ... Sn -> S0 Attr 1 2 0 ributes b ● S* zero or more times S S ; S+ one or more times S ● Lexical syntax and context- -free syntax are similar, but ● {S1 S2}* zero or more ● {S1 S2} times S1 separated by S2 times S1 separated by S2 zero or more – Between the symbols in a production optional layout ● {S1 S2}+ one or more t times S1 separated by S2 symbols may occur in th he input text. – Optional: S? zero or one l S? e occurrences of S f S O ti – A context-free productio on is equivalent with: – Alternative: S | T an S o or a T ● S1 LAYOUT? S2 LAY ● S1 LAYOUT? S2 LAY YOUT? ... LAYOUT? Sn YOUT? LAYOUT? Sn -> S0 S0 for “<” S “,” T “>” – Tuple: <S,T> shorthand f – Parameterized sorts: S[[ [ P1, P2 ]] Introduction to ASF+SDF 15 Introduction to ASF+SDF 16
Recommend
More recommend