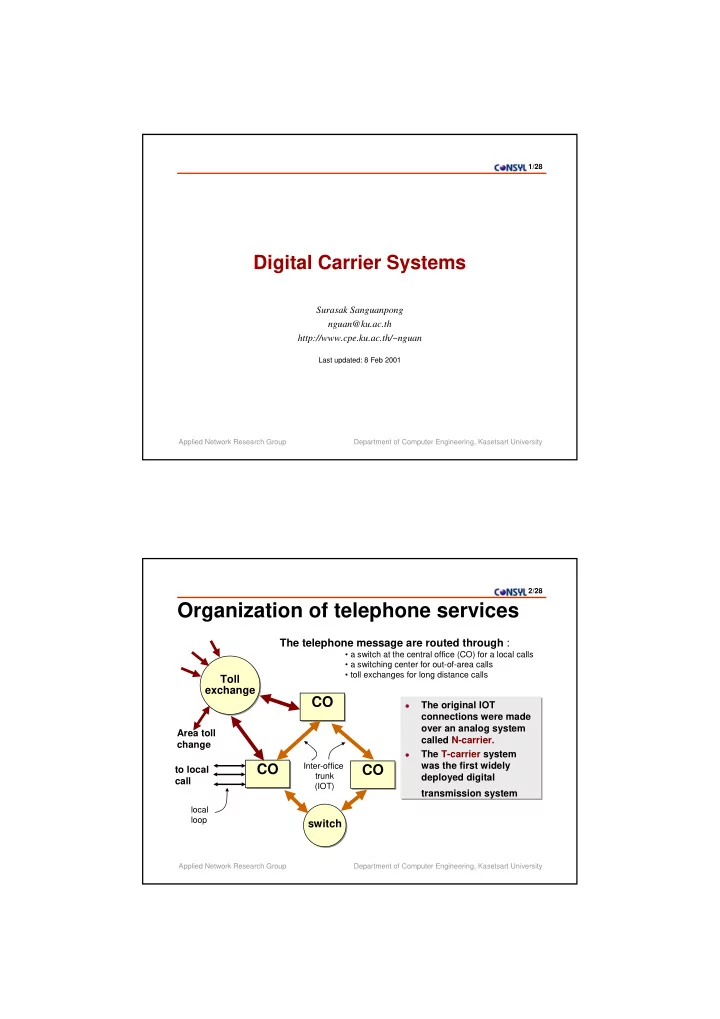

1/28 Digital Carrier Systems Surasak Sanguanpong nguan@ku.ac.th http://www.cpe.ku.ac.th/~nguan Last updated: 8 Feb 2001 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 2/28 Organization of telephone services The telephone message are routed through : • a switch at the central office (CO) for a local calls • a switching center for out-of-area calls • toll exchanges for long distance calls Toll Toll exchange exchange CO CO The original IOT The original IOT � � connections were made connections were made over an analog system over an analog system Area toll called N-carrier. called N-carrier. change The T-carrier system � The T-carrier system � was the first widely CO Inter-office was the first widely CO CO to local CO trunk deployed digital deployed digital call (IOT) transmission system transmission system local loop switch switch Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
3/28 Digital Services Switched/56 Switched/56 Services Digital Data Services Services Digital Data Services Digital Carrier Systems Digital Carrier Systems Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 4/28 Switched/56 Telephone Network (Switching) DSU DSU router router A switched digital service that allows data rate 56 Kbps over � switched synchronous line Switched/56 lines are digital and do not require a modem � Data Service Unit (DSU) is required to convert signals from LAN � devices/multiplexer into the digital signals used by the digital lines Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
5/28 Digital Data Services Telephone Network (Leased) Check! DSU DSU router router A digital leased line is used with a maximum data rate of 64 � Kbps Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 6/28 Digital carrier standard � T-carrier � North America, Japan � E-carrier � Europe, South America � SONET/SDH � world-wide new standard Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
7/28 Comparison of the layer OSI T-1 SONET/SDH Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data link Physical Physical Physical Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 8/28 T-1 carrier system 24 voice channels are sampled, quantized and � encoded into a TDM PCM signal CH1 T-1 carrier has a transmission rate of 1.544 Mbps � CH2 PCM CH1 CH2 CH3 CH23 CH24 CH23 CH24 Bipolar encoding � Bipolar encoding � x x x x x x x x B8ZS for T-1 � B8ZS for T-1 � LSB B3ZS for T-3 � B3ZS for T-3 MSB � Full duplex (sign bit) Full duplex � � Channel-based digital transmission � Channel-based digital transmission � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
9/28 T-1 frame T-1 bit rate : (24x8 +1 bit)/125 μ s = 1.544 Mbps 1 frame bit 125 μ s CH 1 CH 2 CH 24 CH 1 CH 2 CH 24 (8 bit) (8 bit) . . . . . . . (8 bit) (8 bit) (8 bit) . . . . . . . (8 bit) 192 bits The early frame standard called D1, D2 and D3 were used. The early frame standard called D1, D2 and D3 were used. � � There are two framing standard for the T-1, called D4 � There are two framing standard for the T-1, called D4 � (superframe) and extended superframe (ESF) (superframe) and extended superframe (ESF) The T-3 used the M13 framing � The T-3 used the M13 framing � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 10/28 Frame and Superframe 1 superframe = 12 frames (2316 bits in 1.5 ms) F odd 1 0 1 0 1 0 F even 0 0 1 1 1 0 F combine 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 Frame # F data (192 bits) T-1 carrier frames are transmitted in � 1 1 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd groups of 12 called superframes 2 0 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd F-bit in even-numbered frame has a 3 0 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd � 4 0 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd pattern of 101010 for synchronization 5 1 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd Signaling information is accomplished 6 1 dddd dddX -- dddd dddX � 7 0 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd by robbing the LSB position of each 8 1 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd channel. This is performed only in the 9 1 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd 6 th and 12 th frame to keep distortion 10 1 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd 11 0 dddd dddd -- dddd dddd minimum 12 0 dddd dddX -- dddd dddX Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
11/28 Extended Superframe 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Remote configuration and monitoring (4Kbps) CRC Frame synchronization ESF framing groups 24 frames into an ESF superframe � every 193rd bit are used for the above purposes � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 12/28 Multiplexing CSU (Channel Service Unit) � router phone performs several protective and � diagnostic functions DSU (Data Service Unit) � convert the digital data from a (for � example) router to T1 voltages and MUX encoding. CSU/DSU T-carrier Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
13/28 T-carrier Digital Multiplexing Hierarchy T1 DS1 DS1 Two 1.544 Mbps DS1 channels are multiplexed into a single 3.152 Mbps DS1C channel Two DS1C channels are multiplexed into a single 6.312 Mbps DS2 channel DS1C DS1C T1-C Seven DS2 channels are multiplexed T2 DS2 into a single DS2 DS2 DS2 DS2 DS2 DS2 44.736 Mbps DS3 channel T3 DS3 DS3 DS3 DS3 DS3 DS3 Six DS3 channels are multiplexed into a single 274.176 Mbps DS4 DS4 T4 channel Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 14/28 E1-frame 30 voice channels+2 control channels 125 μ s CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH 0 1 2 16 31 0 1 2 16 31 frame signaling synchronization channel T1 bit rate : (32x8 bit)/125 μ s = 2.048 Mbps Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
15/28 E-carrier Thirty two 64 Kbps channels are multiplexed Four E1 channels are to create one multiplexed into a single E1 E1 E1 E1 2.048 Mbps E1 8.448 Mbps E2 channel channel E2 E2 E2 E2 Four E2 channels are multiplexed into a single 34.368 Mbps E3 channel Four E3 channels are multiplexed E3 E3 E3 E3 into a single 139.264 Mbps E4 channel Four E4 channels are E4 E4 E4 E4 multiplexed into a single 565.148 Mbps E5 channel E5 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 16/28 Digital carrier comparison Europe E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 x32 x 4 x 4 x 4 x 4 2.048 8.448 34.368 139.264 564.992 2.048 8.448 34.368 139.264 564.992 T1 x 2 USA x24 T1C x 2 T2 x 7 T3 x 6 T4 64 64 1.544 3.152 6.312 44.736 274.176 1.544 3.152 6.312 44.736 274.176 Japan J1 J2 J3 J4 J5 x24 x 4 x 5 x 3 x 4 1.544 6.312 32.064 97.728 397.200 1.544 6.312 32.064 97.728 397.200 Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
17/28 PDH almost synchronous PDH = Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy � Digital transmission systems (T-carrier, E carrier) combine � lower order multiplex stream to get higher bit rate Each device runs its own free-running clock � Different streams have small differences in clock signals. � Solve by adding justification bit � Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University 18/28 PDH deficiencies (I) � Lack of flexibility � impossible to identify a lower bit rate channel from the higher-order bit stream. Extraction of 2 Mbps channel from 140 Mbps channel 34 Mbps 140 M 140 M 140 140 LTE LTE 34 34 8 Mbps 34 34 8 8 2 Mbps demux the high bit 8 remux back into higher rate down to the lower level 8 2 level for onward transmission 2 Customer site Applied Network Research Group Department of Computer Engineering, Kasetsart University
Recommend
More recommend