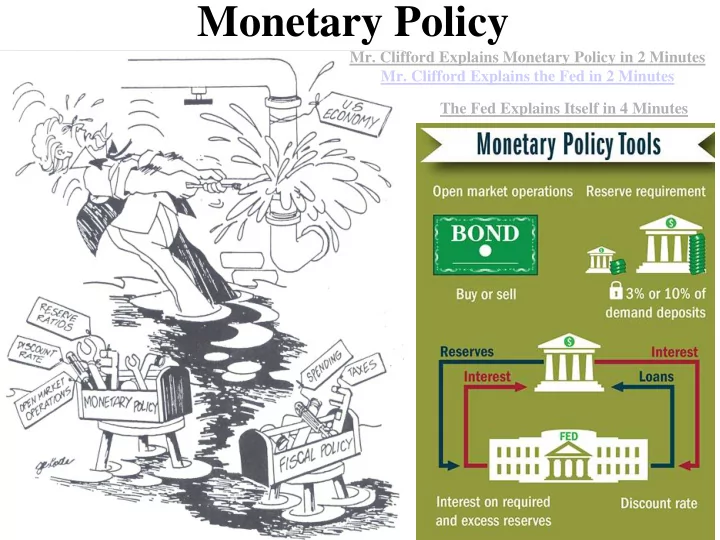

Monetary Policy Mr. Clifford Explains Monetary Policy in 2 Minutes Mr. Clifford Explains the Fed in 2 Minutes The Fed Explains Itself in 4 Minutes
#1: Reserve Requirements If you have a bank account, where is your money? Only a small percent of your money is held in reserve. The rest of your money has been loaned out. This is called “Fractional Reserve Banking”…more on this later The Fed sets the amount that banks must hold…this is called the “Reserve Requirement” The reserve requirement (also called the “reserve ratio”) is the percent of deposits that banks must hold in reserve (the percent they can NOT loan out). Example: If the reserve requirement is 10% and you deposit $1000 in a bank, it can only add $900 of your deposit to its “loanable funds” and must keep at least $100 “in reserve” TAKE AWAYS • When the Fed increases the money supply, it increases the amount of money in bank deposits and therefore the amount of loanable funds. • However, the Fed requires that banks must keep some percentage of deposits “in reserve” and can only loan out “excess reserves”. • These loans eventually become deposits for other bank that will loan out their excess reserves . (Called the “Money Multiplier”…more on this later) • Lowering Reserve Ratios EXPANDS the Money Supply • Increasing Reserve Requirements CONTRACTS the Money Supply
How Reserve Requirements Can Impact Monetary Policy to Stabilize the Economy 1. If there is a RECESSION, what could the Fed do to the reserve requirement? Decrease the Reserve Ratio 1. Banks hold less money and have more excess reserves. 2. Banks create more money by loaning out excess. 3. Money supply increases, interest rates fall, AD up. 2. If there is INFLATION, what could the Fed do to the reserve requirement? Increase the Reserve Ratio 1. Banks hold more money and have fewer excess reserves. 2. Banks create less money. 3. Money supply decreases, interest rates up, AD down.
#2: The Discount Rate The Discount Rate is the interest rate that the Fed charges commercial banks. Example: If Banks of America needs $10 million, they borrow it from the U.S. Treasury (which the Fed controls) but B of A must pay it back with 3% interest…3% is the “discount rate” In a recession, the Fed wants to increase the Money DECREASE supply, the Fed would _________ the Discount Rate (This is called an “Easy Money” Policy). To combat inflation and decrease the Money supply, the Fed would _________ the Discount Rate INCREASE (This is called a “Tight Money” Policy).
#3: Open Market Operations • Open Market Operations is when the Fed buys or sells government bonds (securities). • This is the most important and widely used monetary policy the Fed engages in. In a recession, the Fed wants to increase the Money supply, so it would _________ government securities. BUY To combat inflation, the Fed wants to decrease the Money supply, so it would_________ government SELL securities. A “Trick” to remember: B UY= B IG - Buying bonds INCREASES money supply S ell= S mall - Selling bonds DECREASES money supply
Open Market Operations Explained in 2 Minutes Crash Course Economics Explains Monetary Policy in 9 Minutes
Expansionary & Contractionary Monetary Policy…How & Why?
How The Goals of Monetary Policy Can Monetary Policy impacts the AD-AS & MS Models
Interest Interest Money Supply Loanable Funds Rate (i) Rate (i) S M S M1 10% 10% 5% 5% 2% 2% D M D I Quantity of Money 20 25 Quantity of Loans PL The Fed increases the AD/AS AS money supply to stimulate the economy… PL 1 PL 1. Interest Rates Decreases 2. Investment Increases e AD AD 1 3. AD, GDP and PL Increases GDP R Q e Q 1
Interest Money Supply Loanable Funds Interest Rate (i) Rate (i) S M1 S M 10% 10% 5% 5% 2% 2% D M D I 17 20 Quantity of Money Quantity of Loans PL The Fed decreases the AD/AS AS money supply to slow down the economy… PL 1. Interest Rates increase PL 1 e 2. Investment decreases AD 3. AD, GDP and PL decrease AD 1 GDP R Q 1 Q e
2011 Practice FRQ
2011 Practice FRQ ANSWERS 16
2014 Practice FRQ
2014 Practice FRQ ANSWERS
2014 Practice FRQ ANSWERS
2009 Practice FRQ
2009 Practice FRQ ANSWERS EXPLAINED in 4 Minutes
2009 Practice FRQ ANSWERS
Recommend
More recommend