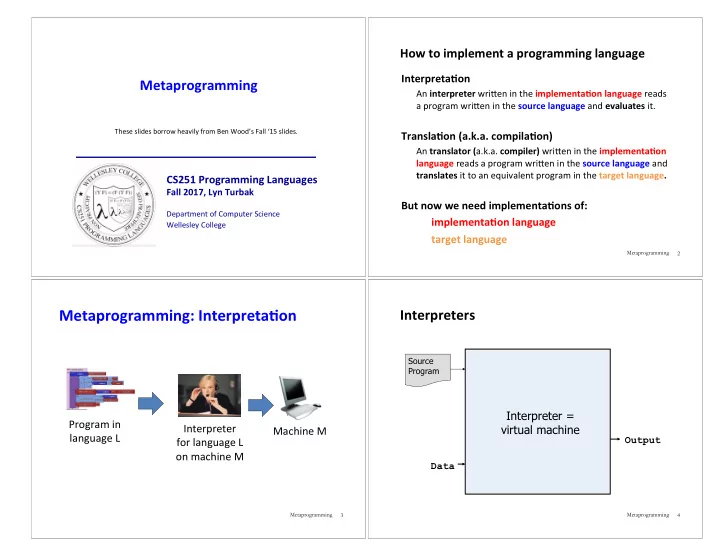

How to implement a programming language InterpretaBon Metaprogramming An interpreter wriDen in the implementaBon language reads a program wriDen in the source language and evaluates it. These slides borrow heavily from Ben Wood’s Fall ‘15 slides. TranslaBon (a.k.a. compilaBon) An translator ( a.k.a. compiler) wriDen in the implementaBon language reads a program wriDen in the source language and translates it to an equivalent program in the target language. CS251 Programming Languages Fall 2017, Lyn Turbak But now we need implementaBons of: Department of Computer Science implementaBon language Wellesley College target language Metaprogramming 2 Metaprogramming: InterpretaBon Interpreters Source Program Interpreter = Program in Interpreter virtual machine Machine M language L for language L Output on machine M Data Metaprogramming Metaprogramming 3 4
Metaprogramming: TranslaBon Compiler C Source x86 Target Program C Compiler Program if (x == 0) { cmp (1000), $0 Program in x = x + 1; bne L Program in language A A to B translator } add (1000), $1 language B ... L: ... x86 Target Program Output x86 computer Interpreter Machine M Thanks to Ben Wood for these for language B Data and following pictures on machine M Metaprogramming Metaprogramming 5 6 Interpreters vs Compilers Java Compiler Interpreters No work ahead of Lme Source Target Incremental Program Java Compiler Program maybe inefficient if (x == 0) { load 0 Compilers x = x + 1; ifne L } load 0 All work ahead of Lme ... inc See whole program (or more of program) store 0 L: Time and resources for analysis and opLmizaLon ... (compare compiled C to compiled Java) Metaprogramming Metaprogramming 7 8
Compilers... whose output is interpreted Interpreters... that use compilers. Source Source Target Program Java Compiler Program Compiler Program Target Program Target Virtual Output Program Java Machine Output Virtual Machine Data Data Doesn’t this look familiar? Metaprogramming Metaprogramming 10 9 JIT Compilers and OpBmizaBon Virtual Machine Model Source Program High-Level Language Program • HotSpot JVM Just In Time • Jikes RVM Bytecode Ahead-of-Lme Compiler • SpiderMonkey compiler compiler Compiler • v8 compile Bme • Transmeta Virtual Machine Language run Bme • ... Target Performance JIT Monitor Program Virtual machine compiler Output (interpreter) Virtual Machine NaLve Machine Language Data Metaprogramming 11 Metaprogramming 12
Typical Compiler How to implement a programming language Can describe by deriving a “proof” of the implementaLon Source Lexical Analyzer using these inference rules: Program Interpreter Rule Syntax Analyzer P-in-L program L interpreter machine Analysis Semantic Analyzer P machine Intermediate Code Synthesis Translator Rule Generator P-in-S program S-to-T translator machine Code Optimizer P-in-T program Code Generator Target Program Metaprogramming 13 Metaprogramming 14 ImplementaBon DerivaBon Example ImplementaBon DerivaBon Example SoluBon Prove how to implement a "251 web page machine" using: • 251-web-page-in-HTML program (a web page wriDen in HTML) • HTML-interpreter-in-C program (a web browser wriDen in C) • C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program (a C compiler wriDen in x86) We can omit some occurrences of “program” and “machine”: • x86 interpreter machine (an x86 computer) No peaking ahead! Metaprogramming 15 Metaprogramming 16
ImplementaBon DerivaBon Are Trees Metaprogramming: Bootstrapping Puzzles And so we can represent them as nested structures, like nested bulleted lists: How can we write Scheme interpreter in Scheme? q 251-web-page-in-HTML program Version that shows o HTML-interpreter-in-C program conclusions below bullets. How can we write a Java-to-x86 compiler in Java? C-to-x86 compiler-in-x86 program • More similar to derivaLons • X86 computer with horizontal lines, but o C-to-x86 compiler machine (I) harder to create and read ² HTML-interpreter-in-x86 program (T) ² x86 computer q HTML interpreter machine (I) 251 web page machine (I) Preferred “top-down” 251 web page machine (I) version that shows q 251-web-page-in-HTML program q HTML interpreter machine (I) conclusions above bullets. ² HTML-interpreter-in-x86 program (T) o HTML-interpreter-in-C program o C-to-x86 compiler machine (I) • C-to-x86 compiler-in-x86 program • X86 computer ² x86 computer Metaprogramming 17 Metaprogramming 18 Metacircularity and Bootstrapping Metacircularity Example 1: Problem Many examples: Suppose you are given: Lisp in Lisp / Scheme in Scheme/Racket in Racket • Scheme-interpreter-in-Python program • Python in Python: PyPy • Python machine • Java in Java: Jikes RVM, Maxine VM • Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program • … • How do you create a Scheme interpreter machine using the C-to-x86 compiler in C • Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program? eval construct in languages like Lisp, JavaScript • How can this be possible? Key insights to bootstrapping: The first implementaLon of a language cannot be in • itself, but must be in some other language. Once you have one implementaLon of a language, you • can implement it in itself. Metaprogramming 19 Metaprogramming 20
Metacircularity Example 1: SoluBon Metacircularity Example 1: More RealisBc Suppose you are given: Suppose you are given: Scheme-interpreter-in-Python program Scheme-subset-interpreter-in-Python program (implements • • only core Scheme features; no desugaring or other frills) Python machine • Python machine Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program • • Full-Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program How do you create a Scheme interpreter machine using the • Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program? How do you create a Full-Scheme interpreter machine using the Full-Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program? Scheme interpreter machine #2 (I) q Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program Full-Scheme interpreter machine (I) q Scheme-interpreter machine #1 (I) q Scheme-interpreter-in-Scheme program ² Scheme-interpreter-in-Python program q Scheme-subset interpreter machine #1 (I) ² Python machine ² Scheme-subset-interpreter-in-Python program ² Python machine But why create Scheme interpreter machine #2 when you already have Scheme-interpreter machine #1? Metaprogramming 21 Metaprogramming 22 Metacircularity Example 2: Problem Metacircularity Example 2: SoluBon Suppose you are given: Suppose you are given: • • C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program (a C compiler wriDen in x86) C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program (a C compiler wriDen in x86) • x86 interpreter machine (an x86 computer) • x86 interpreter machine (an x86 computer) • C-to-x86-translator-in-C-subset program • C-to-x86-translator-in-C program How do you compile the C-to-x86-translator-in-C ? How do you compile the C-to-x86-translator-in-C ? C-to-x86-translator machine #2 (I) q C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program #2 (T) ² C-to-x86-translator-in-C ² C-to-x86-translator machine #1 (I) o C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program #1 o x86 computer q x86 computer But why create C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program #2 (T) when you already have C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program #1? Metaprogramming 23 Metaprogramming 24
A long line of C compilers Metacircularity Example 2: More RealisBc C-version_n-to-target_n-translator machine (I) q C-version_n-to-target_n-translator program in target_n-1 (T) Suppose you are given: ² C-version_n-to-target_n-translator program in C-version_n-1 • C-subset-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program ² C-version_n-1-to-target_n-1 translator machine (I) (a compiler for a subset of C wriDen in x86) o C-version_n-1-to-target_n_1-translator program in target_n-2 (T) • x86 interpreter machine (an x86 computer) … • Full-C-to-x86-translator-in-C-subset program Ø C-version_2-to-target_2-translator-program in target_1 (T) (a compiler for the full C language wriDen in a subset of C) § C-version_2-to-target_2-translator program in C-version_1 How do you create a Full-C-to-x86-translator machine ? § C-version_1-to-target_1 translator machine (I) • C-version_1-to-target_1-translator program in assembly_0 Full-C-to-x86-translator machine (I) • assembly_0 computer q Full-C-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program (T) Ø target_1 computer ² Full-C-to-x86-translator-in-C-subset … o target_n-2 computer ² C-subset-to-x86-translator machine (I) q target_n-1 computer o C-subset-to-x86-translator-in-x86 program o The versions of C and target languages can change at each stage. o x86 computer o Trojan horses from earlier source files can remain in translator machines even if q x86 computer they’re not in later source file! See Ken Thompson’s Reflec4on on Trus4ng Trust Metaprogramming 25 Metaprogramming 26 More Metaprogramming in SML Remember: language != implementaBon • We’ve already seen PostFix and Intex SML Easy to confuse "the way this language is usually • implemented" or "the implementaLon I use" with "the • A sequences of expression languages implemented in language itself.” SML that look closer and closer to Racket: • Bindex: add naming Java and Racket can be compiled to x86 • • Valex: add more value types, dynamic type checking, desugaring C can be interpreted in Racket • • HOFL: first class funcLon values, closure diagrams x86 can be compiled to JavaScript • Can we compile C/C++ to Javascript? • hDp://kripken.github.io/emscripten-site/ Metaprogramming 27 Metaprogramming 28
Recommend
More recommend